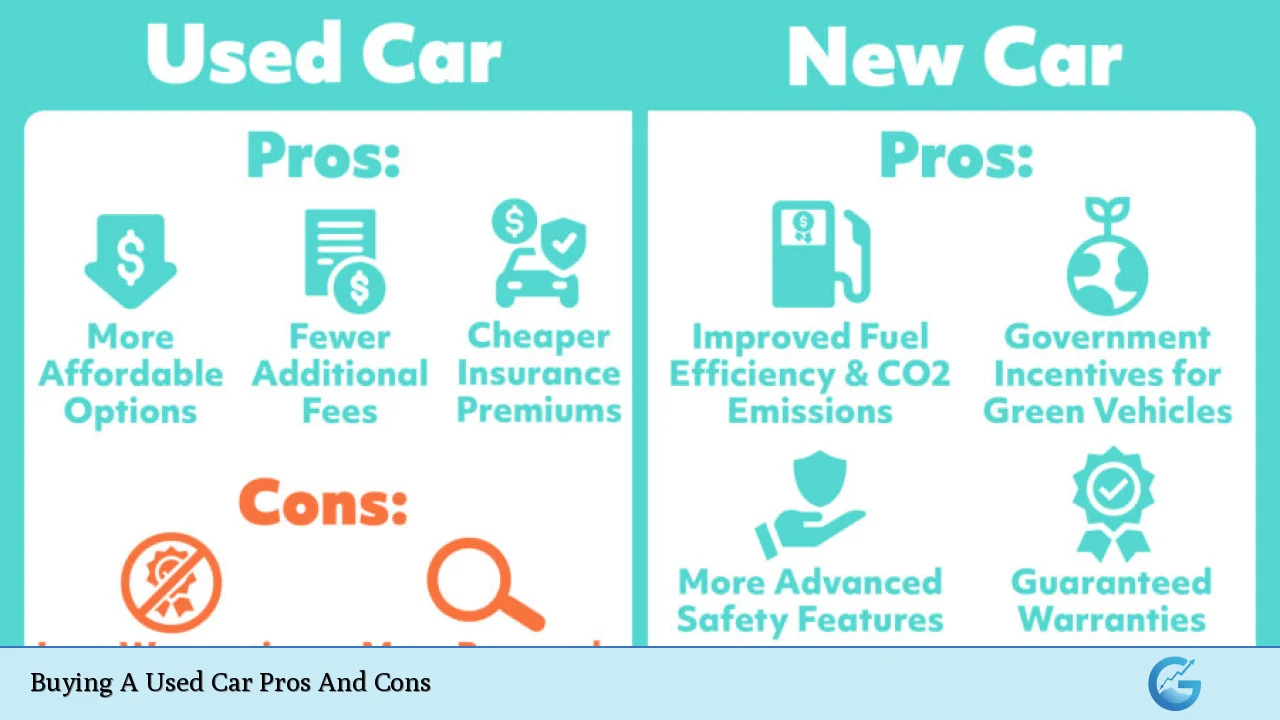
Purchasing a used car can be an attractive option for many consumers, offering potential savings and value. However, like any major financial decision, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. This comprehensive guide will explore the pros and cons of buying a used car, providing you with the information you need to make an informed decision.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower purchase price | Higher maintenance costs |
| Slower depreciation | Limited warranty coverage |
| Lower insurance premiums | Uncertain vehicle history |
| More car for your money | Older technology and features |
| Lower registration fees | Potential for hidden problems |
| Wider selection of models | Higher interest rates on loans |
| Certified Pre-Owned options | Less customization options |
| Lower overall cost of ownership | Shorter remaining lifespan |
Advantages of Buying a Used Car
Lower Purchase Price
One of the most significant advantages of buying a used car is the lower initial cost. Used cars are generally priced substantially lower than their new counterparts, allowing buyers to save thousands of dollars on the purchase price. This lower entry point makes car ownership more accessible to a broader range of consumers and can be particularly attractive for first-time buyers or those on a tight budget.
