The debate surrounding corporate tax rates is a significant and contentious issue in economic policy, particularly in the context of funding government services, addressing income inequality, and stimulating economic growth. Advocates for raising corporate taxes argue that it can lead to a fairer tax system and generate necessary revenue for public services. Conversely, opponents contend that higher corporate taxes can stifle business investment, reduce wages, and ultimately harm the economy. This article explores the pros and cons of raising corporate taxes, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in finance, investment, and economic policy.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increased government revenue for public services | Potential reduction in wages and increased consumer prices |
| Greater equity in the tax system | Risk of businesses relocating overseas |
| Encouragement for domestic investment | Negative impact on economic growth |
| Funding for infrastructure and social programs | Dissuasion of foreign direct investment |
| Reduction of the federal deficit | Increased burden on small businesses |
Increased Government Revenue for Public Services
Raising corporate taxes can significantly increase government revenue, which can be allocated towards essential public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Revenue Generation: Higher corporate tax rates can help alleviate budget deficits by providing a steady stream of income.
- Investment in Public Goods: These funds can be used to improve public infrastructure, which benefits both corporations and citizens by enhancing productivity.
- Social Programs: Increased revenue allows for funding social programs aimed at reducing poverty and inequality.
Potential Reduction in Wages and Increased Consumer Prices
One of the primary concerns regarding higher corporate taxes is the potential negative impact on wages and consumer prices.
- Wage Reductions: Studies indicate that higher corporate taxes often lead to lower wages for employees as businesses attempt to maintain profit margins by cutting costs.
- Increased Prices: Corporations may pass on the burden of higher taxes to consumers through increased prices for goods and services.
- Economic Burden: This can disproportionately affect low- and middle-income families who spend a larger portion of their income on essential goods.
Greater Equity in the Tax System
Proponents argue that raising corporate taxes creates a more equitable tax system where corporations contribute their fair share.
- Fair Share Contribution: Many large corporations benefit from public services without paying proportionate taxes, leading to an unfair burden on individual taxpayers.
- Reducing Income Inequality: Higher corporate taxes can help redistribute wealth more evenly across society.
- Supporting Small Businesses: By ensuring larger corporations pay their fair share, smaller businesses may face less competition from tax-advantaged larger firms.
Risk of Businesses Relocating Overseas
Conversely, increasing corporate tax rates may incentivize companies to relocate their operations to countries with lower tax burdens.
- Offshoring Risks: Corporations may move their headquarters or profits overseas to avoid higher taxes, resulting in job losses domestically.
- Global Competition: The U.S. could lose its competitive edge as businesses seek more favorable tax environments elsewhere.
- Reduced Domestic Investment: Companies may choose not to invest in U.S. operations if they perceive the tax environment as unfavorable.
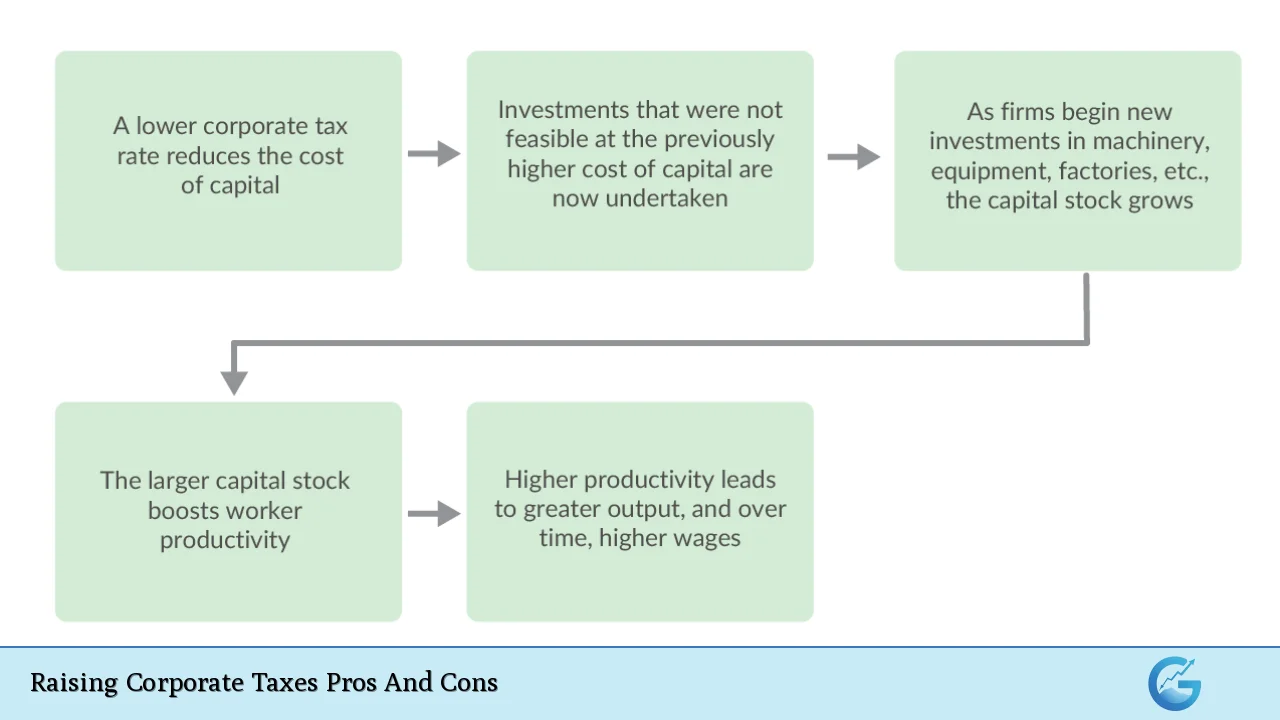
Encouragement for Domestic Investment
Higher corporate taxes can be structured to encourage businesses to invest domestically rather than abroad.
- Incentives for Local Investment: If accompanied by incentives or credits for domestic investment, higher taxes could lead companies to focus on U.S.-based projects.
