When it comes to acquiring a vehicle, individuals often face the decision of whether to lease or buy. This choice can significantly impact personal finances, lifestyle, and long-term satisfaction. Leasing typically involves lower monthly payments and the ability to drive a new car every few years, while buying allows for ownership and the potential for long-term savings. Understanding the pros and cons of each option is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower monthly payments | Higher overall costs in the long run |
| Access to newer models with the latest technology | No ownership or equity in the vehicle |
| Lower repair costs due to warranties | Restrictions on mileage and modifications |
| Flexibility to change vehicles every few years | Potential fees for excess wear and tear |
| Less upfront cash required | Early termination fees if you need to exit the lease early |
| Tax benefits for business use (in some cases) | Complex lease agreements can be confusing |
| No trade-in hassles at lease end | Monthly payments continue indefinitely if leasing repeatedly |
| Possibility of purchasing at lease end at a predetermined price | Limited customization options for the vehicle |
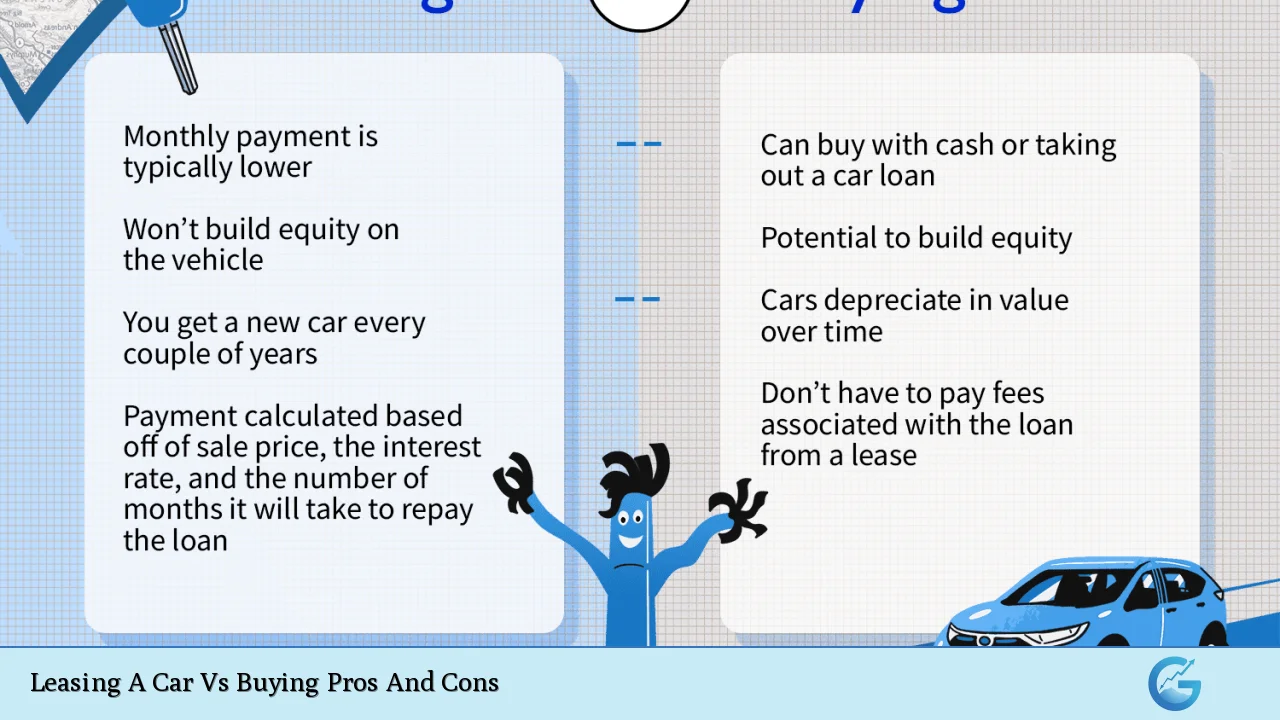
Lower Monthly Payments
One of the most significant advantages of leasing a car is the lower monthly payments compared to buying. Lease payments are typically lower because you are only paying for the vehicle’s depreciation during the lease term, rather than the full purchase price. This can make higher-end vehicles more accessible, allowing drivers to enjoy luxury models without the hefty price tag.
Access to Newer Models
Leasing allows individuals to drive newer models equipped with the latest technology and safety features every few years. This is particularly appealing for those who value having a modern vehicle with up-to-date capabilities. The ability to upgrade frequently means that lessees can enjoy advancements in automotive technology without committing to a long-term investment.
