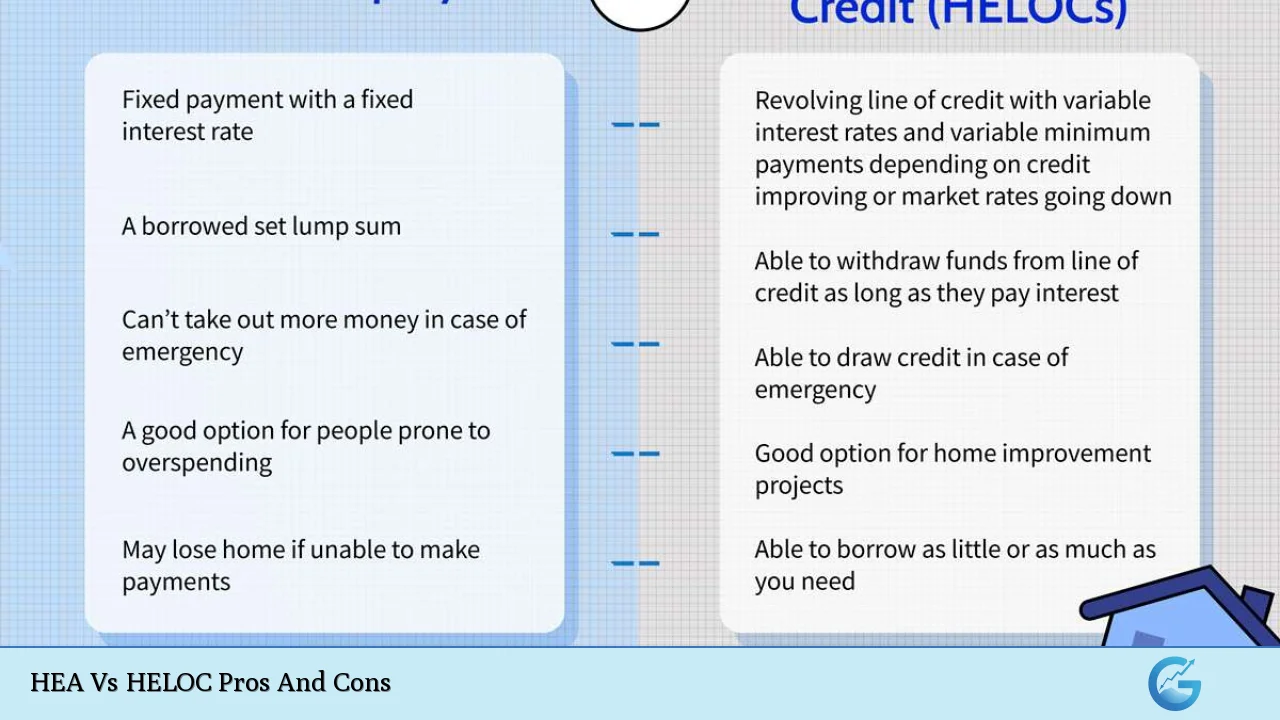
Understanding the various options for leveraging home equity is crucial for homeowners looking to finance projects, consolidate debt, or manage expenses. Two popular methods are Home Equity Agreements (HEAs) and Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs). Each has its unique structure, benefits, and drawbacks. This article will explore the pros and cons of both HEAs and HELOCs, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in financial strategies involving home equity.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| No monthly payments with HEA | HELOCs have variable interest rates |
| Flexible funding options with HELOC | Potential for foreclosure with both options |
| HEA does not affect debt-to-income ratio | Complex agreements with HEAs |
| Lower credit score requirements for HEA | HELOCs may tempt overspending |
| Tax-deductible interest on HELOCs | Fees associated with both products |
| Quick access to funds with HELOC | Long-term financial commitment with HEA |
| Good for large expenses with HEA lump sum | Less flexibility in repayment for HEA |
| No income verification required for HEA | Potentially complicated payoff terms for HEA |
Advantages of Home Equity Agreements (HEAs)
No Monthly Payments
One of the most significant advantages of a Home Equity Agreement is that it does not require monthly payments. This feature allows homeowners to access cash without the burden of regular repayments, freeing up cash flow for other expenses.
Does Not Affect Debt-to-Income Ratio
Because an HEA is not classified as a loan, it does not impact your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals seeking to maintain or improve their creditworthiness.
