Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are popular financial instruments offered by banks and credit unions, providing a secure way to save money while earning interest. These time-bound deposits offer a fixed interest rate for a predetermined period, making them an attractive option for conservative investors seeking stability and guaranteed returns. However, like any investment vehicle, CDs come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential investors should carefully consider.
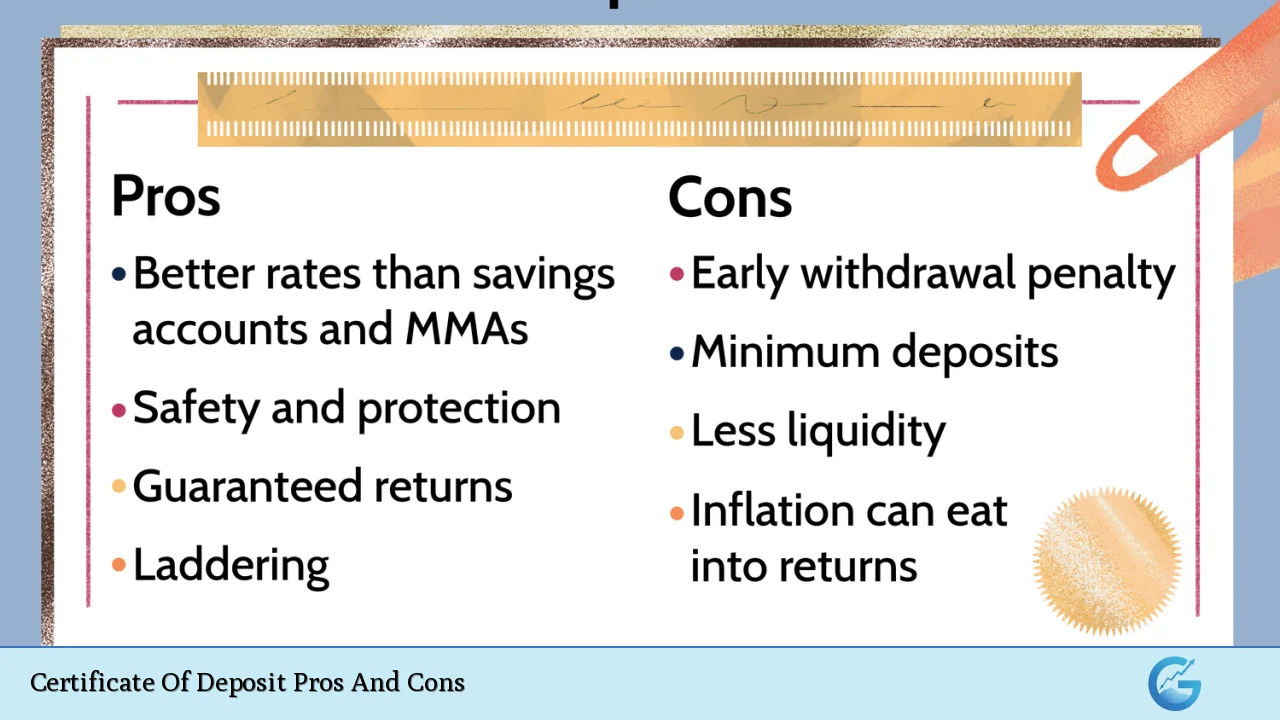
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Guaranteed Returns | Limited Liquidity |
| Higher Interest Rates | Inflation Risk |
| FDIC Insurance | Opportunity Cost |
| Low Risk | Early Withdrawal Penalties |
| Predictable Income | Interest Rate Risk |
| Flexible Terms | Minimum Deposit Requirements |
| Laddering Strategy | Taxable Interest |
| No Fees | Complexity of Some CD Products |
Advantages of Certificates of Deposit
Guaranteed Returns
CDs offer a fixed interest rate for a specified term, providing investors with a predictable and guaranteed return on their investment.
This feature is particularly appealing to risk-averse individuals who prioritize capital preservation and steady income. Unlike volatile investment options such as stocks or mutual funds, CDs ensure that you know exactly how much you’ll earn by the end of the term.
- Predictable earnings
- Peace of mind for conservative investors
- Ideal for short-term financial goals
Higher Interest Rates
Compared to traditional savings accounts or checking accounts, CDs typically offer higher interest rates.