- Significant savings compared to new car prices
- More affordable options for budget-conscious buyers
- Opportunity to own a higher-end model for less money
Slower Depreciation
New cars typically lose a substantial portion of their value within the first few years of ownership. Used cars, having already undergone the steepest part of the depreciation curve, tend to hold their value better over time. This slower rate of depreciation can be beneficial for buyers who plan to sell or trade in their vehicle in the future.
- Less value lost to depreciation over time
- Potential for better resale value
- More stable investment in terms of retained value
Lower Insurance Premiums
Insurance companies typically charge lower premiums for used cars compared to new ones. This is primarily because the replacement value of a used car is lower, resulting in reduced risk for the insurer. The savings on insurance costs can add up significantly over the life of the vehicle, contributing to a lower overall cost of ownership.
- Reduced monthly insurance expenses
- Potential for more comprehensive coverage at a lower cost
- Lower long-term insurance costs over the life of the vehicle
More Car for Your Money
With a used car, buyers can often afford a higher-end model or a vehicle with more features than they could if buying new. This allows consumers to get more value for their money and potentially drive a car that would be out of their price range if purchased new.
- Access to luxury or premium models at a fraction of their original price
- Opportunity to own vehicles with higher-end features and specifications
- Better value proposition in terms of features per dollar spent
Lower Registration Fees
Many states calculate vehicle registration fees based on the car’s value or purchase price. Since used cars are generally less expensive than new ones, the registration fees are often lower. This can result in additional savings for used car buyers, especially in states with high registration costs.
- Reduced annual registration expenses
- Potential for significant savings in states with value-based registration fees
- Lower overall cost of vehicle ownership
Wider Selection of Models
The used car market offers a vast selection of vehicles, including models that may no longer be in production. This wide array of choices allows buyers to find exactly what they’re looking for, whether it’s a specific model year, a rare trim level, or a discontinued vehicle that suits their needs perfectly.
- Access to a broader range of makes, models, and years
- Opportunity to find discontinued or rare models
- Greater flexibility in choosing the perfect vehicle for individual needs
Certified Pre-Owned Options
Many manufacturers offer Certified Pre-Owned (CPO) programs, which provide used cars that have undergone thorough inspections and come with extended warranties. These programs offer a middle ground between new and used cars, providing additional peace of mind and quality assurance for buyers.
- Rigorous inspection and reconditioning processes
- Extended warranty coverage
- Additional perks such as roadside assistance or special financing rates
Lower Overall Cost of Ownership
When factoring in the lower purchase price, reduced depreciation, and potentially lower insurance costs, the overall cost of owning a used car can be significantly less than that of a new car. This makes used cars an attractive option for cost-conscious consumers looking to maximize their automotive investment.
- Reduced total expenditure over the life of the vehicle
- Potential for lower monthly payments if financing
- More budget-friendly option for long-term car ownership
Disadvantages of Buying a Used Car
Higher Maintenance Costs
One of the primary drawbacks of buying a used car is the potential for higher maintenance and repair costs. As vehicles age, they naturally require more frequent repairs and may need major components replaced. These increased maintenance expenses can offset some of the initial savings from the lower purchase price.
- More frequent repairs and maintenance needs
- Potential for costly major repairs
- Higher overall maintenance budget required
Limited Warranty Coverage
Unlike new cars that come with comprehensive manufacturer warranties, used cars often have limited or no warranty coverage remaining. This means that buyers may be responsible for repair costs soon after purchase, which can lead to unexpected expenses.
- Reduced or expired manufacturer warranty
- Potential for out-of-pocket repair costs
- Need for additional extended warranty purchases for peace of mind
Uncertain Vehicle History
When buying a used car, there’s always some uncertainty about its past. While vehicle history reports can provide valuable information, they may not capture every detail of a car’s maintenance and accident history. This lack of complete information can make it challenging to assess the true condition and potential future issues of the vehicle.
