The concept of lease-to-own homes, also known as rent-to-own agreements, has gained traction among potential homeowners who may not be ready to purchase a property outright. This arrangement allows tenants to rent a home with the option to buy it later, providing a unique path to homeownership. For many, it represents a viable alternative in the current housing market, where rising prices and stringent mortgage requirements can make traditional home buying challenging. However, like any financial decision, lease-to-own agreements come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential buyers should carefully consider.
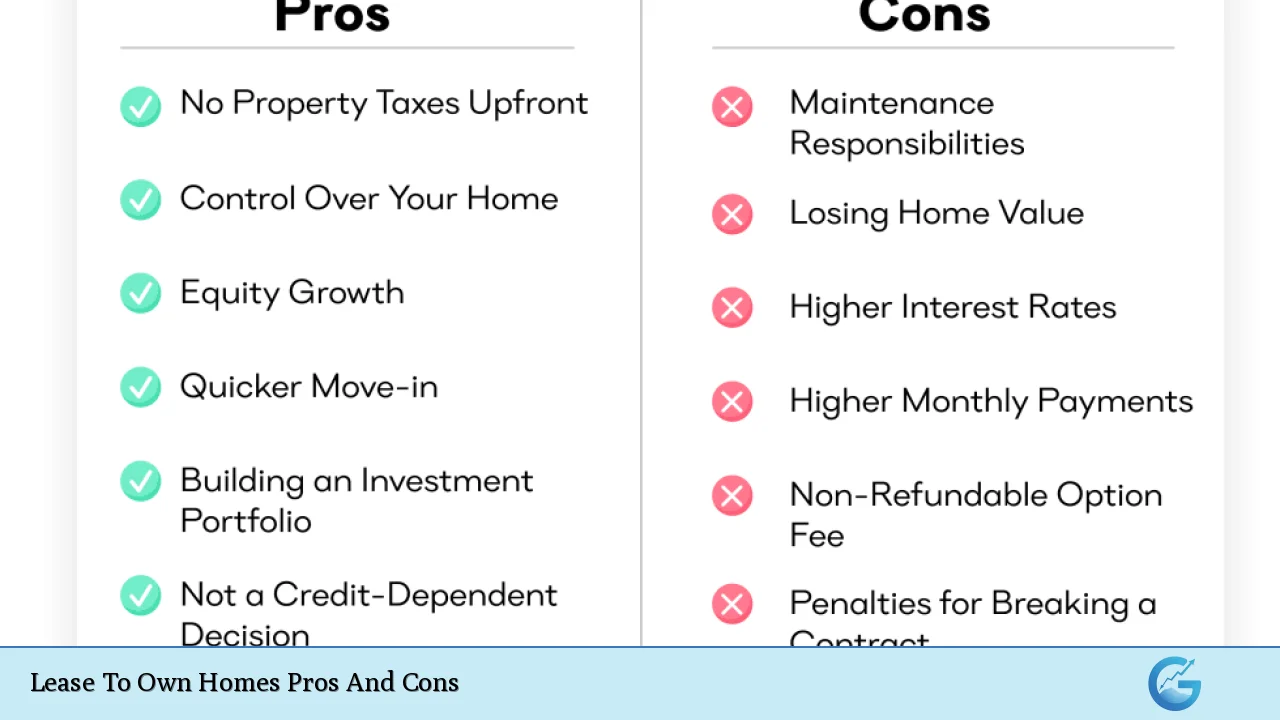
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Pathway to homeownership for those with poor credit or insufficient savings. | Higher overall costs compared to traditional renting. |
| Ability to lock in purchase price at the start of the agreement. | Risk of losing option fees and rent credits if not purchased. |
| Opportunity to improve credit score and save for a down payment. | Maintenance responsibilities typically fall on the tenant. |
| Test living in the home before committing to purchase. | Limited availability of suitable properties. |
| Potential for lower upfront costs compared to traditional home buying. | Market fluctuations could lead to depreciation of the property value. |
Pathway to Homeownership for Those with Poor Credit or Insufficient Savings
One of the most significant advantages of lease-to-own homes is that they provide a pathway to homeownership for individuals who may struggle to qualify for traditional financing due to poor credit or insufficient savings.
- Flexibility in Financing: Lease-to-own agreements often require less stringent credit requirements than conventional mortgages, allowing individuals with lower credit scores a chance at homeownership.
- Time to Improve Financial Standing: The lease period allows tenants time to improve their credit scores and financial situations, making them more eligible for mortgages when it’s time to purchase.
- Building Equity: A portion of the rent paid during the lease may be credited toward the purchase price, helping tenants build equity over time.
Higher Overall Costs Compared to Traditional Renting
While lease-to-own agreements offer unique benefits, they often come at a higher cost than traditional renting.
- Premium Rent Payments: Tenants usually pay a higher monthly rent that includes an option fee and potentially rent credits that contribute toward the purchase price.
