In today’s global economy, large businesses play a pivotal role in shaping markets, influencing consumer behavior, and driving technological advancements. These entities, often characterized by their extensive resources, vast employee bases, and significant market shares, present a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and consumers alike, particularly those involved in finance, cryptocurrency, forex trading, and broader money markets. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of big business, examining both its strengths and weaknesses.
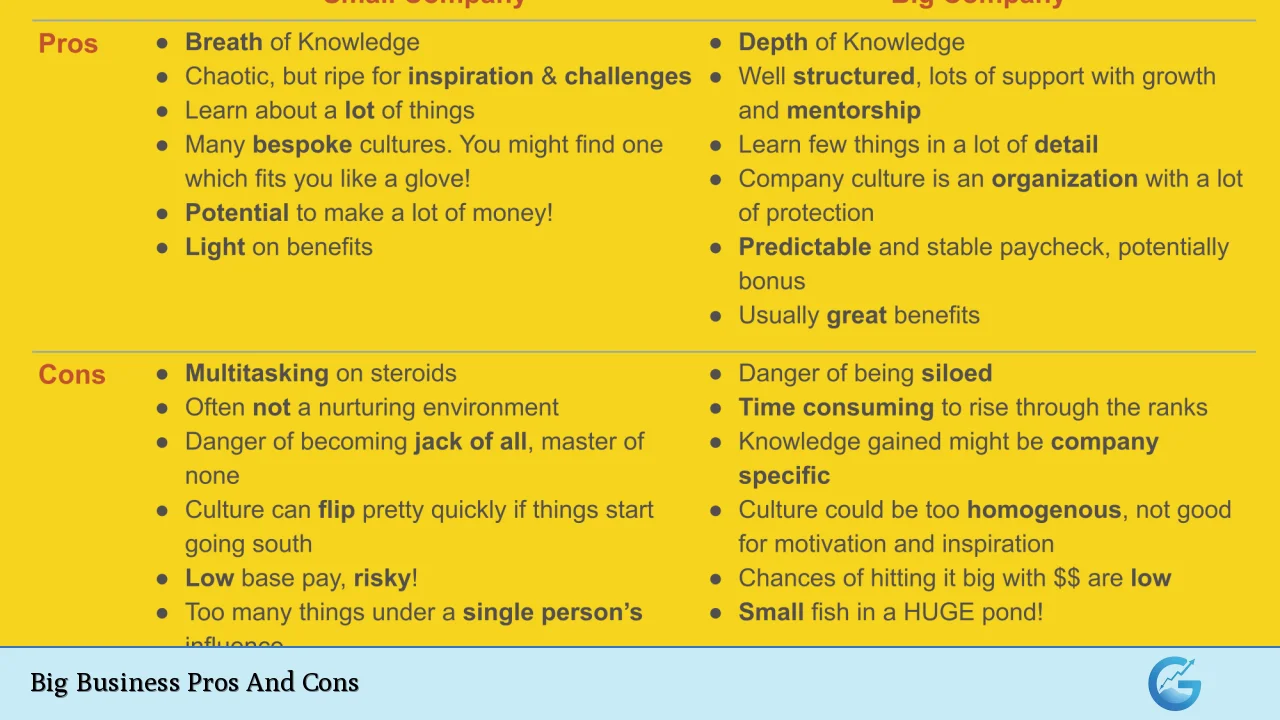
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Access to Capital | Bureaucratic Inefficiencies |
| Economies of Scale | Reduced Flexibility |
| Brand Recognition | Potential for Monopolistic Behavior |
| Diverse Product Offerings | Impact on Local Businesses |
| Global Reach | Environmental Concerns |
| Innovation and R&D Investment | Complex Management Structures |
| Job Creation | Employee Disengagement Risks |
| Market Influence and Stability | Ethical Concerns in Practices |
Access to Capital
Large businesses typically have superior access to capital compared to smaller firms. This advantage stems from their established creditworthiness and the ability to leverage various financing options such as:
- Public Offerings: Large companies can raise funds through stock market listings.
- Debt Financing: They can secure loans from banks at lower interest rates due to their financial stability.
- Investor Confidence: Their established track record attracts institutional investors.
This access allows big businesses to invest in growth opportunities, expand operations, and weather economic downturns more effectively.
