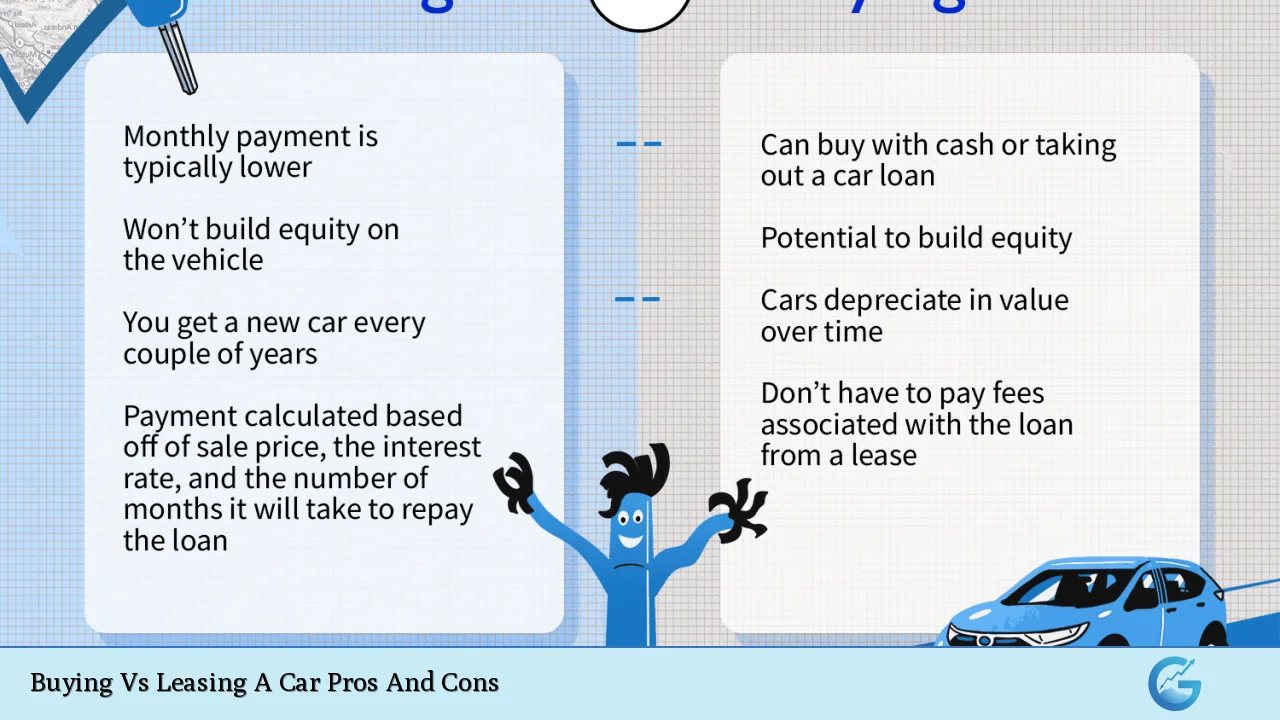
Deciding whether to buy or lease a car is a significant financial decision that many individuals face. Both options come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to weigh them carefully based on personal circumstances, financial goals, and lifestyle preferences. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the pros and cons of buying versus leasing a car, helping you make an informed choice.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Ownership and equity building | Higher monthly payments |
| No mileage restrictions | Depreciation concerns |
| Flexibility in modifications | Maintenance costs after warranty ends |
| Potential resale value | Upfront costs can be high |
| Long-term cost savings if kept long enough | Longer commitment required |
| Tax benefits for business use (if applicable) | No new car every few years |
| Lower overall costs if financed wisely | Potential for negative equity if sold early |
| Freedom to drive as much as desired | Lack of flexibility in changing cars frequently |
| Complete control over the vehicle’s use and care | Higher insurance premiums typically associated with ownership |
| Possibility of lower long-term costs compared to leasing multiple vehicles over time | Risk of costly repairs as the vehicle ages |
Ownership and Equity Building
One of the most significant advantages of buying a car is that you gain ownership once the purchase is complete. This means that every payment you make contributes to building equity in the vehicle.