The longer the term of the CD, the higher the interest rate tends to be.
This makes CDs an attractive option for those looking to maximize their returns on idle cash without taking on significant risk.
- Better returns than standard savings accounts
- Opportunity to earn more on long-term deposits
- Competitive rates among financial institutions
FDIC Insurance
One of the most significant advantages of CDs is the safety they provide.
In the United States, CDs offered by banks are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) for up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
This insurance protects your principal and earned interest even if the bank fails, making CDs one of the safest investment options available.
- Protection against bank failures
- Peace of mind for risk-averse investors
- Guaranteed safety up to insured limits
Low Risk
CDs are considered low-risk investments due to their fixed returns and FDIC insurance.
This makes them an excellent choice for investors who want to preserve capital while earning a modest return.
Unlike stocks or bonds, which can fluctuate in value, CDs provide stability and predictability.
- Minimal risk of losing principal
- Suitable for conservative investment portfolios
- Ideal for emergency funds or short-term savings goals
Predictable Income
The fixed interest rate of CDs allows investors to calculate their earnings accurately over the term of the deposit.
This predictability makes CDs an excellent tool for financial planning and budgeting, especially for those relying on interest income.
Investors can choose to receive interest payments at regular intervals or reinvest the interest to compound their earnings.
- Easy to incorporate into financial plans
- Reliable income stream for retirees
- Options for interest disbursement or reinvestment
Flexible Terms
Banks and credit unions offer CDs with various maturity dates, typically ranging from a few months to several years.
This flexibility allows investors to choose terms that align with their financial goals and liquidity needs.
Whether you’re saving for a short-term purchase or looking for long-term growth, there’s likely a CD term that fits your requirements.
- Options to match various financial timelines
- Ability to customize savings strategy
- Diverse range of maturity dates available
Laddering Strategy
CD laddering is a popular strategy that involves investing in multiple CDs with staggered maturity dates.
This approach provides a balance between earning higher interest rates on longer-term CDs and maintaining liquidity as shorter-term CDs mature.
Laddering can help investors take advantage of rising interest rates while ensuring regular access to funds.
- Optimizes returns and liquidity
- Mitigates interest rate risk
- Provides flexibility in reinvestment decisions
No Fees
Unlike many other financial products, CDs typically do not charge maintenance fees or account management fees.
The absence of ongoing fees means that investors can keep more of their earnings, maximizing the overall return on their investment.
However, it’s essential to be aware of potential early withdrawal penalties, which are not considered fees but rather penalties for breaking the CD agreement.
- Lower costs compared to many investment products
- Transparent earnings without hidden charges
- Maximizes the effective yield on investments
Disadvantages of Certificates of Deposit
Limited Liquidity
One of the primary drawbacks of CDs is the lack of liquidity during the term of the deposit.
When you invest in a CD, you agree to leave your money untouched for a specific period. This lack of access to funds can be problematic if unexpected expenses arise or if better investment opportunities present themselves.
- Funds are locked up for the duration of the term
- May not be suitable for emergency savings
- Potential opportunity cost if rates rise or better investments emerge
Inflation Risk
While CDs offer guaranteed returns, they may not always keep pace with inflation.
In periods of high inflation, the purchasing power of your money can erode, even as your CD earns interest.
This risk is particularly pronounced for long-term CDs in low-interest-rate environments.
- Real returns may be negative in high-inflation periods
- Long-term CDs are more susceptible to inflation risk
- May not preserve purchasing power over time
Opportunity Cost
By locking your money into a CD, you might miss out on potentially higher returns from other investments.
If interest rates rise or the stock market performs well during your CD’s term, you could face significant opportunity costs.
This is especially true for long-term CDs, where your funds are committed for extended periods.
- Potential for lower returns compared to other investments
- Unable to take advantage of rising interest rates
- May miss out on market rallies or economic upturns
Early Withdrawal Penalties
If you need to access your funds before the CD matures, you’ll likely face early withdrawal penalties.
These penalties can be substantial, often amounting to several months’ worth of interest or even eating into your principal.
The severity of the penalty typically depends on the CD’s term and the issuing institution’s policies.