Bureaucratic Inefficiencies
One significant disadvantage of large businesses is the bureaucratic inefficiencies that often arise from their size. These inefficiencies can manifest as:
- Slow Decision-Making: With multiple layers of management, decision-making processes can be prolonged.
- Rigid Structures: Established protocols may hinder innovation and responsiveness to market changes.
- Communication Barriers: Information flow can be obstructed by hierarchical structures, leading to misunderstandings or delays.
These bureaucratic challenges can stifle creativity and adaptability in a rapidly changing business environment.
Economies of Scale
Large businesses benefit from economies of scale, which allow them to reduce costs per unit as production increases. This advantage can lead to:
- Lower Prices: They can offer competitive pricing due to reduced operational costs.
- Increased Profit Margins: Higher production volumes often lead to greater profitability.
- Resource Optimization: Large firms can invest in advanced technologies that further enhance efficiency.
Such benefits enable big businesses to dominate markets and maintain a competitive edge.
Reduced Flexibility
Conversely, the size of large businesses can lead to reduced flexibility. This limitation is evident in:
- Inability to Pivot Quickly: Large organizations may struggle to adapt swiftly to new trends or consumer demands.
- Standardized Products: The need for uniformity across locations can limit customization options for customers.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to new initiatives due to entrenched corporate cultures.
This lack of agility can hinder a company’s ability to innovate or respond effectively to competitive pressures.
Brand Recognition
Big businesses often enjoy substantial brand recognition, which provides several advantages:
- Consumer Trust: Established brands are typically viewed as more reliable by consumers.
- Market Share Dominance: Strong branding helps secure a larger share of the market.
- Marketing Efficiency: Recognizable brands can achieve greater impact with marketing campaigns due to existing consumer familiarity.
This recognition not only drives sales but also fosters customer loyalty over time.
Potential for Monopolistic Behavior
However, brand dominance can lead to monopolistic behavior that stifles competition. This concern includes:
- Price Manipulation: Large firms may engage in price-setting practices that harm consumers.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants may find it challenging to compete against well-established brands with significant market power.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Increased attention from regulators seeking to prevent anti-competitive practices.
Such behaviors can create an uneven playing field in the marketplace.
Diverse Product Offerings
Large companies often provide a diverse range of products and services, which benefits consumers through:
- Variety: A wide selection allows consumers more choices tailored to their needs.
- Bundled Services: Companies can offer comprehensive solutions that enhance customer satisfaction.
- Cross-Selling Opportunities: They can leverage existing customer bases across different product lines.
This diversity enhances consumer experience but also raises concerns about over-reliance on single entities for multiple needs.
Impact on Local Businesses
The expansion of large businesses often negatively impacts local enterprises. Key issues include:
- Market Displacement: Local shops may struggle to compete with the pricing power of larger firms.
- Cultural Homogenization: The proliferation of global brands can erode local cultures and traditions.
- Job Losses: As big businesses grow, local employment opportunities may diminish due to closures of smaller competitors.
These impacts highlight the tension between large corporations and community-level economic health.
Global Reach
The global presence of large businesses allows them to tap into international markets. Benefits include:
- Market Expansion: Accessing new regions increases potential customer bases.
- Resource Acquisition: They can source materials or labor from various countries at competitive rates.
- Risk Diversification: Operating in multiple markets helps mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in any single region.
However, this global reach also raises concerns regarding labor practices and environmental standards across different jurisdictions.
Environmental Concerns
Large corporations face scrutiny over their environmental impact. Key issues involve:
- Resource Consumption: High levels of production often lead to significant resource depletion.
- Pollution and Waste: Manufacturing processes may contribute heavily to environmental degradation.
- Sustainability Practices: There is increasing pressure on big businesses to adopt sustainable practices that minimize harm.
Addressing these concerns is crucial for long-term viability and public perception.
Innovation and R&D Investment
Big businesses typically have the resources necessary for substantial investments in research and development (R&D). This investment leads to:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations can drive entire industries forward.
- Product Development: New products enhance competitiveness and meet evolving consumer needs.
- Industry Leadership: Companies that invest heavily in R&D often set industry standards.
However, this focus on innovation must be balanced against ethical considerations related to patenting practices and access to technology.