Lower Repair Costs
Another advantage of leasing is that most leased vehicles come with warranties that cover repairs during the lease term. This means lessees typically face fewer unexpected expenses related to maintenance and repairs, as major issues are often covered by the manufacturer’s warranty. This can lead to significant savings over time, especially for those who prefer not to deal with repair costs.
Flexibility in Vehicle Choice
Leasing provides flexibility in terms of vehicle choice. At the end of a lease term, individuals have the option to return the car and lease a new one, allowing them to adapt their vehicle choice based on changing needs or preferences. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for those who may need different types of vehicles at different stages of life.
Less Upfront Cash Required
Leasing usually requires less upfront cash than buying. Many leases offer low or no down payment options, making it easier for individuals to get into a new car without a significant initial investment. This can be particularly advantageous for those who may not have substantial savings but need reliable transportation.
Tax Benefits for Business Use
For business owners, leasing may offer certain tax advantages. Lease payments can often be deducted as business expenses if the vehicle is used primarily for business purposes. This can lead to significant tax savings, making leasing an attractive option for entrepreneurs looking to manage their expenses effectively.
No Trade-in Hassles
At the end of a lease, lessees simply return their vehicle without worrying about selling or trading it in. This eliminates potential headaches associated with finding a buyer or negotiating trade-in values, streamlining the process of acquiring a new vehicle.
Higher Overall Costs in the Long Run
Despite its advantages, leasing can lead to higher overall costs compared to buying if one continually leases vehicles over many years. Although monthly payments are lower, lessees may end up paying more in total when considering repeated leasing cycles without ever owning an asset outright.
No Ownership or Equity
A significant disadvantage of leasing is that at the end of the lease term, you do not own the vehicle and have no equity built up. For individuals who prefer owning their cars outright and building equity over time, leasing may not align with their financial goals.
Restrictions on Mileage and Modifications
Leases often come with mileage restrictions—commonly around 12,000 miles per year—meaning that exceeding this limit incurs additional fees. Moreover, lessees typically cannot modify their vehicles as they see fit, which can be limiting for those who enjoy customizing their cars.
Potential Fees for Excess Wear and Tear
At lease end, lessees may face charges for excessive wear and tear beyond what is considered normal. This can include anything from minor scratches to interior damage, leading to unexpected costs that can diminish some of the financial benefits associated with leasing.
Early Termination Fees
If circumstances change and you need to terminate your lease early, you could face substantial penalties. These fees can be quite high and may negate any savings achieved through lower monthly payments during the lease term.
Complex Lease Agreements
Lease agreements can often be complex and filled with unfamiliar terminology, which may confuse some consumers. Understanding all terms and conditions is crucial before signing a lease agreement to avoid any surprises later on.
Monthly Payments Continue Indefinitely if Leasing Repeatedly
For those who choose to lease one car after another continuously, monthly payments become an ongoing expense without ever reaching a point where they own an asset outright. In contrast, purchasing a vehicle allows individuals to eventually eliminate car payments altogether after paying off their loan.
Limited Customization Options
Leased vehicles typically come with restrictions on customization. Lessees may need to revert any modifications made during their lease period before returning the car, which can be inconvenient and costly if significant changes were made.
In conclusion, both leasing and buying have distinct advantages and disadvantages that cater to different financial situations and lifestyle preferences. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your personal circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leasing A Car Vs Buying Pros And Cons
- What are the main differences between leasing and buying a car?
Leasing allows you to drive a car without ownership while paying lower monthly payments; buying means you own the car outright after paying it off. - Is leasing more expensive than buying in the long run?
Yes, leasing can be more expensive over time due to continuous monthly payments without building equity. - Can I customize a leased car?
No, modifications are typically restricted on leased vehicles; any changes must be reverted before returning. - What happens if I exceed my mileage limit on a leased car?
You will incur additional fees based on how many miles you exceed your limit. - Aren’t there tax benefits associated with leasing?
Yes, businesses can often deduct lease payments as business expenses if used primarily for business purposes. - What are early termination fees in leasing?
If you terminate your lease early, you might face substantial penalties that could offset any savings from lower monthly payments. - Is it better financially to buy or lease?
This depends on individual circumstances; buying is generally better if you plan on keeping your car long-term. - How do I decide whether to lease or buy?
Consider your financial situation, driving habits, personal preferences regarding ownership, and how often you want a new vehicle.
Understanding your options when it comes to acquiring a vehicle is crucial in today’s financial landscape. By weighing these factors carefully against your personal circumstances and financial goals, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs.