Deferred fixed annuities are financial products that allow individuals to invest money with the promise of receiving regular payments or a lump sum at a future date. These annuities are particularly appealing for those planning for retirement, as they offer a way to accumulate savings while deferring taxes on investment growth. However, like any financial product, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. This article will explore the pros and cons of deferred fixed annuities in detail, providing insights for potential investors.
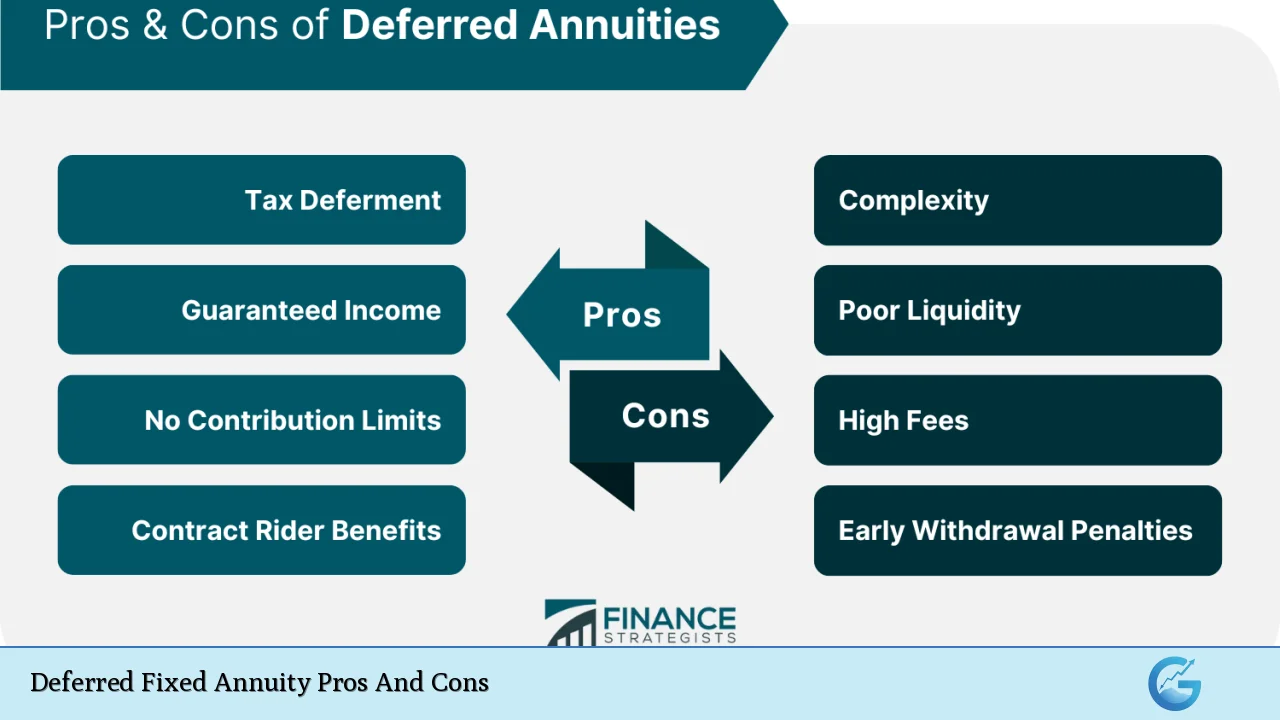
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Tax-deferred growth | Limited liquidity and access to funds |
| Guaranteed income in retirement | Potentially lower returns compared to other investments |
| Principal protection | High fees and surrender charges |
| No contribution limits | Complexity of contracts |
| Death benefits for beneficiaries | Inflation risk affecting purchasing power |
Tax-Deferred Growth
One of the most significant advantages of deferred fixed annuities is the ability to grow your investments on a tax-deferred basis. This means that you won’t owe taxes on the earnings until you withdraw funds from the annuity.
- Compounding Effect: The tax deferral allows your investment to compound over time without the drag of annual taxes, potentially leading to a larger accumulation by retirement.
- Strategic Withdrawals: When you retire and start withdrawing funds, you may be in a lower tax bracket, which can minimize your tax liability.
Guaranteed Income in Retirement
Deferred fixed annuities provide a reliable source of income during retirement, which can be crucial for financial stability.
- Predictable Payments: Many deferred fixed annuities offer guaranteed payments for life, ensuring that retirees do not outlive their savings.
- Pension-like Security: This feature can serve as a personal pension plan, providing peace of mind about future income.
