A national sales tax is a consumption-based tax levied on goods and services purchased by consumers. It is often proposed as a replacement for the current income tax system, aiming to simplify tax collection and broaden the tax base. This taxation method has gained traction in political discussions, especially in the context of tax reform debates. Advocates argue that it could lead to a fairer system, while critics warn of potential regressivity and economic implications. Understanding the pros and cons of a national sales tax is crucial for individuals interested in finance, including those engaged in cryptocurrency, forex, and money markets.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Simplicity in Tax Filing | Regressive Nature |
| Broadens Tax Base | Potential for Increased Prices |
| Encourages Savings and Investment | Administrative Challenges |
| Universal Contribution to Tax Revenue | Impact on Low-Income Families |
| Reduction of Tax Evasion Opportunities | Possible Shift in Economic Behavior |
| Increased Transparency in Taxation | Concerns Over Revenue Stability |
| Potential for Economic Growth | Political Resistance and Implementation Issues |
Simplicity in Tax Filing
One of the most significant advantages of a national sales tax is the simplicity it offers in tax filing.
- Streamlined Process: Unlike the current income tax system, which requires extensive documentation and complex calculations, a national sales tax would allow consumers to pay taxes at the point of sale without needing to file annual returns.
- Reduced Compliance Costs: Businesses would benefit from reduced compliance costs associated with payroll taxes and income taxes, as they would only need to manage sales tax collections.
Regressive Nature
However, a major concern with implementing a national sales tax is its regressive nature.
- Disproportionate Impact on Low-Income Households: Lower-income families tend to spend a larger percentage of their income on consumables. This means that they would pay a higher proportion of their income in taxes compared to wealthier individuals who save more of their income.
- Burden on Essential Goods: Essential items such as food and clothing would also be taxed, exacerbating financial strain on those with limited resources.
Broadens Tax Base
A national sales tax could potentially broaden the tax base significantly.
- Inclusion of All Consumers: Unlike income taxes that primarily target earners, a sales tax captures revenue from all consumers, including those who may evade income taxes.
- Encouragement of Fairness: This system would ensure that everyone contributes to government revenue based on their consumption levels rather than their income levels.
Potential for Increased Prices
On the downside, implementing a national sales tax could lead to increased prices for consumers.
- Higher Costs Passed to Consumers: Businesses may pass on the cost of the sales tax to consumers by raising prices, potentially leading to inflationary pressures.
- Market Response: If prices rise significantly, consumer behavior may shift towards less expensive alternatives or reduce consumption altogether.
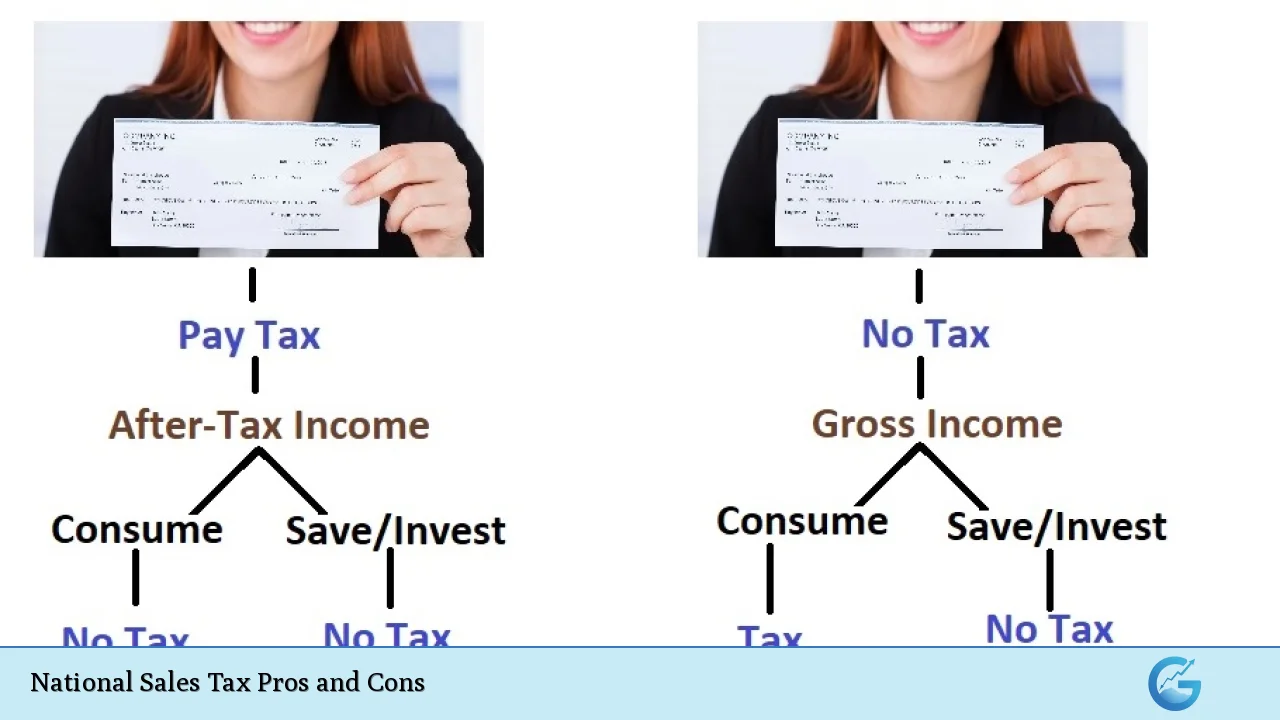
Encourages Savings and Investment
A notable advantage is that a national sales tax may encourage savings and investment.
