Home equity financing is a popular choice for homeowners looking to leverage their property’s value for various financial needs. Two primary options available are Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) and Home Equity Loans. Each option has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact a homeowner’s financial situation. Understanding these can help individuals make informed decisions based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and borrowing needs.
Pros and Cons Overview
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
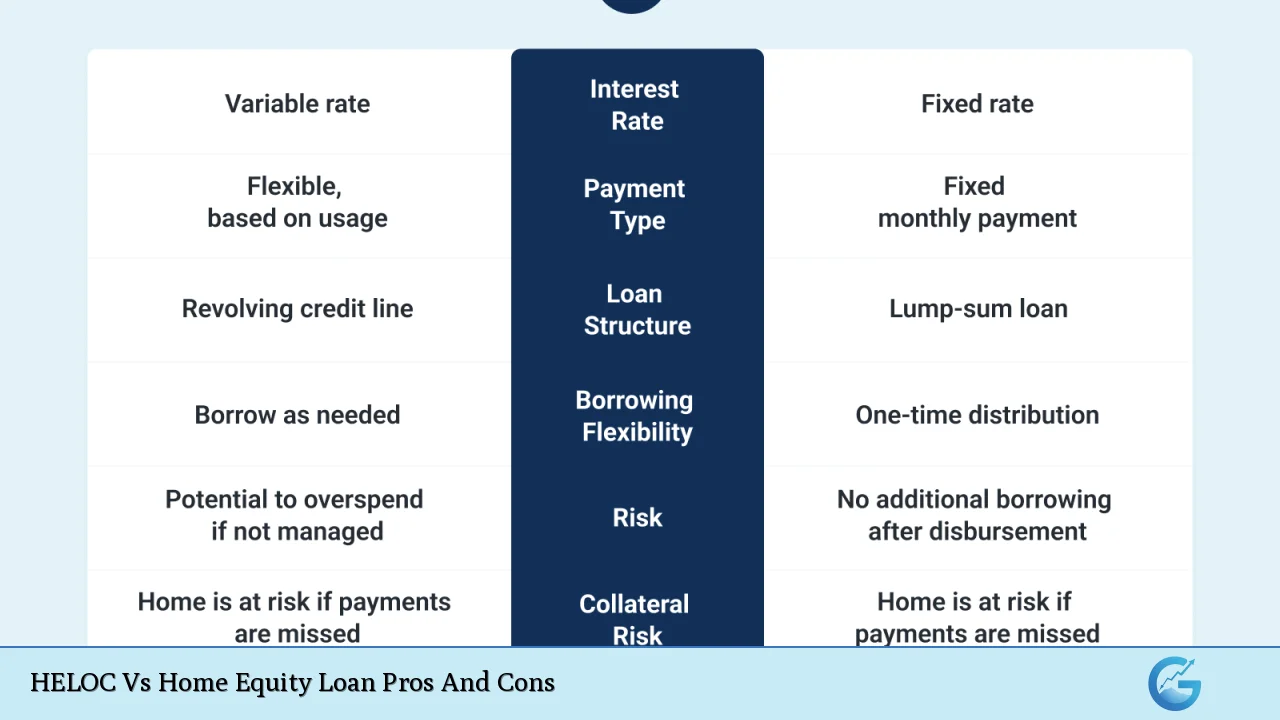
| Lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans | Your home is used as collateral, risking foreclosure |
| Flexibility in borrowing and repayment options | Variable interest rates can lead to unpredictable payments |
| Potential tax deductions on interest payments | Fees and closing costs can add up |
| Access to larger amounts of money than personal loans | Risk of overspending due to easy access to funds |
| Can improve cash flow management with structured payments | Potential for diminished equity if property values decline |
| Can be used for various purposes (home improvements, debt consolidation) | Complexity in understanding terms and conditions |
| Longer repayment periods available for HELOCs | Requires significant equity in the home to qualify |
| On-time payments can boost credit scores over time | Possible penalties for early repayment or missed payments |
Lower Interest Rates Compared to Unsecured Loans
One of the most significant advantages of both HELOCs and home equity loans is that they typically offer lower interest rates than unsecured loans, such as personal loans or credit cards. This is because these loans are secured by the equity in your home, making them less risky for lenders.
- Cost-effective borrowing: Homeowners can access funds at a lower cost.
- Potential savings: Lower interest rates can lead to substantial savings over time.
However, it is essential to compare the rates offered by different lenders, as they can vary widely based on individual circumstances.
Your Home is Used as Collateral, Risking Foreclosure
While leveraging home equity offers financial benefits, it comes with the inherent risk of using your home as collateral. If you fail to make the required payments, you could face foreclosure.
- Serious consequences: Defaulting on a HELOC or home equity loan means risking your home.
- Long-term implications: Losing your home can have lasting impacts on your financial health and credit score.
Homeowners should carefully assess their ability to repay before taking on additional debt secured by their property.
Flexibility in Borrowing and Repayment Options
HELOCs offer flexibility that traditional home equity loans do not. Borrowers can draw funds as needed during the draw period, which typically lasts several years.
- Access to funds: Borrowers can withdraw only what they need when they need it.
- Interest-only payment options: Many HELOCs allow borrowers to pay only interest during the draw period, keeping initial payments lower.
In contrast, home equity loans provide a lump sum with fixed repayment terms, which may be more suitable for specific projects or expenses.
Variable Interest Rates Can Lead to Unpredictable Payments
A significant drawback of HELOCs is that they often come with variable interest rates. This means that monthly payments can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Budgeting challenges: Variable rates make it difficult to predict future payments accurately.
- Financial strain: If interest rates rise significantly, borrowers may face unmanageable payment increases.
