Private student loans are a financial tool that can help students bridge the gap between the cost of education and the funds available through federal loans, scholarships, and grants. As the cost of higher education continues to rise, many students find themselves in need of additional funding. Private student loans can provide this necessary support, but they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. This article will explore the pros and cons of private student loans in detail, helping prospective borrowers make informed decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
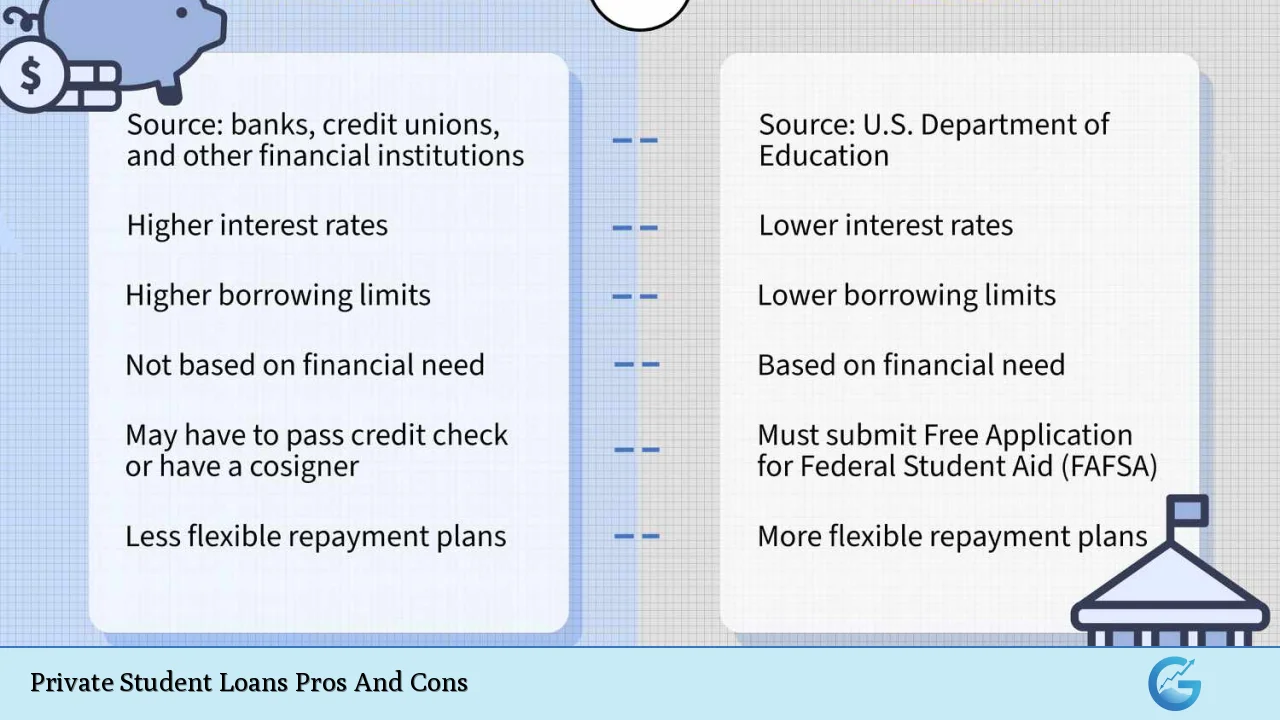
| Higher borrowing limits compared to federal loans | Higher interest rates for those with poor credit |
| Potentially lower interest rates for borrowers with excellent credit | Fewer repayment options and flexibility |
| Quick application and approval process | No access to federal loan forgiveness programs |
| Available to international students and those with DACA status | Requires good credit or a cosigner for most applicants |
| No origination fees in many cases | Limited hardship assistance compared to federal loans |
Higher Borrowing Limits Compared to Federal Loans
One of the most significant advantages of private student loans is their higher borrowing limits.
- Flexibility in Funding: Private lenders often allow students to borrow up to the total cost of attendance, which includes tuition, room and board, books, and other expenses. This is particularly beneficial for students attending expensive institutions or those who have maximized their federal loan limits.
- Accessibility for Graduate Students: Graduate students often face higher costs than undergraduates. Private loans can provide the necessary funding without the strict limits imposed by federal loans.
Potentially Lower Interest Rates for Borrowers with Excellent Credit
For borrowers with strong credit histories, private student loans can offer competitive interest rates.
- Lower Cost of Borrowing: If you have a high credit score, you may qualify for lower interest rates than those available through federal student loans. This can lead to significant savings over the life of the loan.
- Fixed or Variable Rates: Private lenders typically offer both fixed and variable interest rate options, allowing borrowers to choose a plan that fits their financial situation.
