Leasing a car has become an increasingly popular option for many individuals and businesses looking to drive a new vehicle without the long-term commitment of ownership. This arrangement allows lessees to enjoy the benefits of driving a new car every few years while avoiding some of the financial burdens associated with purchasing a vehicle outright. However, like any financial decision, leasing comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential lessees should carefully consider.
This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of the pros and cons of leasing a car, helping readers make informed decisions based on their financial situations and driving needs.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower Monthly Payments | No Ownership Equity |
| Access to Newer Models | Mileage Restrictions |
| Warranty Coverage | Potential for Extra Fees |
| Tax Benefits for Businesses | Limited Customization Options |
| No Resale Hassles | Long-Term Costs Can Add Up |
| Flexibility in Upgrading Vehicles | Early Termination Fees |
| Predictable Monthly Expenses | Insurance Costs May Be Higher |
| Lower Upfront Costs | Potential Damage Fees at Lease End |
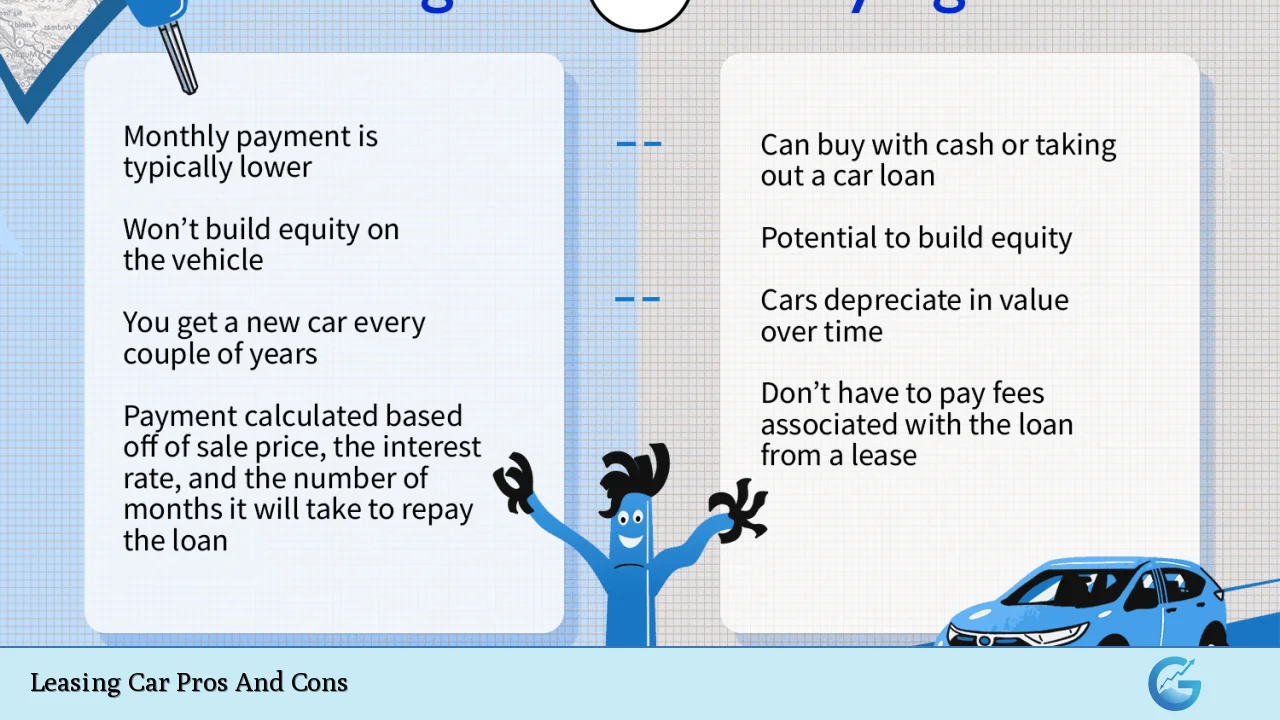
Lower Monthly Payments
One of the most significant advantages of leasing a car is the lower monthly payment compared to financing a purchase. Since you are essentially paying for the depreciation of the vehicle during the lease term rather than its full value, monthly payments can be substantially lower.
- Affordability: Leasing allows individuals to drive more expensive or luxurious vehicles that might be financially out of reach if purchased outright.
- Budgeting: The predictable monthly payments make it easier to budget for transportation costs.
No Ownership Equity
A major downside of leasing is that at the end of the lease term, you do not own the vehicle. This means that all payments made during the lease do not contribute toward ownership.
- No Asset Accumulation: Unlike buying a car, where you build equity over time, leasing means you have no asset to sell or trade in after the lease ends.
- Long-Term Financial Impact: Over time, continuously leasing can lead to higher overall costs compared to owning a vehicle long-term.
Access to Newer Models
Leasing provides an excellent opportunity to drive newer models equipped with the latest technology and safety features.
- Frequent Upgrades: Many leases last around three years, allowing drivers to frequently upgrade to newer models without significant financial strain.
- Latest Technology: Leasing ensures access to modern features and improvements in fuel efficiency and safety.
Mileage Restrictions
Leased vehicles typically come with mileage limits, which can lead to additional costs if exceeded.
- Standard Limits: Most leases allow for 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. Exceeding these limits can incur fees ranging from $0.10 to $0.25 per mile.