- Equity growth: As you pay off your car, you own a tangible asset that can be sold or traded in later.
- Long-term investment: If you keep the vehicle for several years after paying it off, the overall cost per mile decreases significantly.
However, this ownership comes with its drawbacks:
- Depreciation: Cars lose value quickly, especially in the first few years. This rapid depreciation can be concerning if you plan to sell or trade-in soon after purchase.
No Mileage Restrictions
When you buy a car, there are no restrictions on how many miles you can drive. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for individuals who travel frequently or have long commutes.
- Unlimited driving: You can take road trips without worrying about exceeding mileage limits.
On the flip side:
- Higher costs for excessive mileage: If you drive more than average, your vehicle will depreciate faster, potentially affecting resale value.
Flexibility in Modifications
Owning a vehicle allows you to customize it according to your preferences.
- Personalization: You can modify your car’s appearance or performance without restrictions imposed by leasing agreements.
However:
- Cost implications: Customizations may not add value when it comes time to sell or trade-in the vehicle.
Potential Resale Value
A significant advantage of buying is that you have the potential to recoup some of your investment through resale.
- Asset recovery: Depending on market conditions and the condition of your vehicle, you can sell it and recover part of your initial investment.
Conversely:
- Market fluctuations: The resale value can be unpredictable due to market demand and economic conditions, impacting your financial return.
Long-Term Cost Savings If Kept Long Enough
Buying a car can lead to significant savings over time, especially if you keep it for several years after paying off the loan.
- Lower total cost: After paying off the loan, your only expenses will be maintenance and insurance, which can be less than ongoing lease payments.
However:
- Initial financial burden: The upfront costs associated with purchasing a vehicle are typically higher than those for leasing.
Tax Benefits for Business Use (If Applicable)
For those who use their vehicles for business purposes, buying may offer tax advantages.
- Deductions: Business owners can deduct depreciation and other expenses related to vehicle ownership on their taxes.
Yet:
- Complexity in tax filings: Navigating tax benefits can be complicated and may require professional assistance.
Lower Overall Costs If Financed Wisely
If financed wisely, buying a car can result in lower overall costs compared to leasing multiple vehicles over time.
- Smart financing: By securing favorable loan terms and interest rates, buyers can minimize their total expenditure on transportation.
On the downside:
- Interest payments: Depending on credit scores and market conditions, financing can lead to substantial interest payments over time.
Freedom to Drive as Much as Desired
Owning a car provides unparalleled freedom regarding how much you drive and where you go.
- No penalties: You won’t face penalties for exceeding mileage limits or wear-and-tear charges that are common with leases.
However:
- Increased wear and tear: More driving can lead to higher maintenance costs as the vehicle ages.
Complete Control Over Vehicle’s Use and Care
As an owner, you have complete control over how your vehicle is used and maintained.
- Personal preferences: You decide when to service it, what parts to use, and how often it gets washed or detailed.
But:
- Responsibility for repairs: Once warranties expire, all repair costs fall on you as the owner.
Higher Monthly Payments
One of the main disadvantages of buying a car is that monthly payments are generally higher than lease payments.
- Budget impact: This can strain monthly budgets, especially for those who are tight on cash flow or have other financial commitments.
In contrast:
- Lower lease payments: Leasing often involves lower monthly payments because you’re only paying for depreciation during the lease term rather than the full purchase price of the vehicle.
Depreciation Concerns
New cars depreciate rapidly; they can lose 15%–25% of their value within the first few years.
- Investment risk: For buyers who consider their vehicles an investment, this rapid depreciation poses a significant risk.
Conversely:
- Leasing mitigates depreciation risk: Lessees do not bear this risk directly since they return the car at lease end without worrying about its market value at that point.
