Investing in precious metals, such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, has long been a popular strategy for diversifying investment portfolios and hedging against economic uncertainty. These metals are not only valued for their intrinsic worth but also serve as a store of value during times of inflation and market volatility. However, like any investment, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential investors should carefully consider.
This article will explore the pros and cons of investing in precious metals, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions.
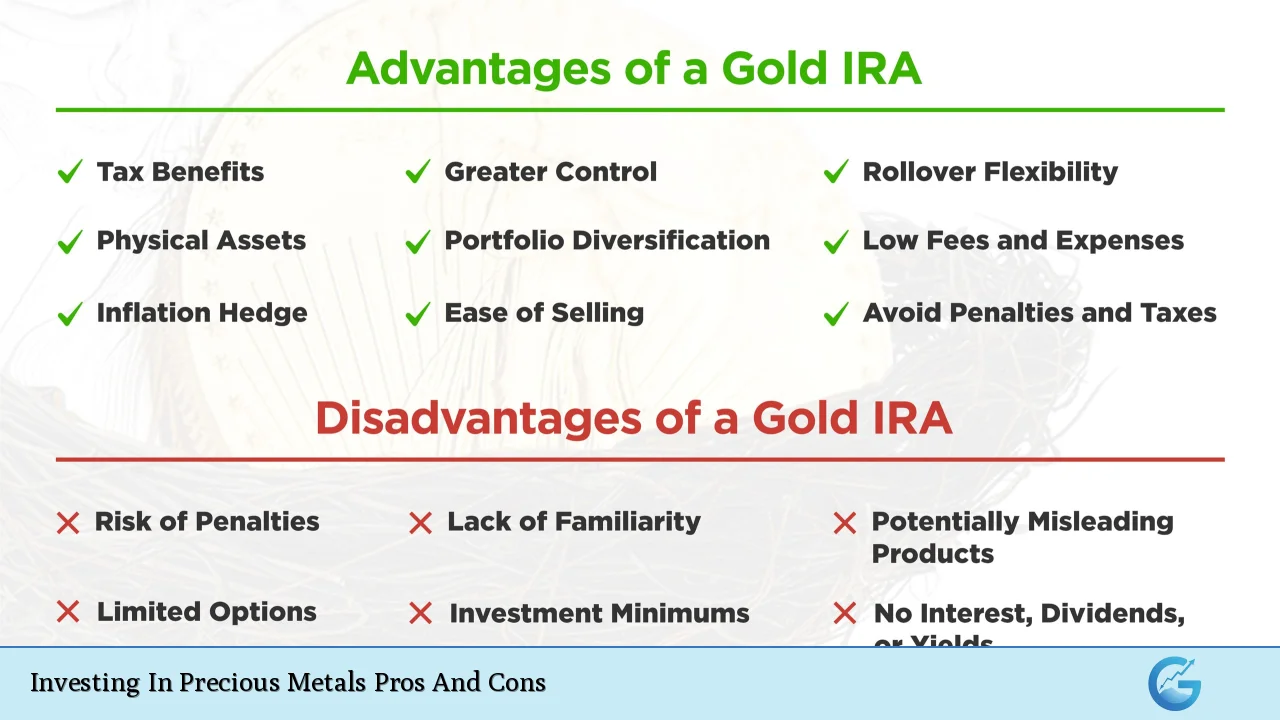
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Hedge against inflation | Lack of income generation |
| Diversification benefits | Storage and insurance costs |
| Long-term value appreciation potential | Market volatility |
| Safe haven during economic uncertainty | Limited liquidity |
| Tax advantages in some jurisdictions | Opportunity costs |
Hedge Against Inflation
One of the most significant advantages of investing in precious metals is their ability to act as a hedge against inflation. Historically, when the purchasing power of fiat currencies declines due to inflation, the prices of precious metals tend to rise. This characteristic makes them a reliable store of value, helping investors preserve their wealth over time.
- Intrinsic Value: Precious metals have intrinsic value that is not solely dependent on market conditions.
- Historical Performance: Over decades, gold and silver have maintained their purchasing power better than many currencies.
Diversification Benefits
Including precious metals in your investment portfolio can provide essential diversification benefits. Precious metals often exhibit low correlation with other asset classes like stocks and bonds.
- Risk Mitigation: When traditional investments are underperforming, precious metals may increase in value, thereby offsetting potential losses.
- Portfolio Stability: The inclusion of these assets can stabilize your portfolio during market downturns.
