Lease to own car agreements, also known as rent-to-own or lease-purchase agreements, offer a unique approach to vehicle acquisition. This financing option combines elements of leasing and buying, providing individuals with an alternative path to car ownership. As the automotive industry evolves and consumers seek flexible options, understanding the intricacies of lease to own arrangements becomes crucial for making informed decisions.
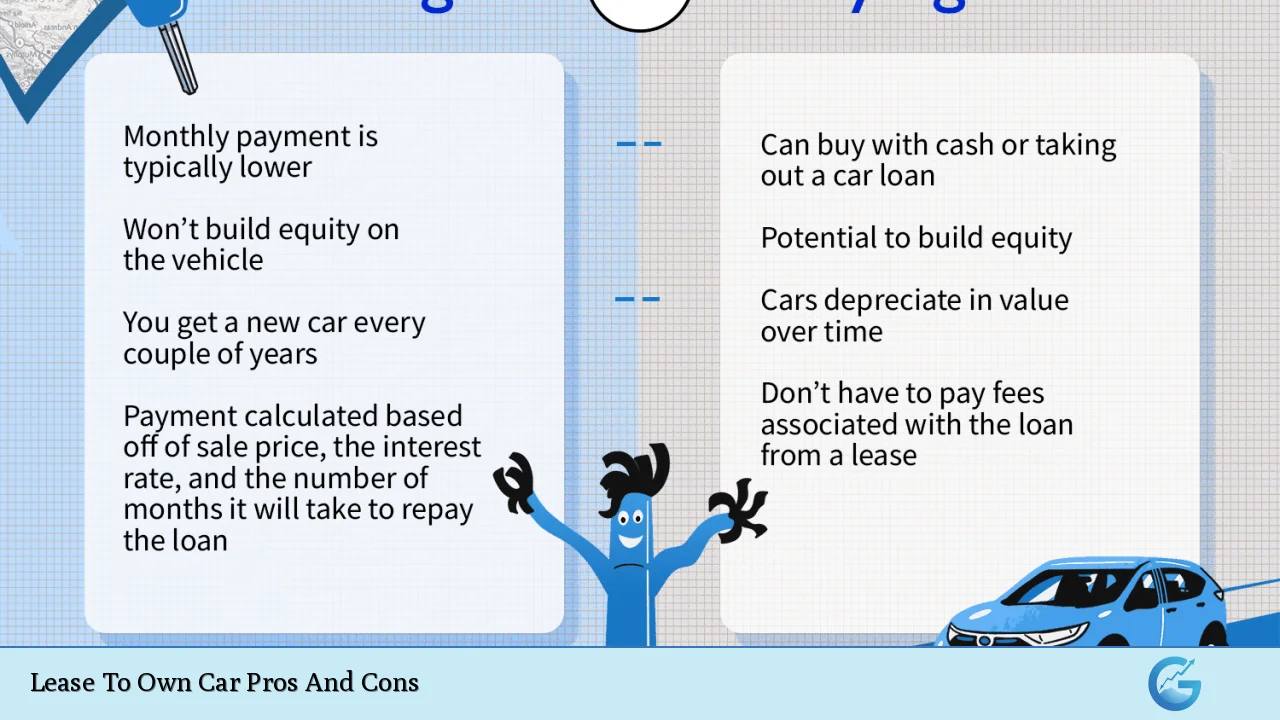
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower initial costs | Higher overall expense |
| Flexibility in ownership | Mileage restrictions |
| Access to newer vehicles | Potential for negative equity |
| Simplified approval process | Limited customization options |
| Opportunity to build credit | Responsibility for maintenance and repairs |
| Option to walk away | Complex contracts and hidden fees |
Advantages of Lease to Own Car Agreements
Lower Initial Costs
One of the primary attractions of lease to own car agreements is the reduced upfront financial commitment. Unlike traditional car purchases that often require substantial down payments, lease to own arrangements typically feature:
- Lower down payments
- Reduced monthly installments
- Smaller initial cash outlay
This financial structure makes it easier for individuals with limited savings or those looking to preserve capital for other investments to acquire a vehicle. In the context of personal finance management, this can be particularly advantageous for those seeking to maintain liquidity or diversify their investment portfolio.