Quick Application and Approval Process
The application process for private student loans is often faster than that for federal loans.
- Rapid Access to Funds: Many private lenders can approve applications and disburse funds within days. This quick turnaround can be crucial for students who need immediate financial support.
- Streamlined Process: The online application process is usually straightforward, requiring only basic personal and financial information.
Available to International Students and Those with DACA Status
Unlike federal student loans, which are not available to international students or those with Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) status, many private lenders offer loan options to these groups.
- Broader Access: This inclusivity allows a more diverse range of students to pursue higher education without being limited by their immigration status.
- Support for Diverse Educational Goals: International students often face unique financial challenges; private loans can help alleviate some of these burdens.
No Origination Fees in Many Cases
Many private lenders do not charge origination fees on their student loans.
- Cost Savings: This absence of fees means that borrowers can receive the full loan amount without deductions at disbursement, making it easier to cover educational expenses.
- Transparent Pricing: Without hidden fees, borrowers can better understand their total loan costs upfront.
Higher Interest Rates for Those with Poor Credit
One of the major drawbacks of private student loans is that they tend to have higher interest rates compared to federal loans, especially for borrowers with poor credit histories.
- Increased Financial Burden: Borrowers who do not qualify for low-interest rates may find themselves paying significantly more over time due to higher rates.
- Risk of Default: Higher monthly payments can lead to increased financial strain, potentially resulting in default if borrowers cannot keep up with payments.
Fewer Repayment Options and Flexibility
Private student loans generally offer fewer repayment options than federal loans.
- Lack of Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Unlike federal loans that provide income-driven repayment plans based on earnings, private lenders typically require fixed monthly payments. This rigidity can be challenging for borrowers facing financial difficulties.
- Limited Deferment and Forbearance Options: While some private lenders may offer limited hardship assistance, these options are often less generous than those available through federal programs.
No Access to Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs
Private student loans do not qualify for federal forgiveness programs that are available to certain public service workers or teachers.
- Long-Term Financial Implications: Borrowers in public service roles may miss out on significant savings if they rely solely on private loans without considering their eligibility for forgiveness programs associated with federal loans.
- Increased Debt Burden: The inability to discharge debt through forgiveness programs means that borrowers must plan for full repayment over time, which can be daunting.
Requires Good Credit or a Cosigner for Most Applicants
To qualify for a private student loan, most lenders require borrowers to have a good credit score or a cosigner with strong credit history.
- Challenges for Young Borrowers: Many students lack established credit histories, making it difficult to secure a loan without a cosigner. This requirement can limit access to funding for those who need it most.
- Responsibility of Cosigners: If a cosigner is required, they assume equal responsibility for the debt. This can strain relationships if repayment becomes an issue.
Limited Hardship Assistance Compared to Federal Loans
Private lenders are not obligated to offer the same level of hardship assistance as federal loan programs.
- Potential Financial Strain During Hard Times: In times of economic difficulty or personal hardship, borrowers may find it challenging to manage payments without robust support options from their lender.
- Need for Proactive Management: Borrowers must be proactive in managing their finances and understanding their lender’s policies regarding repayment flexibility during difficult times.
In conclusion, private student loans can be an essential resource for financing higher education when other forms of aid fall short. However, they come with significant risks and limitations that potential borrowers must carefully consider.
While they offer advantages such as higher borrowing limits and potentially lower interest rates for qualified individuals, they also present challenges like higher costs for those with poor credit and fewer repayment options.
Before deciding on a private student loan, it is crucial to exhaust all other funding avenues—such as scholarships, grants, and federal aid—and thoroughly assess your financial situation and repayment capabilities. Making informed choices about borrowing will help ensure that you can manage your educational debt effectively while pursuing your academic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Private Student Loans
- What are private student loans?
Private student loans are non-federal loans offered by banks or other financial institutions that help cover educational costs. - How do I qualify for a private student loan?
To qualify, you typically need a good credit score or a cosigner with strong credit history; you must also be enrolled in an eligible school. - What is the difference between federal and private student loans?
Federal loans are government-funded with fixed interest rates and flexible repayment options; private loans are offered by banks with varying terms based on creditworthiness. - Can I use private student loans for living expenses?
Yes, you can use them to cover tuition as well as living expenses like room and board. - What happens if I can’t repay my private student loan?
If you default on your loan, it could negatively impact your credit score and lead to collections actions. - Are there any benefits unique to private student loans?
Some benefits include potentially lower interest rates if you have excellent credit and quicker access to funds. - Can I refinance my private student loan?
Yes, refinancing is an option that may allow you to secure better terms or lower your interest rate. - Do private student loans have any protections like federal ones?
No, they typically lack protections such as income-driven repayment plans or forgiveness options available through federal programs.