Maintenance Costs After Warranty Ends
Once warranties expire, owners are responsible for all maintenance costs.
- Potentially high expenses: Older vehicles may require costly repairs that could outweigh any savings from not having monthly payments.
On the other hand:
- Leasing often includes maintenance coverage: Many leases come with warranties that cover most repairs during the lease period.
Upfront Costs Can Be High
Buying typically requires higher upfront costs compared to leasing.
- Down payment requirements: Buyers often need to make a substantial down payment or pay sales tax on the full purchase price upfront.
In contrast:
- Leasing usually has lower initial costs: Many leases require little to no down payment, making it easier for individuals to get into a new vehicle without significant financial strain initially.
Longer Commitment Required
Purchasing a car usually involves a longer commitment compared to leasing.
- Financial obligation: Buyers may feel locked into their purchase until they pay off their loan or sell their vehicle, which might not align with changing personal circumstances or preferences.
Conversely:
- Flexibility with leasing contracts: Leases typically last two to three years, allowing lessees to change vehicles more frequently based on their evolving needs or preferences.
No New Car Every Few Years
Buying means that once you’ve paid off your loan, you’re stuck with that particular vehicle until you’re ready to sell or trade it in.
- Long-term ownership drawbacks: This could lead some individuals to miss out on newer models with advanced technology and features available every few years through leasing options.
However:
- Stability in ownership: Some individuals prefer having a reliable vehicle they know well rather than constantly switching cars every few years through leasing arrangements.
Higher Insurance Premiums Typically Associated With Ownership
Insurance premiums may be higher for owned vehicles compared to leased ones due to factors like increased liability coverage requirements.
- Cost consideration: This added expense should be factored into overall ownership costs when deciding between buying and leasing options.
In contrast:
- Leased vehicles often come with lower insurance requirements, reducing monthly expenses associated with coverage while under lease terms.
Risk of Costly Repairs As Vehicle Ages
As cars age beyond their warranty periods, owners may face unexpected repair bills that can accumulate quickly.
- Financial unpredictability: This risk makes budgeting difficult for some owners who may not have set aside funds specifically for maintenance issues arising from an older vehicle’s age and usage patterns.
On the other hand:
- Leasing minimizes repair responsibilities, as most repairs are covered under warranty during the lease term.
In conclusion, both buying and leasing have distinct advantages and disadvantages that cater to different financial situations and personal preferences. Buying offers long-term benefits such as ownership equity, flexibility in usage without mileage restrictions, and potential resale value. However, it also comes with higher upfront costs and risks associated with depreciation and maintenance once warranties expire. Conversely, leasing provides lower monthly payments, access to new vehicles every few years without worrying about depreciation but lacks equity building and comes with mileage limitations. Evaluating these factors based on individual circumstances will ultimately guide prospective buyers or lessees toward making an informed decision that aligns best with their lifestyle needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Buying Vs Leasing A Car Pros And Cons
- What is typically cheaper in the short term—buying or leasing?
Leasing usually has lower monthly payments compared to buying since you’re only paying for depreciation during the lease term. - Can I modify my leased car?
No, modifications are generally not allowed on leased vehicles unless approved by the leasing company. - What happens at the end of a lease?
You typically return the vehicle; however, some leases offer an option to buy at predetermined prices. - Are there any tax benefits associated with leasing?
If used for business purposes, lessees may deduct certain expenses related to leasing on their taxes. - How does mileage affect leasing?
Most leases have mileage restrictions; exceeding them incurs additional fees. - If I buy a car outright, do I own it immediately?
Yes, once paid in full or financed completely through loans, ownership is yours. - Is it better financially in the long run to buy rather than lease?
If you keep your car long enough after paying it off, buying is generally more cost-effective than continually leasing. - What should I consider before deciding between buying or leasing?
Your driving habits (mileage), budget constraints (upfront/down payment), desire for new technology frequently (leasing), and long-term plans should all factor into this decision.