Indexed annuities are a unique financial product that combines features of both fixed and variable annuities. They are designed to provide investors with the potential for higher returns linked to a stock market index, such as the S&P 500, while also offering some degree of protection against market downturns. This balance of risk and reward has made indexed annuities increasingly popular among those planning for retirement. However, like any financial instrument, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential investors should carefully consider.
The following table summarizes the key pros and cons of indexed annuities:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Potential for higher returns than traditional fixed annuities | Limited upside due to caps on returns |
| Principal protection from market losses | Complexity in understanding terms and conditions |
| Tax-deferred growth until withdrawal | Surrender charges for early withdrawals |
| Guaranteed minimum return | Missed dividend income from underlying index stocks |
| Flexibility in investment options and strategies | Potentially high fees and commissions |
| Can provide a steady income stream during retirement | Liquidity issues due to long-term commitment |
| Inflation protection through market-linked growth | Returns may be lower than direct stock market investments |
Potential for Higher Returns than Traditional Fixed Annuities
Indexed annuities offer the possibility of earning returns that can exceed those provided by traditional fixed annuities. This is achieved by linking the returns to a specific market index. Investors can benefit from market upswings while still enjoying a level of security not typically found in variable annuities.
- Market Participation: The returns on indexed annuities are tied to the performance of an index, allowing for potentially greater earnings during bullish market conditions.
- Hybrid Nature: They combine features of both fixed and variable annuities, providing some growth potential while protecting the principal.
Limited Upside Due to Caps on Returns
While indexed annuities can provide higher returns compared to fixed annuities, they often come with caps that limit the maximum return an investor can earn.
- Cap Rates: Many indexed annuities set a cap on the percentage of index gains that will be credited to the account, which can significantly reduce potential earnings during strong market years.
- Participation Rates: The participation rate determines how much of an index’s gain will be credited to the annuity. If an index rises by 10% and the participation rate is 80%, only 8% will be credited.
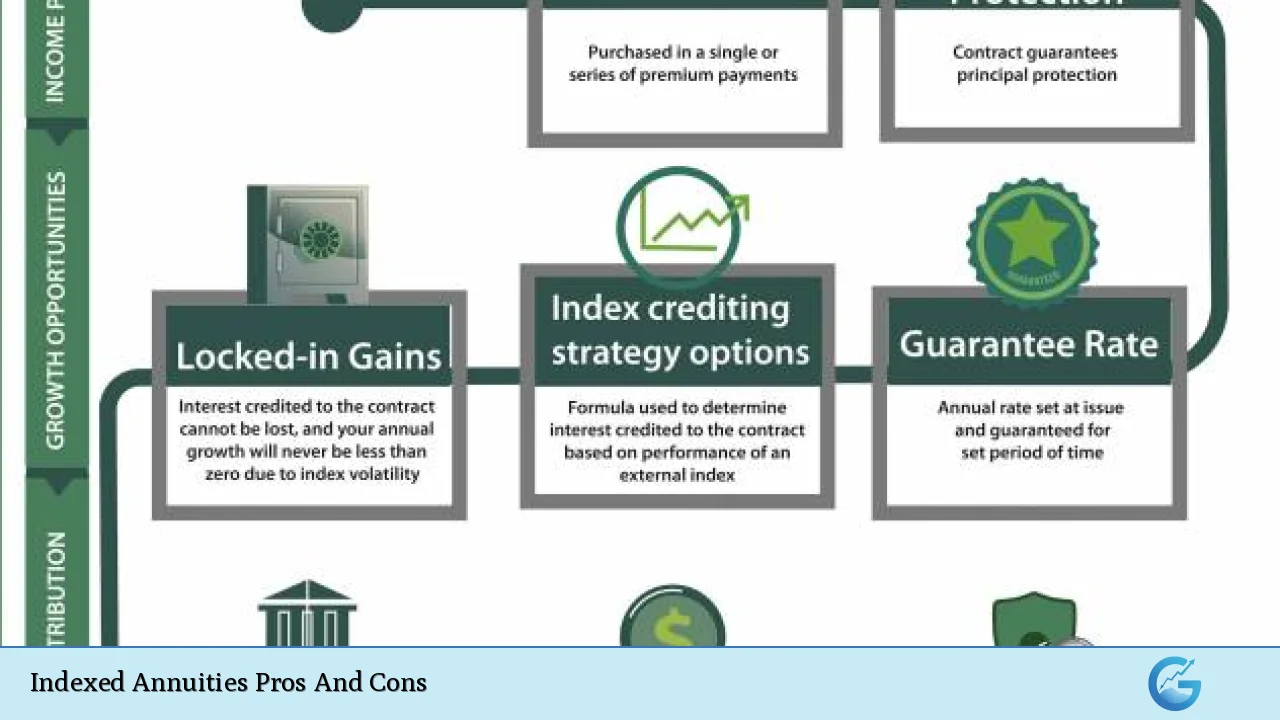
Principal Protection from Market Losses
One of the most appealing features of indexed annuities is their ability to protect investors’ principal from market downturns.
- Downside Risk Mitigation: Investors will not lose their initial investment even if the linked index performs poorly.
- Guaranteed Minimum Return: Indexed annuities typically offer a guaranteed minimum return, ensuring that investors receive some level of income regardless of market performance.
