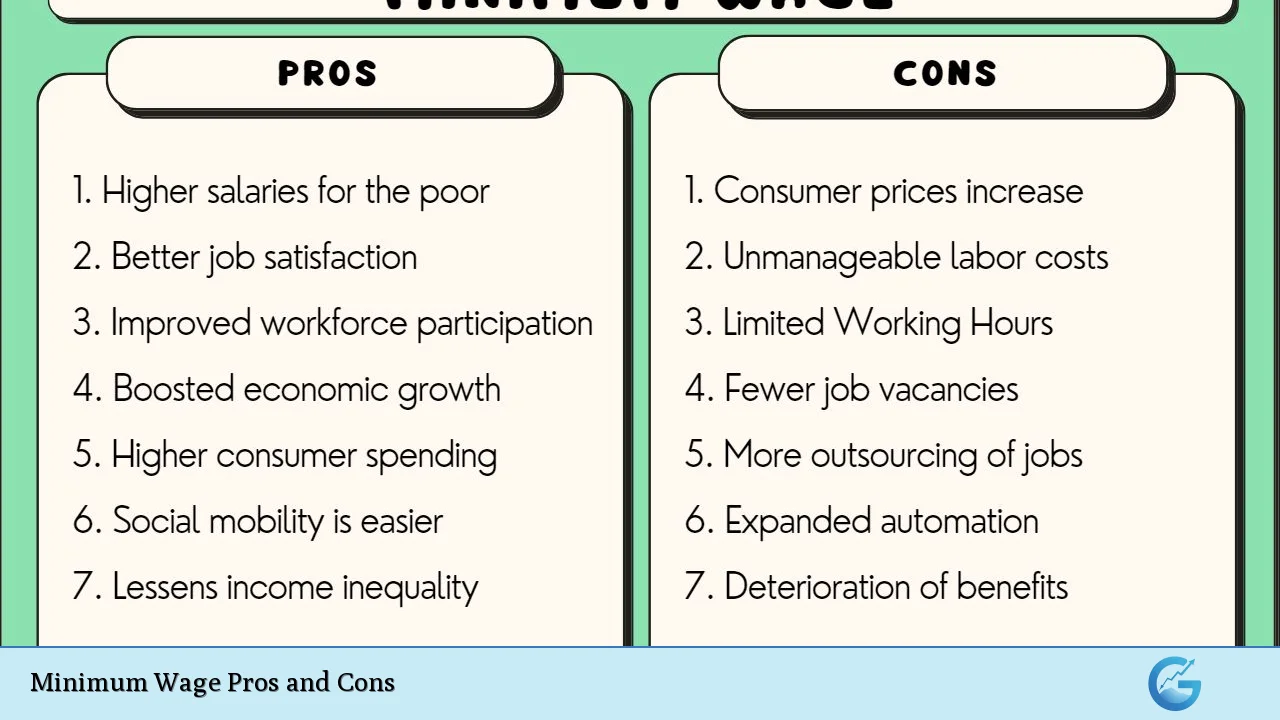
The minimum wage is a critical topic in economic discussions, especially as it relates to labor markets, income inequality, and social welfare. It represents the lowest legal remuneration that employers can pay their workers, and its implications are far-reaching. Advocates argue that raising the minimum wage can alleviate poverty and stimulate economic growth, while opponents warn that it may lead to job losses and increased prices for goods and services. Understanding the pros and cons of minimum wage policies is essential for anyone interested in finance, economics, or labor markets.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improves standard of living for low-wage workers | May lead to job losses as businesses cut costs |
| Reduces poverty rates and income inequality | Increases operational costs for businesses, potentially leading to higher prices |
| Stimulates consumer spending and economic growth | Can create a competitive disadvantage for small businesses |
| Encourages higher productivity among workers | May result in increased automation as businesses seek to reduce labor costs |
| Enhances employee morale and retention rates | Could lead to reduced hours or benefits for some employees |
| Promotes social equity by addressing wage disparities | Might exacerbate unemployment among younger or less skilled workers |
| Reduces reliance on government assistance programs | Can lead to regional disparities in wage standards affecting local economies differently |
| Supports a fairer labor market by establishing a wage floor | May create a distortion in the labor market dynamics, impacting supply and demand |
Improves Standard of Living for Low-Wage Workers
One of the most significant advantages of raising the minimum wage is its potential to enhance the standard of living for low-wage workers.