Homeowners should consider their risk tolerance regarding fluctuating payments when choosing between a HELOC and a fixed-rate home equity loan.
Potential Tax Deductions on Interest Payments
Interest paid on both HELOCs and home equity loans may be tax-deductible if the funds are used for qualified expenses, such as home improvements. This potential tax benefit makes these financing options attractive for many homeowners.
- Tax savings: Deductions can lower the overall cost of borrowing.
- Informed use of funds: Using borrowed funds for improvements can increase property value while providing tax benefits.
However, tax laws change frequently; homeowners should consult with a tax professional to understand current regulations regarding deductions.
Fees and Closing Costs Can Add Up
Both HELOCs and home equity loans may come with various fees, including application fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs. These costs can diminish the overall benefit of borrowing against home equity.
- Initial costs: Borrowers should be aware of upfront costs associated with securing these loans.
- Long-term expenses: Ongoing fees may apply throughout the life of the loan or line of credit.
It’s crucial for borrowers to read the fine print and understand all potential costs before committing to either option.
Access to Larger Amounts of Money Than Personal Loans
Both HELOCs and home equity loans allow homeowners to borrow larger amounts compared to unsecured personal loans. This access can be beneficial for significant expenses like renovations or debt consolidation.
- Financial flexibility: Borrowers can secure substantial funding based on their home’s equity.
- Investment opportunities: Larger amounts enable homeowners to invest in projects that could yield returns exceeding borrowing costs.
However, taking out large sums also increases financial responsibility; borrowers must ensure they can manage repayments effectively.
Risk of Overspending Due to Easy Access to Funds
The flexibility provided by HELOCs can sometimes lead to overspending. Because borrowers have ongoing access to funds, there is a temptation to withdraw more than necessary.
- Self-discipline required: Homeowners must maintain strict budgeting practices when using a HELOC.
- Debt accumulation risk: Unchecked borrowing could lead to unmanageable debt levels over time.
Borrowers should be cautious about their spending habits when considering a HELOC as a financial tool.
Can Improve Cash Flow Management with Structured Payments
Home equity loans typically come with fixed monthly payments that make budgeting easier. Conversely, HELOCs allow for interest-only payments during the draw period but require full repayments later on.
- Predictable budgeting: Fixed payments help homeowners plan their finances effectively over time.
- Cash flow benefits: Flexible payment structures can aid in managing cash flow during periods of variable income or unexpected expenses.
Understanding how each option affects cash flow is crucial for effective financial planning.
Potential for Diminished Equity if Property Values Decline
Borrowing against home equity inherently reduces the amount of unencumbered equity you have in your property. If property values decline after taking out a HELOC or home equity loan, you may owe more than your home is worth (underwater mortgage).
- Market risk exposure: Homeowners face potential losses if market conditions worsen after borrowing against their property’s value.
- Equity depletion: Using too much equity may limit future borrowing options or financial flexibility.
Homeowners should consider market trends before deciding how much equity to leverage through these financing options.
Complexity in Understanding Terms and Conditions
Both HELOCs and home equity loans come with complex terms that may confuse borrowers. Understanding these terms is crucial for making informed decisions about which product best suits individual needs.
- Need for diligence: Borrowers must thoroughly review loan agreements and ask questions about any unclear terms before signing anything.
- Potential pitfalls: Misunderstanding terms could lead to financial difficulties down the road if borrowers are unaware of specific obligations or fees associated with their loan products.
Seeking advice from financial professionals can help clarify any uncertainties related to these financing options.
Requires Significant Equity in the Home to Qualify
To qualify for either a HELOC or a home equity loan, homeowners typically need at least 20% equity in their homes. This requirement limits access for those who have recently purchased homes or whose property values have depreciated since purchase.
- Equity assessment: Homeowners must evaluate their current mortgage balance against their home’s market value before applying for either product.
- Access limitations: Those without sufficient equity may need alternative financing options if they require immediate funds or wish to consolidate debt.
Understanding one’s own financial situation is critical when considering leveraging home equity through these products.
Frequently Asked Questions About HELOC Vs Home Equity Loan Pros And Cons
- What is the main difference between a HELOC and a home equity loan?
The primary difference lies in how funds are accessed; a HELOC provides a revolving line of credit while a home equity loan offers a lump sum payment. - Are interest rates fixed or variable?
A home equity loan typically has fixed interest rates, whereas most HELOCs come with variable rates that fluctuate based on market conditions. - What are common uses for these types of loans?
Both products can be used for various purposes such as home renovations, debt consolidation, or covering major expenses like education costs. - Can I lose my house if I fail to repay?
Yes, both types of loans are secured by your property; failure to repay could result in foreclosure. - What happens when the draw period ends on a HELOC?
Once the draw period ends, borrowers must start repaying both principal and interest according to the agreed-upon terms. - How does borrowing against my home’s equity affect my credit score?
Responsible use of either product can improve your credit score over time; however, missed payments will negatively impact it. - Are there any tax benefits associated with these loans?
If used for qualified expenses like renovations, interest paid may be tax-deductible; consult a tax professional for specifics. - What should I consider before choosing between a HELOC and a home equity loan?
Your financial needs, budget management preferences, risk tolerance regarding variable rates, and how much equity you have are all important factors.
In conclusion, both HELOCs and home equity loans offer unique advantages and disadvantages that cater to different financial needs. While they provide opportunities for accessing funds at lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans, they also carry risks associated with using one’s home as collateral. By carefully weighing these pros and cons against individual circumstances—such as income stability, spending habits, and long-term financial goals—homeowners can make informed decisions about leveraging their property’s value effectively.