Complex Management Structures
The size of large organizations often results in complex management structures that pose challenges such as:
- Coordination Difficulties: Managing diverse teams across various locations becomes increasingly complicated.
- Employee Morale Issues: Employees may feel disconnected from the company’s mission due to hierarchical divisions.
- Decision-Making Delays: The need for consensus among multiple stakeholders can slow down critical decisions.
These complexities necessitate effective leadership strategies that promote cohesion and clarity within the organization.
Job Creation
Large businesses are significant job creators within economies. Benefits include:
- Employment Opportunities: They provide jobs across various sectors, contributing positively to local economies.
- Career Development Programs: Large firms often offer training programs that enhance employee skills and career prospects.
- Economic Stability: A robust job market supported by large employers contributes overall economic health.
Yet, reliance on these entities for employment raises concerns about job security during economic downturns or corporate restructuring efforts.
Employee Disengagement Risks
Despite their size, large companies face risks associated with employee disengagement. Issues include:
- Lack of Personal Connection: Employees may feel like just another number within a vast organization.
- Limited Career Advancement Opportunities: Competition for promotions can be fierce in large firms, potentially leading employees to feel stagnant.
- Workplace Culture Challenges: A formal corporate culture may not resonate with all employees, impacting morale and productivity.
Addressing these risks is vital for maintaining a motivated workforce capable of driving company success.
Market Influence and Stability
Large businesses wield considerable influence over market dynamics. Their impact includes:
- Price Setting Power: Major players can dictate prices within industries due to their market share.
- Stability During Crises: Established companies often weather economic downturns better than smaller firms due to their resources.
- Investment Attraction: Their presence in markets attracts additional investment opportunities from various stakeholders.
However, this influence must be managed responsibly to prevent negative repercussions on competition and consumer choice.
Ethical Concerns in Practices
Finally, ethical concerns surrounding large businesses cannot be overlooked. Areas of concern include:
- Labor Practices: Issues such as wage disparity or poor working conditions are prevalent in some large corporations.
- Corporate Governance Issues: Transparency in decision-making processes is essential but not always present in large firms.
- Social Responsibility Obligations: Companies face increasing pressure from consumers and regulators regarding their roles in society beyond profit generation.
Navigating these ethical challenges is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, while big businesses offer numerous advantages such as access to capital, economies of scale, brand recognition, diverse offerings, global reach, innovation potential, job creation, market stability, they also come with significant disadvantages including bureaucratic inefficiencies, reduced flexibility, potential monopolistic behavior, impacts on local economies, environmental concerns, complex management structures, employee disengagement risks, and ethical dilemmas. Understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders involved in finance-related fields as they navigate an increasingly complex economic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About Big Business Pros And Cons
- What are the primary advantages of big businesses?
Big businesses benefit from access to capital, economies of scale that reduce costs per unit produced, strong brand recognition that builds consumer trust, diverse product offerings that cater to various needs, global reach for market expansion opportunities, substantial investment capabilities in research and development (R&D), job creation across sectors. - What are some disadvantages associated with large corporations?
Bureaucratic inefficiencies leading to slow decision-making processes; reduced flexibility making it hard for them to adapt quickly; potential monopolistic behavior harming competition; negative impacts on local businesses; environmental concerns related to resource consumption; complex management structures causing coordination difficulties; risks of employee disengagement. - How do big businesses influence the economy?
They create jobs contributing positively towards local economies; they stabilize markets during economic downturns; they attract investments which further stimulate growth. - Are there ethical concerns tied with big corporations?
Yes; issues such as labor practices including wage disparity or poor working conditions exist alongside corporate governance challenges regarding transparency; social responsibility obligations are increasingly scrutinized. - How do economies of scale benefit large companies?
Easier access leads them towards lower operational costs per unit produced enabling competitive pricing strategies while also increasing profit margins. - What role does innovation play within big business?
A significant role; through substantial investments into R&D they drive technological advancements leading industries forward while meeting evolving consumer needs. - Can small businesses compete effectively against large corporations?
This is challenging due primarily because larger firms possess greater resources allowing them advantages like better marketing reach or pricing power. - What should consumers consider when engaging with big brands?
The balance between convenience offered by established brands versus potential negative impacts on local economies or ethical considerations surrounding their practices.