Principal Protection
Investors appreciate that deferred fixed annuities typically offer principal protection, meaning that the initial investment is safeguarded against market fluctuations.
- Low Risk: Unlike stocks or mutual funds, the principal amount invested in a fixed annuity is protected from loss due to market downturns.
- Guaranteed Minimum Interest Rate: Most contracts specify a minimum interest rate, ensuring some level of return regardless of market conditions.
No Contribution Limits
Unlike many retirement accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k)s, deferred fixed annuities do not impose contribution limits.
- Flexibility for High Earners: This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who have maxed out other tax-advantaged accounts and wish to continue saving for retirement.
- Increased Savings Potential: Investors can allocate significant sums into these annuities without worrying about annual limits.
Death Benefits for Beneficiaries
Deferred fixed annuities often include death benefits that can be passed on to beneficiaries.
- Financial Security for Loved Ones: In the event of the investor’s death before the payout phase begins, beneficiaries may receive the full account value or predetermined benefits.
- Avoiding Probate: The death benefit typically bypasses probate, allowing quicker access to funds for heirs.
Limited Liquidity and Access to Funds
A notable disadvantage of deferred fixed annuities is their limited liquidity.
- Withdrawal Restrictions: Funds are generally locked in until the contract matures or until a specified period has elapsed. Early withdrawals often incur penalties.
- Surrender Charges: Many contracts impose surrender charges if you withdraw funds before a certain period, which can significantly reduce your returns.
Potentially Lower Returns Compared to Other Investments
While deferred fixed annuities offer security, their returns may not be as high as other investment options.
- Fixed Interest Rates: The guaranteed interest rates are often lower than potential returns from stocks or mutual funds over the long term.
- Opportunity Cost: By locking funds into an annuity, investors may miss out on higher-yielding investment opportunities elsewhere.
High Fees and Surrender Charges
Deferred fixed annuities can come with various fees that may eat into overall returns.
- Administrative Fees: These can include management fees and costs associated with maintaining the account.
- Surrender Charges: If you need to access your money early, surrender charges can apply, making it costly to withdraw funds prematurely.
Complexity of Contracts
The terms and conditions associated with deferred fixed annuities can be complex and challenging to understand fully.
- Lengthy Documentation: Contracts often consist of extensive legal language that may confuse investors who are not financially savvy.
- Need for Professional Guidance: It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor familiar with annuity products to navigate these complexities effectively.
Inflation Risk Affecting Purchasing Power
One significant concern with deferred fixed annuities is inflation risk.
- Fixed Payments Lose Value Over Time: While payments are guaranteed, they do not adjust for inflation, which can erode purchasing power over time.
- Long-Term Considerations: Investors must consider whether their future needs will be met by fixed payments that may not keep pace with rising costs of living.
In conclusion, deferred fixed annuities present both opportunities and challenges for investors looking to secure their financial futures. They offer unique benefits such as tax-deferred growth, guaranteed income in retirement, principal protection, and no contribution limits. However, potential downsides include limited liquidity, lower returns compared to other investments, high fees, complexity in contracts, and inflation risk. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone considering adding deferred fixed annuities to their retirement strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Deferred Fixed Annuity Pros And Cons
- What is a deferred fixed annuity?
A deferred fixed annuity is an insurance contract that promises to pay you regular income or a lump sum at a future date while allowing your investment to grow tax-deferred. - What are the main advantages of deferred fixed annuities?
The main advantages include tax-deferred growth, guaranteed income during retirement, principal protection from market volatility, no contribution limits, and death benefits for beneficiaries. - What are the disadvantages of deferred fixed annuities?
The disadvantages include limited liquidity due to withdrawal restrictions and penalties, potentially lower returns compared to other investments, high fees including surrender charges, complexity in understanding contracts, and inflation risk affecting purchasing power. - How do I access my money in a deferred fixed annuity?
You typically cannot access your money without penalties until the contract matures or after a specified period; early withdrawals may incur surrender charges. - Are there any tax implications with deferred fixed annuities?
Earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal; however, withdrawals are subject to ordinary income tax and may incur additional penalties if taken before age 59½. - Can I lose my principal investment in a deferred fixed annuity?
No; most deferred fixed annuities guarantee principal protection against market losses. - How do inflation rates affect my payments from a deferred fixed annuity?
The payments remain constant over time; therefore, if inflation rises significantly, your purchasing power may decrease. - Should I consult a financial advisor before purchasing a deferred fixed annuity?
Yes; due to their complexity and long-term commitment involved in these products, consulting a financial advisor is highly recommended.