- Significant financial penalties for early access
- May negate interest earnings or reduce principal
- Discourages flexibility in financial planning
Interest Rate Risk
When interest rates are low, locking your money into a long-term CD can be risky.
If rates rise significantly during your CD’s term, you’ll be stuck earning below-market returns until maturity.
This interest rate risk can be particularly problematic in volatile economic environments.
- Potential for below-market returns if rates rise
- Long-term CDs are more vulnerable to interest rate fluctuations
- May lead to opportunity costs in rising rate environments
Minimum Deposit Requirements
Many banks and credit unions impose minimum deposit requirements for CDs, which can be higher than those for regular savings accounts.
These minimums can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, potentially limiting access for some investors.
Higher minimum deposits are often required to qualify for the best interest rates.
- May exclude investors with limited funds
- Best rates often require larger deposits
- Can complicate diversification strategies for smaller portfolios
Taxable Interest
The interest earned on CDs is generally taxable as ordinary income in the year it’s earned, even if you don’t withdraw the funds.
This can create a tax liability without a corresponding cash flow, potentially causing liquidity issues for some investors.
It’s important to consider the tax implications when calculating the effective yield of a CD.
- Interest is taxed as ordinary income
- May create tax liability without cash distribution
- Can reduce the effective after-tax return
Complexity of Some CD Products
While traditional CDs are straightforward, some banks offer more complex CD products with variable rates, call features, or market-linked returns.
These specialized CDs can be difficult to understand and may come with additional risks or restrictions that are not immediately apparent.
Investors should carefully review the terms and conditions of any non-standard CD product.
- Specialized CDs may have complex terms
- Potential for hidden risks or restrictions
- May require more financial sophistication to evaluate
In conclusion, Certificates of Deposit offer a secure and predictable way to save money and earn interest. They provide guaranteed returns, FDIC insurance, and the flexibility to choose terms that align with your financial goals. However, the limitations on liquidity, potential for below-inflation returns, and the risk of missing out on higher-yielding investments are significant factors to consider.
Investors should carefully weigh these pros and cons against their financial objectives, risk tolerance, and overall investment strategy before committing funds to CDs.
For many, CDs can play a valuable role as part of a diversified portfolio, offering stability and predictable income in an otherwise volatile financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About Certificate Of Deposit Pros And Cons
- What is the main advantage of investing in a CD?
The primary advantage of a CD is the guaranteed return at a fixed interest rate, which is typically higher than standard savings accounts. This provides a safe and predictable way to grow your savings. - How does CD laddering work, and what are its benefits?
CD laddering involves investing in multiple CDs with staggered maturity dates. This strategy provides a balance between earning higher interest rates on longer-term CDs and maintaining liquidity as shorter-term CDs mature, allowing for flexibility and potentially higher overall returns. - Are CDs a good investment during periods of high inflation?
CDs may not be ideal during high inflation as their fixed returns might not keep pace with rising prices. In such periods, the real (inflation-adjusted) return on CDs could be low or even negative, potentially eroding the purchasing power of your savings. - What happens if I need to withdraw money from my CD before it matures?
Early withdrawal from a CD typically results in penalties, which can be substantial and may even eat into your principal. The exact penalty varies by institution and CD term, but it often amounts to several months’ worth of interest. - How do CDs compare to other low-risk investments like savings accounts or money market accounts?
CDs generally offer higher interest rates than savings or money market accounts, but with less liquidity. They provide a fixed rate for a set term, whereas savings and money market accounts typically have variable rates and allow easier access to funds. - Can CDs be part of a diversified investment portfolio?
Yes, CDs can be an important component of a diversified portfolio, especially for conservative investors or those nearing retirement. They provide stability and predictable income, balancing out riskier investments like stocks or mutual funds. - Are there any tax advantages to investing in CDs?
CDs don’t offer special tax advantages; interest earned is typically taxed as ordinary income. However, for retirement accounts like IRAs, the tax treatment follows the rules of the account type rather than standard CD taxation. - How do rising interest rates affect existing CD investments?
Existing CDs are not affected by rising interest rates as they maintain their fixed rate until maturity. However, this can result in opportunity cost if new CDs or other investments start offering significantly higher rates during your CD’s term.