Lower Credit Score Requirements
HEAs typically have more lenient credit score requirements compared to HELOCs. Many providers may allow individuals with credit scores as low as 500 to qualify, making this option accessible to a broader range of homeowners.
Lump Sum Payment
With an HEA, homeowners receive a lump sum payment upfront. This can be ideal for financing significant expenses such as home renovations or debt consolidation, providing immediate access to funds without the need for ongoing borrowing.
No Income Verification Required
Many HEA providers do not require income verification, making it easier for individuals who may have fluctuating incomes or those who are self-employed to access funds.
Disadvantages of Home Equity Agreements (HEAs)
Complex Agreements
The structure of an HEA can be intricate, often involving detailed contracts that may be difficult to understand. Homeowners must carefully review the terms to ensure they fully comprehend their obligations.
Long-Term Financial Commitment
While HEAs offer flexibility in terms of repayment timing, they also represent a long-term financial commitment. Homeowners must plan for how they will repay the agreement when it comes due, often requiring the sale of the home or refinancing.
Potentially Complicated Payoff Terms
Paying off an HEA can be complex, especially if homeowners do not have a clear plan in place. The final payment is typically due at the end of the agreement term, which may catch some homeowners off guard if they are unprepared.
Advantages of Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs)
Flexible Funding Options
HELOCs provide flexible access to funds, allowing homeowners to borrow only what they need when they need it. This can be particularly useful for ongoing projects or expenses that may vary over time.
Tax-Deductible Interest
Interest paid on a HELOC may be tax-deductible if used for home improvements. This can provide significant savings during tax season and make borrowing more affordable.
Quick Access to Funds
Once approved, homeowners can quickly access their line of credit without needing to reapply each time they want to borrow. This ease of access makes HELOCs an attractive option for those who need funds on short notice.
Lower Interest Rates Compared to Other Loans
Typically, interest rates on HELOCs are lower than those associated with unsecured loans or credit cards because the loan is secured by the home. This can result in substantial savings over time.
Disadvantages of Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs)
Variable Interest Rates
One major drawback of HELOCs is that they often come with variable interest rates. This means that monthly payments can fluctuate based on market conditions, making budgeting more challenging.
Risk of Foreclosure
Both HEAs and HELOCs carry the risk of foreclosure if payments are not made. Since these products are secured by the home, failure to repay can lead to losing one’s property.
Temptation to Overspend
The flexibility offered by a HELOC can lead some borrowers to overspend. Without strict budgeting, it’s easy to draw more than necessary, resulting in higher debt levels than intended.
Fees Associated with Both Products
Both options often come with various fees, including origination fees and closing costs. These additional expenses can reduce the overall benefit gained from accessing home equity.
Closing Thoughts
Choosing between a Home Equity Agreement and a Home Equity Line of Credit requires careful consideration of your financial situation and goals. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses that cater to different needs.
It is essential to assess your ability to manage repayments, understand the potential risks involved, and consider how each option aligns with your long-term financial strategy. Consulting with a financial advisor may also provide valuable insights tailored specifically to your circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions About HEA Vs HELOC Pros And Cons
- What is a Home Equity Agreement (HEA)?
A Home Equity Agreement allows homeowners to receive cash upfront in exchange for a share of their home’s future value without monthly payments. - How does a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) work?
A HELOC provides homeowners with a revolving line of credit based on their home equity that they can draw from as needed. - What are the main differences between an HEA and a HELOC?
The primary difference lies in repayment; an HEA requires no monthly payments while a HELOC does. - Can I qualify for an HEA if I have bad credit?
Yes, many providers allow individuals with lower credit scores (as low as 500) to qualify for an HEA. - Are there any risks associated with these options?
Yes, both options involve risks such as potential foreclosure if payments are missed. - Is interest on a HELOC tax-deductible?
If used for qualifying home improvements, interest on a HELOC may be tax-deductible. - Can I use funds from an HELOC for any purpose?
Yes, funds from a HELOC can typically be used for various purposes including home improvements or debt consolidation. - What happens if I cannot repay my HEA?
If you cannot repay your HEA at its due date, you may need to sell your home or refinance.
This comprehensive analysis should equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding leveraging your home equity through either an HEA or a HELOC.