Flexibility in Ownership
Lease to own agreements offer a unique blend of leasing and purchasing, providing consumers with enhanced flexibility:
- Option to buy the vehicle at the end of the lease term
- Ability to return the vehicle without further obligation
- Opportunity to reassess financial situation before committing to ownership
This flexibility aligns well with the dynamic nature of personal finance, allowing individuals to adapt their vehicle ownership strategy based on changing economic conditions or personal circumstances. For investors in volatile markets such as forex or cryptocurrency, this adaptability can be particularly valuable, enabling them to adjust their asset allocation without being tied to a long-term car loan.
Access to Newer Vehicles
Lease to own arrangements often provide access to newer, more technologically advanced vehicles that might otherwise be out of reach:
- Latest safety features and fuel-efficient technologies
- Advanced infotainment systems
- Improved reliability and performance
For professionals in finance-related fields, driving a newer vehicle can project an image of success and reliability, potentially enhancing client relationships and business opportunities. Moreover, the ability to upgrade to newer models more frequently can be seen as a hedge against rapid technological obsolescence in the automotive sector.
Simplified Approval Process
Compared to traditional auto loans, lease to own agreements often feature a more lenient approval process:
- Less stringent credit requirements
- Faster approval times
- Increased accessibility for those with limited credit history
This aspect of lease to own agreements can be particularly beneficial for young professionals or entrepreneurs in the finance sector who may not have established extensive credit histories. It provides an opportunity to acquire necessary transportation while simultaneously building a positive credit profile, which can be crucial for future financial endeavors.
Opportunity to Build Credit
Regular, timely payments on a lease to own agreement can contribute positively to an individual’s credit score:
- Consistent payment history reported to credit bureaus
- Potential for credit score improvement over time
- Demonstration of financial responsibility
For those looking to strengthen their financial profile, this aspect of lease to own agreements can serve as a strategic tool. A robust credit score is invaluable in the finance industry, potentially leading to better terms on future loans, increased negotiating power in business deals, and enhanced credibility in financial circles.
Option to Walk Away
Unlike traditional car loans, lease to own agreements typically offer the option to return the vehicle at the end of the lease term without further obligation:
- No long-term commitment required
- Ability to adapt to changing financial circumstances
- Protection against being stuck with a depreciating asset
This exit strategy can be particularly appealing to those working in dynamic financial markets. For forex traders or cryptocurrency investors, the ability to quickly adjust personal expenses in response to market fluctuations can be crucial for maintaining overall financial stability.
Disadvantages of Lease to Own Car Agreements
Higher Overall Expense
While lease to own agreements may offer lower monthly payments, they often result in a higher total cost over time:
- Higher interest rates compared to traditional auto loans
- Extended payment periods leading to increased interest accumulation
- Additional fees and charges embedded in the agreement
For the financially savvy, it’s crucial to calculate the total cost of ownership, including all fees and interest, to accurately compare lease to own options with traditional purchasing methods. This higher overall expense can potentially impact long-term wealth accumulation strategies, especially for those focused on maximizing returns in other investment vehicles.
Mileage Restrictions
Most lease to own agreements come with strict mileage limits:
- Typical annual limits range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles
- Excess mileage fees can be substantial
- Potential for unexpected costs at the end of the lease term
For finance professionals who frequently travel for client meetings or those who enjoy road trips, these mileage restrictions can be particularly limiting. Exceeding mileage limits can result in significant additional costs, potentially eroding the perceived financial benefits of the lease to own arrangement.