- Consideration for Frequent Drivers: Individuals with long commutes or those who frequently travel may find leasing less suitable due to these restrictions.
Warranty Coverage
Many leases cover vehicles that are still under warranty, which can alleviate concerns about repair costs during the lease period.
- Maintenance Costs: Typically, lessees are not responsible for major repairs as long as they adhere to maintenance schedules outlined in their lease agreements.
- Peace of Mind: This coverage can provide peace of mind regarding unexpected repair expenses.
Potential for Extra Fees
Leasing can come with various fees that may not be immediately apparent at signing.
- Excess Mileage Fees: As mentioned earlier, exceeding mileage limits can lead to significant extra charges.
- Wear and Tear Charges: Lessees may also incur costs for any damage beyond normal wear and tear when returning the vehicle at lease end.
Tax Benefits for Businesses
For business owners, leasing can offer tax advantages that purchasing may not provide.
- Deductible Expenses: Lease payments may be deductible as a business expense on taxes, depending on how the vehicle is used in business operations.
- Cash Flow Management: This can improve cash flow management by reducing upfront costs associated with purchasing vehicles outright.
Limited Customization Options
Leased vehicles often come with restrictions on modifications or customizations.
- No Personal Touches: Lessees cannot make significant changes or upgrades to the vehicle without incurring fees or penalties.
- Standardization: This limitation can be frustrating for those who wish to personalize their driving experience.
No Resale Hassles
One of the appealing aspects of leasing is that it eliminates concerns about selling or trading in a vehicle at the end of its useful life.
- Easy Returns: At lease end, lessees simply return the vehicle without worrying about its resale value or finding a buyer.
- Predictable Process: This process simplifies transitions between vehicles and reduces stress associated with ownership responsibilities.
Long-Term Costs Can Add Up
While leasing may seem cheaper initially, it can become more expensive over time compared to purchasing a vehicle outright and keeping it long-term.
- Cumulative Payments: Continuous leasing over many years may result in higher overall payments than if one were to buy and hold a vehicle for several years.
- Financial Strategy Consideration: Individuals should evaluate their long-term transportation needs before committing to a leasing strategy.
Early Termination Fees
Ending a lease early can lead to significant financial penalties, which can deter individuals from making changes in their transportation plans.
- Costly Penalties: If personal circumstances change (e.g., job relocation), breaking a lease could result in substantial fees that negate any initial savings from leasing.
- Contractual Obligations: Understanding all terms related to early termination is crucial before entering into a lease agreement.
Predictable Monthly Expenses
Leasing offers predictable monthly expenses that can aid in financial planning and budgeting efforts.
- Fixed Payments: Unlike ownership where maintenance and repair costs can fluctuate significantly, leased vehicles typically have fixed monthly payments that include road tax and sometimes maintenance packages.
- Financial Clarity: This predictability helps individuals manage their finances better without unexpected automotive expenses disrupting their budgets.
Insurance Costs May Be Higher
While leasing may provide lower monthly payments, insurance costs can sometimes be higher than those associated with owned vehicles due to required coverage levels set by leasing companies.
- Full Coverage Requirement: Leasing companies often require lessees to carry full coverage insurance, which can increase monthly insurance premiums compared to basic liability coverage typically sufficient for owned vehicles.
- Financial Impact on Budgeting: These increased insurance costs should be factored into overall budgeting when considering leasing as an option.
Potential Damage Fees at Lease End
At lease termination, lessees must return the vehicle in good condition; otherwise, they may face additional charges for repairs deemed necessary by the lessor.
- Assessment Criteria: Normal wear and tear is usually acceptable; however, anything deemed excessive could lead to costly repairs billed back to the lessee.
- Inspection Process Awareness: Understanding how inspections are conducted at lease end is essential for avoiding unexpected fees after returning the vehicle.
In conclusion, leasing a car presents both compelling advantages and notable disadvantages that potential lessees must weigh carefully. On one hand, it offers lower monthly payments, access to newer models, warranty coverage, and no resale hassles. On the other hand, it lacks ownership equity, imposes mileage restrictions, incurs potential fees, and limits customization options.
Ultimately, whether leasing is appropriate depends on individual circumstances such as driving habits, financial goals, and preferences regarding vehicle ownership. Those interested in exploring this option should conduct thorough research and consider their unique needs before making any commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leasing Car Pros And Cons
- What are the main advantages of leasing a car?
Leasing offers lower monthly payments, access to new models every few years, warranty coverage during the lease period, and no hassle with resale. - What are some common disadvantages of leasing?
The primary drawbacks include no ownership equity built up over time, mileage restrictions leading to potential extra fees, and limited customization options. - Can businesses benefit from car leasing?
Yes! Businesses may deduct lease payments as expenses on taxes and enjoy improved cash flow management. - Are there any hidden fees associated with leasing?
Yes! Lessees should be aware of excess mileage fees, wear-and-tear charges upon return, and potential early termination penalties. - How does insurance work with leased cars?
Lessees often need full coverage insurance which may result in higher premiums compared to owned vehicles. - What happens at the end of a car lease?
Lessees return the vehicle; however, they must ensure it meets condition standards outlined in their contract or face additional charges. - Is it better to lease or buy a car?
This depends on individual circumstances such as budget constraints and personal preferences regarding ownership; both options have unique benefits. - How long do most leases last?
The average car lease lasts about three years but can vary based on individual agreements.