- Long-Term Financial Commitment: The total cost of renting over several years can exceed what would have been paid in a standard rental agreement without an option to buy.
- Potential for Lost Investment: If tenants decide not to purchase the property, they may lose all additional payments made toward the purchase.
Ability to Lock in Purchase Price at the Start of the Agreement
Another key advantage is the ability to lock in a purchase price at the beginning of the lease term.
- Protection Against Rising Prices: In markets where home prices are increasing rapidly, locking in a price can save buyers money compared to purchasing later at market value.
- Predictability in Financial Planning: Knowing the future purchase price allows tenants to plan their finances better and save accordingly.
Risk of Losing Option Fees and Rent Credits if Not Purchased
However, one notable risk associated with lease-to-own agreements is financial loss if the tenant chooses not to buy.
- Non-refundable Option Fees: Typically, tenants pay an upfront option fee that is non-refundable if they do not proceed with purchasing the home.
- Loss of Rent Credits: Any additional payments made towards rent credits are forfeited if the tenant decides against purchasing.
Opportunity to Improve Credit Score and Save for a Down Payment
The structure of lease-to-own agreements can also facilitate personal financial growth.
- Time for Financial Improvement: Tenants can use this time to improve their credit scores by making timely payments and managing debts effectively.
- Saving for Down Payment: The arrangement allows tenants to save money during their rental period that can be used as a down payment when they choose to buy.
Maintenance Responsibilities Typically Fall on the Tenant
One disadvantage that often surprises tenants is that maintenance responsibilities usually shift from landlords to tenants in lease-to-own agreements.
- Increased Responsibility: Tenants may be responsible for upkeep and repairs during their lease term, which can add unexpected costs.
- Financial Burden: If significant repairs are needed, it could strain finances further, especially if tenants are already managing higher monthly payments.
Test Living in the Home Before Committing to Purchase
A unique benefit of lease-to-own arrangements is that they allow potential buyers to “test” living in a home before making a long-term commitment.
- Neighborhood Familiarity: This arrangement provides an opportunity for renters to assess whether they enjoy living in a specific neighborhood without committing immediately.
- Assessing Property Condition: Tenants can evaluate any issues with the property firsthand before deciding whether it’s worth purchasing.
Limited Availability of Suitable Properties
Despite its advantages, finding suitable properties under lease-to-own agreements can be challenging.
- Market Limitations: Not all areas have homes available under this arrangement, which can limit options for interested buyers.
- Seller Willingness: Sellers may be hesitant or unwilling to enter into lease-to-own contracts, further narrowing available choices.
Potential for Lower Upfront Costs Compared to Traditional Home Buying
For many prospective buyers, one of the appealing aspects of lease-to-own homes is lower upfront costs compared to traditional purchases.
- Reduced Down Payment Requirements: Lease-to-own arrangements often require smaller initial payments than conventional mortgages, making them more accessible for many people.
- No Immediate Need for Full Financing: This structure allows individuals who may not yet have sufficient funds saved up for a down payment time to gather resources while living in their future home.
Market Fluctuations Could Lead to Depreciation of Property Value
On the flip side, there is always a risk associated with real estate investments due to market fluctuations.
- Potential Losses: If property values decline during the lease period, buyers could end up paying more than market value when it’s time to purchase.
- Investment Risk: This situation could lead tenants into negative equity situations where they owe more on their mortgage than what their home is worth if they proceed with buying after depreciation occurs.
In conclusion, while lease-to-own homes present an attractive option for many aspiring homeowners—especially those facing financial hurdles—it’s crucial for potential buyers to weigh both advantages and disadvantages carefully. Understanding these factors will help inform decisions about whether this pathway aligns with individual financial goals and circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease To Own Homes
- What are lease-to-own homes?
Lease-to-own homes allow renters to live in a property while having an option or obligation to purchase it later. - How does a rent-to-own agreement work?
A tenant pays rent along with an option fee; part of this rent may contribute toward the future down payment on purchasing the home. - What happens if I decide not to buy?
If you choose not to buy at the end of your lease term, you typically lose your option fee and any rent credits accumulated. - Can I negotiate terms in a lease-to-own agreement?
Yes, terms such as purchase price and monthly payments can often be negotiated prior to signing the contract. - Who is responsible for repairs during the lease?
The tenant usually assumes responsibility for maintenance and repairs unless otherwise specified in the contract. - What are common pitfalls of rent-to-own agreements?
Common pitfalls include hidden fees, loss of investment if you don’t buy, and potential repair costs falling on tenants. - Is it easier than getting a mortgage?
Yes, lease-to-own agreements often have less stringent qualification criteria compared to traditional mortgages. - How long do lease-to-own contracts typically last?
The duration varies but commonly lasts between one and three years before needing renewal or purchase decision.