Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are essential financial tools for retirement planning, offering various tax advantages and investment opportunities. They come in several forms, primarily Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs, each with distinct features that cater to different financial situations and goals. Understanding the pros and cons of IRAs is crucial for individuals looking to maximize their retirement savings while navigating the complexities of tax implications and investment strategies.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the advantages and disadvantages of IRAs, helping you make informed decisions about your retirement planning.
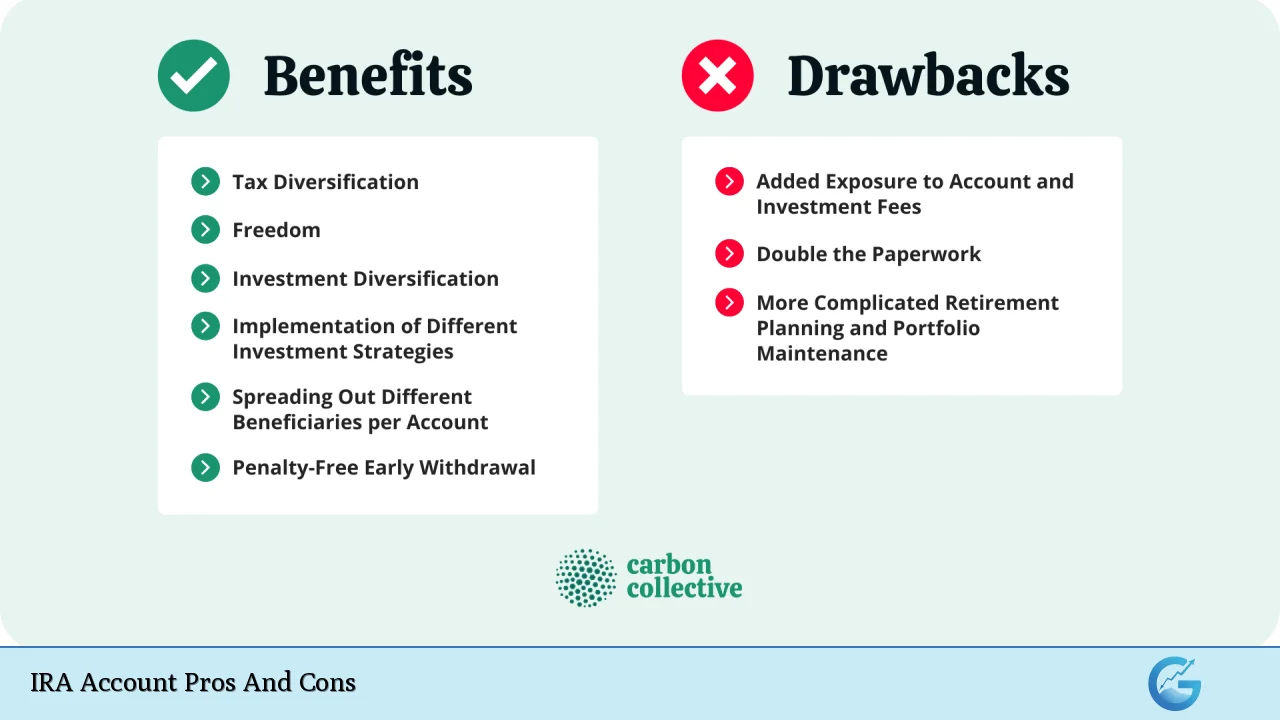
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Tax advantages for retirement savings | Contribution limits restrict savings potential |
| Diverse investment options available | Penalties for early withdrawals can apply |
| Potential for compound growth over time | Required minimum distributions (RMDs) for Traditional IRAs |
| No taxes on qualified withdrawals from Roth IRAs | Income limits may restrict Roth IRA contributions |
| Flexibility in accessing contributions from Roth IRAs | No immediate tax deduction for Roth IRA contributions |
| Ability to pass on tax-free benefits to heirs (Roth IRA) | Complex rules regarding withdrawals and penalties |
| Can be used to roll over funds from other retirement accounts | Potentially high fees depending on the provider |
| Encourages disciplined saving habits through auto contributions | Investment choices may be limited by some custodians |
Tax Advantages for Retirement Savings
One of the primary benefits of IRAs is their tax advantages.
- Traditional IRAs allow individuals to deduct contributions from their taxable income, effectively reducing their current tax liability. This means that you can contribute pre-tax dollars, allowing your investments to grow without being taxed until withdrawal during retirement.
- Roth IRAs, on the other hand, require contributions to be made with after-tax dollars. However, they offer the significant advantage of tax-free withdrawals in retirement, provided certain conditions are met.
These tax benefits can significantly enhance your retirement savings over time by allowing your investments to grow without immediate tax consequences.
Diverse Investment Options Available
IRAs provide a broad range of investment options, allowing account holders to customize their portfolios according to their risk tolerance and financial goals.
- You can invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, real estate, and even alternative assets like precious metals or cryptocurrencies through self-directed IRAs.
- This diversity enables investors to create a balanced portfolio that can adapt to changing market conditions and personal financial objectives.
Potential for Compound Growth Over Time
The power of compound interest plays a crucial role in growing retirement savings.
- By investing early and consistently in an IRA, you can benefit from compounding returns, where your earnings generate additional earnings over time.
- This effect is particularly pronounced in accounts with tax-deferred growth like Traditional IRAs or tax-free growth like Roth IRAs, making them effective vehicles for long-term savings.
No Taxes on Qualified Withdrawals from Roth IRAs
Roth IRAs offer a unique advantage: qualified withdrawals are entirely tax-free.
- Once you reach age 59½ and have held the account for at least five years, you can withdraw both contributions and earnings without incurring any taxes.
- This feature is especially beneficial for those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement compared to their current income level.