Complexity in Understanding Terms and Conditions
Indexed annuities are often criticized for their complexity, which can make it difficult for investors to fully understand what they are purchasing.
- Variety of Features: Different contracts may include various indexing methods, caps, floors, and participation rates that can be challenging to navigate.
- Misleading Marketing: The marketing materials may highlight potential gains without adequately explaining the limitations and risks involved.
Tax-Deferred Growth Until Withdrawal
Investors in indexed annuities enjoy tax-deferred growth on their earnings until they withdraw funds.
- Tax Efficiency: This allows for potentially greater accumulation over time compared to taxable investment accounts.
- Retirement Planning: Many investors find this feature beneficial as they prepare for retirement, allowing them to grow their savings without immediate tax implications.
Surrender Charges for Early Withdrawals
While indexed annuities provide many benefits, they also impose penalties for early withdrawals, which can significantly affect liquidity.
- Surrender Periods: Most indexed annuities have surrender periods ranging from several years during which withdrawals may incur substantial fees.
- Long-Term Commitment: Investors must be prepared for a long-term commitment as accessing funds early can lead to financial penalties.
Guaranteed Minimum Return
Indexed annuities typically guarantee a minimum return that provides some security against poor market performance.
- Safety Net: This feature ensures that even in declining markets, investors will receive some return on their investment.
- Predictability: This predictability can be particularly appealing for conservative investors looking for stability in their portfolios.
Missed Dividend Income from Underlying Index Stocks
Investors in indexed annuities do not receive dividends paid out by the stocks within the underlying index.
- Total Return vs. Price Return: Indexed annuities generally only account for price appreciation rather than total return, which includes dividends.
- Impact on Returns: Over time, this can result in lower overall returns compared to direct investments in index funds or stocks that pay dividends.
Flexibility in Investment Options and Strategies
Indexed annuities often provide various options regarding how funds are allocated within different indices or strategies.
- Customizable Strategies: Investors can choose how much exposure they want to different indices or select specific crediting methods based on their risk tolerance.
- Diversification Opportunities: This flexibility allows for diversification within a single product, potentially enhancing overall portfolio performance.
Potentially High Fees and Commissions
One significant downside of indexed annuities is the potential for high fees associated with them.
- Sales Commissions: Agents selling these products may earn high commissions, which can affect overall returns.
- Ongoing Fees: Some contracts may include management fees or other costs that could diminish investor returns over time.
Can Provide a Steady Income Stream During Retirement
Many individuals purchase indexed annuities as part of their retirement strategy because they can provide a reliable income stream.
- Lifetime Income Options: Some contracts offer options for lifetime income benefits that ensure retirees do not outlive their savings.
- Predictable Payments: This predictability can help retirees manage their budgets more effectively during retirement years.
Liquidity Issues Due to Long-Term Commitment
Investing in an indexed annuity often means committing funds for an extended period, which may limit liquidity when needed most.
- Access Limitations: Investors may find it challenging to access funds without incurring penalties during surrender periods.
- Planning Considerations: Those considering an indexed annuity should carefully evaluate their need for liquidity against the benefits offered by these products.
Inflation Protection Through Market-Linked Growth
Indexed annuities provide some level of inflation protection through their connection to market indices, which tend to rise over time with inflation.
- Growth Potential: As markets grow, so too does the value of an investor’s account, helping maintain purchasing power.
- Long-Term Hedge Against Inflation: This characteristic is particularly important for retirees who need their income to keep pace with rising costs over time.
Returns May Be Lower Than Direct Stock Market Investments
Despite offering some advantages over traditional fixed products, indexed annuities often underperform compared to direct investments in equities over long periods.
- Opportunity Cost: By capping returns and excluding dividends, investors may miss out on significant gains available through direct stock investments or low-cost index funds.
- Investment Horizon Considerations: For those willing to accept more risk directly in equities, alternatives may yield higher long-term returns than indexed annuities.
In conclusion, indexed annuities present a compelling option for many investors seeking a balance between growth potential and security. However, understanding both their advantages and disadvantages is crucial before making any investment decisions. Prospective buyers should conduct thorough research and consider consulting with financial professionals to ensure these products align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Indexed Annuities
- What is an indexed annuity?
An indexed annuity is a type of insurance product that provides returns based on the performance of a specified market index while offering principal protection. - How do I benefit from an indexed annuity?
You benefit from potential market-linked growth while enjoying downside protection against losses. - What are common risks associated with indexed annuities?
The main risks include limited upside due to caps on returns, complexity in understanding terms, and potential penalties for early withdrawals. - Are there any tax advantages?
Yes, earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal, which can enhance long-term growth compared to taxable accounts. - How do surrender charges work?
Surrender charges are fees imposed if you withdraw funds before a specified period ends; these charges can significantly reduce your investment’s value. - Can I lose money with an indexed annuity?
You cannot lose your principal investment; however, your returns may be lower than expected due to caps or other limitations. - What should I consider before purchasing an indexed annuity?
You should evaluate your financial goals, risk tolerance, need for liquidity, and understand all terms associated with the product. - How do I compare different indexed annuity products?
Compare features such as caps, participation rates, fees, and guarantees across different products before making a decision.