- Increased Earnings: Workers earning minimum wage often struggle to afford basic necessities such as housing, food, and healthcare. A higher minimum wage can provide them with a more livable income.
- Greater Financial Stability: With increased wages, workers are less likely to rely on government assistance programs, which can alleviate pressure on public resources.
- Improved Quality of Life: Higher earnings can lead to better health outcomes, increased educational opportunities for children, and overall improved well-being.
May Lead to Job Losses as Businesses Cut Costs
On the flip side, opponents argue that increasing the minimum wage can result in job losses.
- Cost-Cutting Measures: Businesses facing higher payroll expenses may resort to layoffs or hiring freezes to maintain profitability.
- Automation Adoption: Higher labor costs may incentivize companies to invest in automation technologies instead of hiring human workers.
- Reduced Job Opportunities: As businesses streamline operations or close altogether due to increased costs, fewer job opportunities may be available for low-skilled workers.
Reduces Poverty Rates and Income Inequality
Raising the minimum wage is often seen as a tool for reducing poverty levels.
- Poverty Alleviation: Studies have shown that increasing the minimum wage can lift many families above the poverty line, contributing to a decrease in overall poverty rates.
- Narrowing Income Gaps: A higher minimum wage can help reduce income inequality by providing lower-income workers with a more equitable share of economic growth.
- Enhanced Economic Mobility: By improving financial conditions for low-wage earners, a higher minimum wage can facilitate upward mobility and long-term economic stability.
Increases Operational Costs for Businesses, Potentially Leading to Higher Prices
However, raising the minimum wage also has implications for business operations.
- Higher Prices for Goods and Services: To offset increased labor costs, businesses may raise prices on products and services, which could negate some benefits of higher wages for consumers.
- Impact on Small Businesses: Smaller enterprises may struggle more than larger corporations with increased payroll expenses, potentially leading to closures or reduced hiring.
- Market Adjustments: Businesses may need time to adjust their pricing strategies and operational models in response to increased labor costs.
Stimulates Consumer Spending and Economic Growth
An increase in minimum wage can have positive effects on consumer spending patterns.
- Increased Disposable Income: When low-wage workers earn more money, they are likely to spend it on goods and services, stimulating demand within the economy.
- Boosting Local Economies: Increased consumer spending can lead to greater economic activity in local communities, supporting businesses and creating jobs.
- Multiplier Effect: The additional income earned by low-wage workers can circulate through the economy, benefiting various sectors and contributing to overall economic growth.
Can Create a Competitive Disadvantage for Small Businesses
Despite these benefits, there are concerns about how minimum wage increases affect competition among businesses.
- Disproportionate Impact on Small Firms: Smaller businesses often operate with tighter margins than larger corporations; thus, they may find it harder to absorb increased labor costs without raising prices or reducing staff.
- Market Consolidation Risks: If small businesses struggle due to higher wages while larger firms thrive due to economies of scale, this could lead to market consolidation where fewer companies dominate the landscape.
- Innovation Stifling: Increased operational costs might deter small business owners from innovating or expanding their offerings due to financial constraints.
Encourages Higher Productivity Among Workers
Higher wages can also lead to improved productivity levels among employees.
- Motivation Boost: Workers who feel they are compensated fairly are often more motivated and engaged in their jobs.
- Reduced Turnover Rates: Companies that pay higher wages tend to experience lower turnover rates, which reduces recruitment and training costs associated with high employee turnover.
- Attracting Talent: A competitive wage can attract more skilled workers who contribute positively to company performance.
May Result in Increased Automation as Businesses Seek to Reduce Labor Costs
Conversely, one of the unintended consequences of raising the minimum wage could be an increase in automation within industries reliant on low-wage labor.
- Investment in Technology: Businesses might invest in technology that replaces human labor as a cost-saving measure when faced with higher payroll expenses.
- Job Displacement Risks: Automation could displace many low-skilled jobs traditionally held by minimum wage workers, exacerbating unemployment issues within certain sectors.
- Long-Term Employment Impacts: While automation may enhance efficiency for companies, it could also limit job opportunities for future generations entering the workforce.