Flexibility in Accessing Contributions from Roth IRAs
Another significant benefit of Roth IRAs is the flexibility they provide regarding withdrawals.
- You can withdraw your contributions at any time without incurring taxes or penalties since you’ve already paid taxes on that money.
- This makes Roth IRAs an attractive option for those who want a backup emergency fund while still saving for retirement.
Ability to Pass on Tax-Free Benefits to Heirs (Roth IRA)
Roth IRAs also provide an estate planning advantage by allowing account holders to pass on their wealth tax-free.
- Beneficiaries of a Roth IRA can inherit the account without having to pay income taxes on distributions.
- This feature makes Roth IRAs an effective tool for transferring wealth while minimizing tax liabilities for heirs.
Can Be Used to Roll Over Funds from Other Retirement Accounts
IRAs offer flexibility when it comes to managing existing retirement accounts.
- You can roll over funds from other qualified plans like 401(k)s into an IRA without incurring taxes or penalties.
- This consolidation allows for better management of your retirement savings and may provide access to a wider range of investment options.
Encourages Disciplined Saving Habits Through Auto Contributions
Many financial institutions allow automatic contributions to IRAs, which can help individuals maintain consistent saving habits.
- Setting up automatic transfers from checking accounts into IRAs ensures that you regularly contribute towards your retirement goals without having to think about it actively.
- This approach fosters discipline and can significantly enhance long-term savings potential.
Contribution Limits Restrict Savings Potential
Despite their many advantages, one notable drawback of IRAs is the annual contribution limits set by the IRS.
- For 2024 and 2025, individuals under 50 can contribute up to $7,000 per year ($8,000 if aged 50 or older).
- These limits may restrict higher earners or those looking to save aggressively for retirement compared to other investment vehicles like 401(k) plans which often allow higher annual contributions.
Penalties for Early Withdrawals Can Apply
Early withdrawal penalties are a significant consideration when investing in an IRA.
- If you withdraw funds from a Traditional IRA before age 59½, you typically face a 10% penalty in addition to regular income taxes on the amount withdrawn.
- While Roth IRA contributions can be accessed penalty-free at any time, withdrawing earnings before meeting specific criteria (age 59½ and five-year rule) incurs penalties.
This limitation makes it essential for investors to consider their liquidity needs before committing funds to an IRA.
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) for Traditional IRAs
Traditional IRAs come with required minimum distribution rules that mandate account holders begin withdrawing funds at age 73 (as of December 31, 2024).
- Failing to take these distributions results in severe penalties—50% of the amount that should have been withdrawn.
- This requirement can force individuals into unfavorable market conditions where they must sell investments at a loss just to meet RMD obligations.
Income Limits May Restrict Roth IRA Contributions
Roth IRAs have specific income limits that may prevent high earners from contributing directly.
- For single filers in 2024, the ability to contribute phases out at modified adjusted gross incomes above $161,000; married couples filing jointly face limits starting at $240,000.
- Those exceeding these thresholds must explore alternative strategies like backdoor Roth conversions or other retirement accounts.
No Immediate Tax Deduction for Roth IRA Contributions
While Traditional IRAs offer immediate tax deductions on contributions, Roth IRA contributions do not provide this benefit.
- Investors must wait until retirement age (and after five years) to enjoy the full benefits of their contributions through tax-free withdrawals.
- This delayed gratification may not appeal to individuals seeking upfront tax relief during their working years.
Complex Rules Regarding Withdrawals and Penalties
Navigating the rules surrounding IRA withdrawals can be complex and daunting for many investors.
- Each type of IRA has different regulations concerning early withdrawals, penalties, and taxation upon distribution.
- Misunderstanding these rules could lead to costly mistakes or unexpected tax liabilities during retirement planning efforts.
Potentially High Fees Depending on the Provider
The fees associated with managing an IRA can vary significantly based on the provider chosen.
- Some institutions charge high management fees or commissions that can erode investment returns over time.
- It’s essential for investors to carefully compare providers and understand fee structures before opening an account.
Investment Choices May Be Limited by Some Custodians
While many custodians offer diverse investment options within an IRA, some may impose restrictions on available assets or charge additional fees for certain types of investments.
- Investors should research potential custodians thoroughly before committing funds to ensure they align with their investment strategies and preferences.
In conclusion, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) present both significant advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully weighed when planning for retirement. The decision between Traditional and Roth IRAs largely depends on individual financial situations, future expectations regarding income levels during retirement, and personal investment strategies. By understanding these pros and cons thoroughly, investors can make informed choices that best suit their long-term financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions About IRA Account Pros And Cons
- What is an IRA?
An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a type of savings account designed specifically for retirement savings with various tax advantages. - What are the main types of IRAs?
The two main types are Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs; each has different tax implications regarding contributions and withdrawals. - Can I withdraw money from my IRA before retirement?
You can withdraw contributions from a Roth IRA without penalties; however, early withdrawals from a Traditional IRA typically incur taxes and penalties. - What are required minimum distributions (RMDs)?
RMDs are mandatory withdrawals that must begin at age 73 from Traditional IRAs; failing to take them incurs heavy penalties. - Are there contribution limits for IRAs?
Yes, as of 2024, individuals under 50 can contribute up to $7,000 annually ($8,000 if aged 50 or older). - What happens if I exceed my income limits for a Roth IRA?
If your income exceeds certain thresholds, you may not be eligible to contribute directly; alternatives include backdoor conversions. - Can I roll over my 401(k) into an IRA?
Yes, you can roll over funds from a 401(k) into either a Traditional or Roth IRA without incurring taxes. - What fees should I consider when choosing an IRA provider?
Look out for management fees, transaction costs, and any additional charges associated with specific investments.