Long-Term Value Appreciation Potential
Precious metals have shown the potential for long-term appreciation due to factors such as limited supply and increasing global demand.
- Supply Constraints: The finite nature of these resources means that as demand increases, so does their value.
- Investment Demand: In times of crisis or economic instability, demand for precious metals often surges, driving up prices.
Safe Haven During Economic Uncertainty
During periods of economic instability or geopolitical tensions, precious metals are often viewed as safe-haven assets. Investors flock to these tangible assets when confidence in financial markets wanes.
- Wealth Preservation: Precious metals can help safeguard wealth during tumultuous times.
- Crisis Response: They often retain or increase in value when other investments falter.
Tax Advantages in Some Jurisdictions
In certain jurisdictions, investing in precious metals can offer favorable tax treatment compared to other forms of investment.
- Lower Tax Rates: Some countries impose lower capital gains taxes on precious metals than on stocks or real estate.
- Retirement Accounts: Investors can include precious metals in self-directed IRAs or similar retirement accounts, benefiting from tax-deferred growth.
Lack of Income Generation
One notable disadvantage of investing in precious metals is that they do not generate income. Unlike stocks or bonds that provide dividends or interest payments, precious metals rely solely on price appreciation for returns.
- No Cash Flow: Investors must wait for the value to increase rather than receiving regular income from their investments.
- Income-focused Strategy Limitation: This makes them less attractive for those seeking steady cash flow from their investments.
Storage and Insurance Costs
Investing in physical precious metals requires secure storage solutions, which can incur additional costs.
- Physical Security Needs: Storing gold or silver at home poses risks such as theft or loss; thus, many investors opt for safety deposit boxes or private vaults.
- Insurance Premiums: Protecting these assets against theft or damage adds another layer of expense that can erode profits.
Market Volatility
While precious metals are generally considered stable investments over the long term, they are still susceptible to market volatility.
- Price Fluctuations: Prices can swing dramatically based on economic indicators, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment.
- Risk Exposure: This volatility can lead to rapid changes in the value of your investment, making it riskier for those seeking stable returns.
Limited Liquidity
Although precious metals are generally liquid assets, selling physical metal may not be as straightforward as selling stocks or bonds.
- Finding Buyers: It may take time to locate a buyer willing to pay your desired price for physical metal.
- Market Conditions Impact: During periods of economic stress or uncertainty, liquidity can become restricted further complicating sales processes.
Opportunity Costs
Investors must also consider the opportunity costs associated with investing in precious metals.
- Missed Opportunities: By allocating funds to precious metals instead of other potentially higher-yielding investments (like stocks), you might miss out on superior returns elsewhere.
- Market Timing Risks: Timing purchases and sales effectively is crucial; poor timing can lead to losses compared to other asset classes that may perform better at different times.
In summary, investing in precious metals offers both significant advantages and notable disadvantages. It serves as a hedge against inflation and provides diversification benefits while also acting as a safe haven during economic uncertainties. However, it lacks income generation capabilities and incurs costs related to storage and insurance. Additionally, market volatility and limited liquidity present challenges that investors must navigate carefully.
Before making any investment decisions regarding precious metals, it’s essential to assess your financial goals and risk tolerance thoroughly. As always, consulting with a financial advisor familiar with your individual circumstances can provide valuable insights tailored to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Investing In Precious Metals
- What are the best precious metals to invest in?
The most commonly recommended precious metals include gold and silver due to their historical performance and liquidity. - How do I invest in physical precious metals?
You can purchase physical gold or silver from reputable dealers online or at local stores; ensure you understand the current market prices. - Are there tax implications when investing in precious metals?
Yes, tax treatment varies by jurisdiction; some regions offer lower capital gains taxes on precious metal investments. - How should I store my physical precious metals?
Physical assets should be stored securely either at home (in a safe), in bank safety deposit boxes, or at specialized vault facilities. - Can I include precious metals in my retirement account?
Yes, many self-directed IRAs allow you to hold certain types of precious metals within your retirement portfolio. - What is the liquidity like for physical precious metals?
While generally liquid, selling physical metal may take time compared to more conventional assets like stocks. - How do I determine the right time to buy or sell?
Market analysis using both technical indicators and fundamental news can help inform optimal buying and selling times. - What are the risks associated with investing in mining stocks?
Mining stocks are subject to operational risks specific to the companies involved; they may not always correlate directly with metal prices.
Investing in precious metals requires careful consideration of both its strengths and weaknesses. By understanding these factors clearly, investors can make informed choices aligned with their financial strategies.