Potential for Negative Equity
The structure of lease to own agreements can sometimes lead to a situation where the amount owed on the vehicle exceeds its market value:
- Rapid depreciation of vehicle value
- Extended payment terms
- Higher interest rates contributing to slower principal reduction
This scenario, known as negative equity, can be particularly problematic for those looking to transition to a different vehicle or seeking to leverage their assets. In the context of personal finance management, negative equity in a vehicle can be seen as a liability, potentially impacting overall net worth calculations and financial planning strategies.
Limited Customization Options
Lease to own agreements often come with restrictions on vehicle modifications:
- Prohibition of aftermarket upgrades
- Limited ability to personalize the vehicle
- Potential penalties for any alterations made
For car enthusiasts or those who view their vehicle as an extension of their personal brand, these limitations can be frustrating. In the image-conscious world of finance and business, the inability to customize a vehicle to reflect personal or professional status may be seen as a significant drawback.
Responsibility for Maintenance and Repairs
Unlike traditional leases, lease to own agreements often place the responsibility for maintenance and repairs on the lessee:
- Costs for regular maintenance fall to the driver
- Unexpected repair expenses can disrupt budgeting
- Potential for higher insurance premiums
This aspect of lease to own agreements introduces an element of financial uncertainty. For those accustomed to the precise calculations and risk management strategies common in finance and investment, the unpredictable nature of vehicle maintenance costs can be a significant concern.
Complex Contracts and Hidden Fees
Lease to own agreements are often characterized by intricate contractual terms and potential hidden costs:
- Lengthy contracts with complex legal language
- Acquisition fees, disposition fees, and early termination penalties
- Potential for unexpected charges at the end of the lease term
The complexity of these agreements demands careful scrutiny and potentially legal consultation, adding an additional layer of effort and expense to the vehicle acquisition process. For finance professionals accustomed to analyzing complex financial instruments, the opacity of some lease to own contracts may raise red flags and require additional due diligence.
In conclusion, lease to own car agreements present a mixed bag of opportunities and challenges. While they offer increased accessibility and flexibility, particularly for those with limited credit history or capital, they also come with potential financial pitfalls and restrictions. For individuals in the finance, crypto, forex, and money market sectors, the decision to enter a lease to own agreement should be approached with the same level of analysis and strategic thinking applied to other financial decisions. By carefully weighing the pros and cons against personal financial goals and market conditions, one can make an informed decision that aligns with their overall financial strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease To Own Car Pros And Cons
- How does a lease to own car agreement differ from a traditional car lease?
A lease to own agreement combines elements of leasing and buying, with payments contributing towards eventual ownership. Traditional leases typically don’t offer an ownership option without additional negotiations or payments at the end of the term. - Can a lease to own agreement improve my credit score?
Yes, if the lessor reports payments to credit bureaus, consistent on-time payments can positively impact your credit score. However, it’s essential to confirm the reporting practices with the lessor before entering the agreement. - What happens if I want to end a lease to own agreement early?
Early termination often involves penalties and fees. The specific consequences depend on the contract terms, but they may include paying the remaining balance or a predetermined termination fee. - Are maintenance costs included in a lease to own car agreement?
Generally, maintenance costs are the responsibility of the lessee in a lease to own agreement. Unlike some traditional leases, these agreements typically don’t include maintenance packages. - How does depreciation affect a lease to own car agreement?
Depreciation is factored into the agreement’s structure, often resulting in higher overall costs compared to buying outright. The lessee essentially pays for the vehicle’s depreciation during the lease term, plus interest and fees. - Can I negotiate the terms of a lease to own car agreement?
While some aspects may be negotiable, many terms are standardized. Key areas for potential negotiation include the purchase price, interest rate, and length of the agreement. - How does a lease to own agreement impact my debt-to-income ratio?
Lease to own payments are typically considered debt and can increase your debt-to-income ratio. This can affect your ability to secure other loans or credit during the lease term. - What happens at the end of a lease to own term if I decide not to purchase the vehicle?
If you choose not to purchase the vehicle, you typically return it to the lessor. However, you may be responsible for excess wear and tear charges or mileage fees, depending on the agreement terms.