Leasing a car has become a popular option for many consumers, particularly those who prefer driving new vehicles without the long-term commitment of ownership. This arrangement allows individuals to enjoy the benefits of a new car while avoiding some of the financial burdens associated with buying. However, leasing also comes with its own set of disadvantages that potential lessees should carefully consider. This article explores the pros and cons of leasing cars, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make an informed decision.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
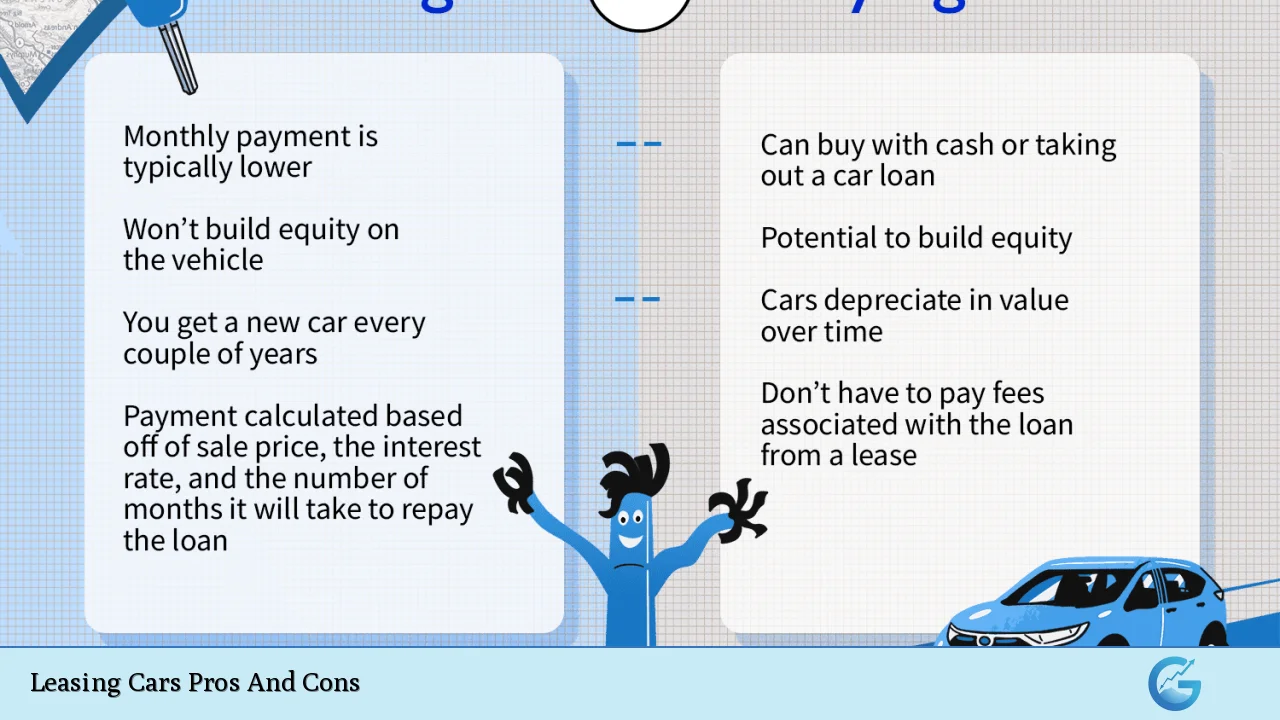
| Lower monthly payments compared to buying | No ownership or equity in the vehicle |
| Access to newer models and technology | Mileage restrictions and penalties for excess mileage |
| Worry-free maintenance under warranty | Fees for wear and tear and modifications |
| No need to deal with resale or depreciation concerns | Long-term costs can exceed buying a car outright |
| Potential tax benefits for business use | Limited customization options |
| Flexibility to upgrade vehicles frequently | Early termination fees can be costly |
| Fixed monthly payments simplify budgeting | Insurance requirements can be higher than for owned vehicles |
| Included road tax in lease payments | No asset accumulation or trade-in value at lease end |
Lower Monthly Payments Compared to Buying
One of the most significant advantages of leasing a car is the lower monthly payments compared to financing a purchase. When you lease, you are essentially paying for the vehicle’s depreciation during the lease term rather than its total value. This often results in payments that are substantially lower than those associated with a traditional auto loan. For many individuals, this means they can afford a more luxurious model or additional features that might otherwise be out of reach.
Key Points:
- Leasing typically requires a lower down payment.
- Monthly payments are often 30% to 60% less than buying.
- Budgeting becomes easier with predictable payment amounts.
No Ownership or Equity in the Vehicle
While leasing offers lower payments, it also means that you do not own the vehicle at the end of the lease term. This lack of ownership means you do not build any equity in the car, which can be viewed as a significant disadvantage, especially for those who prefer to invest in assets that appreciate over time.
Key Points:
- At lease end, you must return the vehicle with no residual value.
- Payments contribute to rental costs rather than ownership.
- No potential for trade-in value or resale profits.
Access to Newer Models and Technology
Leasing allows consumers to drive newer models more frequently, often every two to three years. This is particularly appealing for tech enthusiasts who want access to the latest automotive advancements, safety features, and fuel efficiency improvements without committing long-term.
Key Points:
- Frequent upgrades keep drivers in modern vehicles.
- Access to cutting-edge technology and safety features.
- Ideal for those who enjoy driving new cars regularly.