- Tax-Free Savings: Since income earned would not be taxed under this system, individuals might be incentivized to save more or invest their earnings rather than spend them immediately.
- Economic Growth Potential: Increased savings could lead to greater capital availability for businesses, fostering economic growth.
Administrative Challenges
Despite its potential benefits, a national sales tax could introduce several administrative challenges.
- Implementation Complexity: Transitioning from an income-based system to a consumption-based one would require significant changes in legislation and administration.
- Compliance Burden on Businesses: Small businesses may face difficulties in adapting to new systems for collecting and remitting sales taxes, potentially leading to increased operational costs.
Universal Contribution to Tax Revenue
A national sales tax ensures that all individuals contribute to government revenue regardless of their income source.
- Inclusivity: This approach captures revenue from various sectors of the economy, including informal markets where transactions typically go untaxed.
- Enhanced Revenue Stability: By taxing consumption rather than income, governments may achieve more stable revenue streams during economic fluctuations since consumption tends to remain steady even during downturns.
Impact on Low-Income Families
While the idea of universal contribution sounds appealing, low-income families might bear an unfair burden under this system.
- Limited Relief Measures: Although some proposals include rebates or exemptions for essential goods, these measures may not sufficiently offset the regressive nature of the sales tax for those living paycheck-to-paycheck.
- Increased Financial Strain: The cumulative effect of higher prices due to taxation could lead low-income families into deeper financial distress.
Reduction of Tax Evasion Opportunities
A national sales tax could significantly reduce opportunities for tax evasion compared to an income-based system.
- Transparency in Transactions: Since all purchases would be taxed at the point of sale, it becomes harder for individuals or businesses to evade taxes compared to reporting income which can be manipulated or hidden.
- Broad Coverage: By taxing all goods and services uniformly, the government can capture revenue from various sectors that currently escape taxation under an income-based system.
Possible Shift in Economic Behavior
The introduction of a national sales tax could alter consumer behavior significantly.
- Changes in Spending Habits: Consumers might become more cautious about spending due to perceived higher costs associated with purchases.
- Potential Growth in Black Markets: If prices rise significantly due to taxation, some consumers might turn to black markets or informal economies where goods are sold without taxes.
Increased Transparency in Taxation
A national sales tax can enhance transparency within the taxation system.
- Clear Understanding of Taxation: Consumers would have a clearer understanding of how much they are paying in taxes based on their purchases rather than hidden deductions from their paychecks.
- Public Awareness: This transparency could foster greater civic engagement regarding government spending and taxation policies as taxpayers become more aware of their contributions.
Concerns Over Revenue Stability
While proponents argue that a national sales tax could stabilize revenues, there are concerns about its reliability over time.
- Dependence on Consumption Patterns: Revenue generated from consumption taxes can fluctuate based on economic conditions; during recessions when spending decreases, so too does tax revenue.
- Uncertainty in Forecasting Revenue: Predicting future revenues becomes challenging when relying solely on consumer spending patterns which can be volatile and unpredictable.
Political Resistance and Implementation Issues
Finally, political resistance poses significant challenges for implementing a national sales tax.
- Opposition from Various Sectors: Many stakeholders—including low-income advocates and small business owners—may resist changes that they perceive as detrimental or unfair.
- Complexity of Transitioning Systems: The logistics involved in transitioning from an established income-based system to a new consumption-based model can be daunting and politically contentious.
In conclusion, while a national sales tax presents several advantages such as simplicity in filing, broadening the tax base, encouraging savings, and enhancing transparency in taxation, it also poses significant challenges including regressive impacts on low-income families, potential price increases for consumers, administrative complexities, and political resistance. As discussions around this topic continue within financial circles and among policymakers, understanding both sides will be crucial for informed decision-making regarding future taxation frameworks.
Frequently Asked Questions About National Sales Tax
- What is a national sales tax?
A national sales tax is a consumption-based levy applied at the point of sale on goods and services purchased by consumers. - How does it differ from income tax?
A national sales tax taxes purchases rather than earnings; this means individuals are taxed based on what they consume rather than what they earn. - What are the main advantages?
The main advantages include simplicity in filing taxes, broadening the taxpayer base, encouraging savings and investment, and reducing opportunities for evasion. - What are its disadvantages?
The disadvantages include its regressive nature impacting low-income households disproportionately and potential price increases for consumers. - Could it affect consumer behavior?
Yes, it could lead consumers to alter their spending habits due to perceived higher costs associated with purchases. - How would it impact small businesses?
Small businesses may face challenges adapting their operations for collecting and remitting sales taxes under this new system. - Is there any relief for low-income families?
Some proposals suggest rebates or exemptions; however, these may not sufficiently mitigate the overall burden imposed by the sales tax. - What political challenges exist?
The transition faces significant political resistance from various stakeholders who may oppose changes perceived as detrimental or unfair.