- Potential for undisclosed accidents or damage
- Uncertainty about previous maintenance and care
- Risk of inheriting problems from previous owners
Older Technology and Features
Used cars, especially older models, may lack the latest technology and safety features found in newer vehicles. This can mean missing out on advanced driver assistance systems, improved fuel efficiency technologies, and modern infotainment options.
- Outdated safety features compared to newer models
- Less advanced infotainment and connectivity options
- Potentially lower fuel efficiency due to older technology
Potential for Hidden Problems
Despite careful inspections and vehicle history checks, used cars can sometimes have hidden issues that may not be immediately apparent. These problems can surface after purchase, leading to unexpected repair costs and frustration for the buyer.
- Risk of undiscovered mechanical issues
- Potential for costly repairs shortly after purchase
- Need for thorough pre-purchase inspections
Higher Interest Rates on Loans
Financing a used car often comes with higher interest rates compared to new car loans. Banks and lenders typically charge higher rates for used car loans due to the increased risk associated with older vehicles. These higher interest rates can increase the overall cost of the car if financing is required.
- Potentially less favorable loan terms
- Higher monthly payments relative to the car’s value
- Increased total interest paid over the life of the loan
Less Customization Options
When buying a used car, buyers are limited to the existing configurations and options available in the market. Unlike new cars, where buyers can often customize features and colors to their liking, used car purchasers must choose from what’s already available.
- Limited ability to select specific features or options
- Restricted color and trim choices
- Potential compromise on desired specifications
Shorter Remaining Lifespan
Used cars have already been driven for a portion of their useful life, which means they may have a shorter remaining lifespan compared to new vehicles. This can result in the need to replace the car sooner, potentially offsetting some of the initial cost savings.
- Reduced overall longevity of the vehicle
- Potential need for earlier replacement
- Consideration of long-term ownership costs
In conclusion, buying a used car offers significant financial advantages, including lower purchase prices, reduced depreciation, and potentially lower insurance costs. However, these benefits come with trade-offs such as increased maintenance needs, limited warranty coverage, and potential uncertainties about the vehicle’s history and condition. By carefully weighing these pros and cons and conducting thorough research, buyers can make an informed decision that aligns with their financial situation and automotive needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Buying A Used Car Pros And Cons
- Is it always cheaper to buy a used car instead of a new one?
While used cars generally have lower purchase prices, the total cost of ownership can vary. Factors like maintenance, repairs, and fuel efficiency should be considered when comparing overall costs. - How can I minimize the risks of buying a used car?
To minimize risks, obtain a vehicle history report, have a trusted mechanic perform a pre-purchase inspection, and consider certified pre-owned vehicles. Additionally, research the specific model’s reliability and common issues. - Are certified pre-owned cars worth the extra cost?
Certified pre-owned cars often offer a good balance between cost and peace of mind. They typically undergo thorough inspections, come with extended warranties, and may have lower interest rates, making them a worthwhile option for many buyers. - How much can I expect to save on insurance with a used car?
Insurance savings can vary widely depending on the specific car, your location, and your driving history. However, used cars generally cost less to insure, with potential savings ranging from 10% to 50% compared to new cars. - What are the best resources for researching used car reliability?
Consumer Reports, J.D. Power, and Kelley Blue Book offer reliable information on used car reliability. Additionally, model-specific forums and professional automotive reviews can provide valuable insights into long-term reliability. - How does buying a used car affect my financing options?
Used car loans typically have higher interest rates than new car loans. However, many lenders offer competitive rates for newer used cars. Shop around for the best rates, and consider credit unions, which often offer favorable terms for used car loans. - Is it worth paying extra for an extended warranty on a used car?
The value of an extended warranty depends on the car’s reliability and your risk tolerance. Research the specific model’s common issues and repair costs to determine if the potential savings justify the warranty’s cost. - How does depreciation differ between new and used cars?
New cars typically depreciate 20-30% in the first year and about 50% over three years. Used cars, having already undergone this initial depreciation, tend to lose value more slowly, potentially offering better long-term value retention.