Mileage Restrictions and Penalties for Excess Mileage
One of the primary downsides of leasing is the mileage restrictions imposed by most contracts. Typically, leases allow between 10,000 and 15,000 miles per year. Exceeding this limit can result in hefty penalties, often ranging from $0.10 to $0.50 per mile overage. For individuals with long commutes or those who frequently travel, this can become an expensive burden.
Key Points:
- Standard mileage limits may not suit all drivers.
- Excess mileage fees can accumulate quickly.
- Unused miles do not contribute to any credit or refund.
Worry-Free Maintenance Under Warranty
Many leases come with vehicles still under manufacturer warranty, meaning that most maintenance costs are covered during the lease term. This aspect provides peace of mind as lessees avoid unexpected repair bills that often accompany older vehicles.
Key Points:
- Most repairs are covered by warranty.
- Regular maintenance is typically included in lease agreements.
- Reduces financial risk associated with vehicle upkeep.
Fees for Wear and Tear and Modifications
While leasing has many benefits, it also includes potential fees associated with excess wear and tear or unauthorized modifications. At lease end, any damage beyond normal wear can result in additional charges, which can add up significantly if the vehicle has not been well maintained.
Key Points:
- Lessees are responsible for maintaining vehicle condition.
- Fees may apply for modifications or customization.
- End-of-lease inspections can lead to unexpected costs.
No Need to Deal with Resale or Depreciation Concerns
Leasing eliminates concerns about depreciation and resale value since lessees return the vehicle at the end of their contract. This aspect is particularly beneficial in markets where cars depreciate rapidly within the first few years.
Key Points:
- Avoids complexities associated with selling a used car.
- Depreciation is borne by the leasing company.
- Simplifies transition to a new vehicle at lease end.
Long-Term Costs Can Exceed Buying a Car Outright
Despite lower initial costs, leasing can become more expensive over time compared to purchasing a vehicle outright. Continuous leasing means ongoing monthly payments without ever owning an asset. Over several lease cycles, these costs can accumulate significantly.
Key Points:
- Long-term leasing may exceed total purchase costs.
- Monthly payments continue indefinitely if leasing repeatedly.
- Buying and keeping a car long-term is often more economical.
Flexibility to Upgrade Vehicles Frequently
Leasing provides flexibility for consumers who enjoy driving different cars frequently. The ability to switch vehicles every few years allows lessees to adapt their choice based on changing needs or preferences without being tied down by ownership commitments.
Key Points:
- Easily switch between different models as needs change.
- Experience various brands and features without long-term commitment.
- Ideal for those who value variety in their driving experience.
Limited Customization Options
Another downside of leasing is that lessees typically cannot customize their vehicles as they would if they owned them. Any alterations may violate lease terms and incur additional fees when returning the car.
Key Points:
- Modifications may lead to penalties at lease end.
- Limited ability to personalize your driving experience.
- Must adhere strictly to manufacturer specifications.
Early Termination Fees Can Be Costly
If circumstances change and you need to terminate your lease early, you may face significant penalties. Early termination fees can be substantial, often requiring payment of all remaining lease payments plus additional charges.
Key Points:
- Early termination can lead to financial strain.
- Contracts often include stiff penalties for breaking leases early.
- Consider your long-term plans before committing.
Insurance Requirements Can Be Higher Than for Owned Vehicles
Leased vehicles often require higher insurance coverage levels than what might be necessary for owned cars. This requirement adds another layer of cost that needs consideration when budgeting for a leased vehicle.
Key Points:
- Leasing companies may mandate comprehensive insurance coverage.
- Higher premiums could impact overall affordability.
- Must factor insurance into total cost calculations when leasing.
Included Road Tax in Lease Payments
Many leases include road tax (Vehicle Excise Duty) within their monthly payments, simplifying budgeting as lessees do not have separate tax obligations. This aspect makes it easier for individuals to manage their finances without worrying about fluctuating tax rates or deadlines.
Key Points:
- Simplifies financial planning by bundling costs into one payment.
- Reduces administrative burden related to vehicle taxes.
- Provides clarity on total monthly expenses related to vehicle use.
In conclusion, leasing a car presents both advantages and disadvantages that potential lessees should weigh carefully. While it offers lower monthly payments, access to new models, and minimal maintenance concerns, it also lacks ownership benefits and comes with various restrictions and fees. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leasing Cars Pros And Cons
- What are the primary benefits of leasing a car?
The main benefits include lower monthly payments, access to newer models frequently, worry-free maintenance under warranty, and no concerns about depreciation. - What are common drawbacks associated with leasing?
The common drawbacks include no ownership equity, mileage restrictions leading to potential fees, additional charges for wear and tear, and high early termination penalties. - Is leasing more affordable than buying?
In terms of monthly payments, leasing is generally more affordable; however, over time it may become more expensive than buying due to ongoing payment cycles. - Can I customize my leased vehicle?
No, modifications are typically restricted in lease agreements; any unauthorized changes may incur fees upon returning the vehicle. - What happens if I exceed my mileage limit?
If you exceed your agreed mileage limit during your lease term, you will incur additional charges per mile overage. - Are there tax benefits associated with leasing?
If used for business purposes, there can be tax deductions available on leased vehicles that might not apply when purchasing. - What should I consider before deciding whether to lease?
You should evaluate your driving habits (mileage), budget constraints (including insurance), desire for new technology versus long-term cost implications. - How do I avoid excessive fees at lease end?
To avoid excessive fees at lease end, maintain your vehicle well within its mileage limits and ensure it’s returned in good condition.