Enhances Employee Morale and Retention Rates
A higher minimum wage can significantly impact employee morale within organizations.
- Job Satisfaction Improvement: Employees who feel valued through fair compensation are likely to exhibit higher job satisfaction levels.
- Loyalty Development: Fair wages foster loyalty among employees; satisfied workers are less likely to seek employment elsewhere.
- Positive Workplace Culture: Companies that prioritize fair compensation often cultivate a positive workplace culture that enhances collaboration and productivity among employees.
Could Lead to Reduced Hours or Benefits for Some Employees
While raising wages has many benefits, there are potential drawbacks regarding employee hours and benefits structure.
- Reduced Hours Offered: Employers might respond by reducing hours worked per employee to manage payroll expenses effectively.
- Benefit Cuts: To offset increased wages without compromising profitability, some employers may cut back on additional benefits such as healthcare or retirement contributions.
- Impact on Part-Time Workers: Part-time employees could face reduced hours or shifts as employers adjust staffing models in response to rising labor costs.
Promotes Social Equity by Addressing Wage Disparities
Raising the minimum wage is often viewed as a means of promoting social equity within society.
- Addressing Gender Pay Gaps: Many low-wage jobs disproportionately employ women; thus, raising the minimum wage can help close gender-based pay gaps.
- Reducing Racial Inequities: Increasing wages can also benefit minority groups who are overrepresented in low-wage positions.
- Fostering Inclusive Growth: A commitment to fair wages supports broader societal goals centered around inclusivity and equity within economic systems.
Might Exacerbate Unemployment Among Younger or Less Skilled Workers
One significant concern regarding an increase in minimum wage is its potential adverse effect on youth employment opportunities.
- Entry-Level Job Availability Decline: As employers adjust their workforce strategies due to increased costs associated with higher wages, entry-level positions may become scarcer.
- Competitive Job Market Dynamics: An influx of overqualified candidates applying for limited positions could make it challenging for younger individuals seeking their first job experience.
- Long-Term Career Implications: Limited access to entry-level jobs could hinder young people’s ability to gain necessary work experience crucial for career advancement later on.
May Create Regional Disparities in Wage Standards Affecting Local Economies Differently
Finally, implementing a federal minimum wage does not account for regional economic differences across states or cities.
- Cost of Living Variations: Regions with lower living costs might struggle with federally mandated increases compared to areas where living expenses are already high.
- Economic Strain on Local Businesses: Areas with weaker economies might see more significant negative impacts from mandated increases than economically robust regions where businesses can adapt more easily.
- Potential Migration Patterns: Disparities in local economies could encourage migration patterns where individuals move from high-cost areas seeking better opportunities elsewhere—potentially exacerbating existing regional inequalities.
In conclusion, while raising the minimum wage presents several advantages such as improving living standards and reducing poverty levels, it also poses challenges including potential job losses and increased operational costs for businesses. The debate surrounding this issue remains complex, reflecting broader economic conditions and varying perspectives on how best to support low-wage workers while maintaining healthy business environments. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for investors and stakeholders engaged in finance-related fields as they navigate potential impacts on markets influenced by changes in labor policies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Minimum Wage
- What is the current federal minimum wage?
The current federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour; however, many states have set higher rates. - How does raising the minimum wage affect inflation?
An increase in minimum wage can contribute to inflation if businesses pass on higher labor costs through increased prices. - Are there any exemptions from paying minimum wage?
Certain categories of workers such as tipped employees may have different minimum pay requirements under federal law. - What impact does minimum wage have on employment rates?
The relationship between minimum wage increases and employment rates is complex; while some studies suggest job losses occur, others indicate minimal impact. - How does minimum wage vary across states?
States have the authority to set their own minimum wages; therefore rates vary significantly depending on local laws. - Can raising the minimum wage reduce government welfare spending?
A higher minimum wage may decrease reliance on government welfare programs by providing individuals with sufficient income. - What are potential long-term effects of consistently raising the minimum wage?
Long-term effects could include shifts in employment patterns toward automation or changes in consumer behavior due to altered purchasing power. - How do economists generally view increases in the minimum wage?
Econonmists remain divided; some argue it stimulates growth while others caution against potential negative impacts on employment.