- Job Creation: Increased domestic investment often leads to job creation, benefiting local economies.
- Long-Term Growth: By fostering an environment where companies invest in innovation and infrastructure within the country, overall economic growth can be stimulated.
Negative Impact on Economic Growth
Critics argue that raising corporate taxes can hinder overall economic growth by discouraging investment.
- Investment Disincentives: Higher taxes reduce the capital available for companies to invest in new projects or technologies, which can stifle innovation.
- Job Growth Stagnation: Reduced investment often leads to slower job growth or even layoffs as companies adjust to increased taxation burdens.
- GDP Impact: Studies have shown that increases in corporate tax rates can lead to significant reductions in GDP over time due to decreased business activity.
Funding for Infrastructure and Social Programs
Increased corporate tax revenues can directly fund critical infrastructure projects and social programs that benefit society as a whole.
- Infrastructure Development: Improved infrastructure supports economic activity by facilitating transportation and communication networks essential for business operations.
- Social Welfare Programs: Enhanced funding for social programs can improve quality of life and economic stability for lower-income individuals and families.
- Long-Term Economic Benefits: Investments in infrastructure often yield long-term economic benefits that outweigh initial costs through enhanced productivity and reduced operational inefficiencies.
Dissuasion of Foreign Direct Investment
Higher corporate taxes may deter foreign direct investment (FDI), which is crucial for economic growth.
- Less Attractive Business Environment: A higher tax burden makes a country less appealing to foreign investors looking for profitable opportunities.
- Competitive Disadvantage: If competing nations maintain lower corporate tax rates, they will likely attract more foreign capital at the expense of the U.S. economy.
- Impact on Innovation: Fewer foreign investments may result in reduced access to new technologies and innovations that typically accompany FDI.
Reduction of the Federal Deficit
Raising corporate taxes could play a role in reducing the federal deficit by increasing government revenue without directly taxing individuals.
- Budgetary Relief: Increased revenues from corporations could help balance budgets and reduce national debt levels over time.
- Sustainable Fiscal Policy: A more robust tax base allows for sustainable fiscal policies that do not rely solely on individual income taxes or consumption taxes.
- Long-Term Economic Stability: Reducing deficits contributes to overall economic stability which is beneficial for all sectors of the economy.
Increased Burden on Small Businesses
While large corporations may bear the brunt of increased taxes, small businesses often feel the effects as well.
- Cost Pass-throughs: Small businesses may face increased operational costs if larger competitors pass their higher tax burdens onto consumers through price increases.
- Limited Resources: Unlike larger firms, small businesses may lack the resources or flexibility to absorb additional costs associated with higher corporate taxation.
- Risk of Closure or Downsizing: In extreme cases, increased taxation could lead small businesses to downsize or close altogether if they cannot cope with rising expenses.
In conclusion, raising corporate taxes presents both advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully weighed. While it has the potential to generate significant revenue for essential public services and create a fairer tax system, it also poses risks such as reduced wages, increased consumer prices, potential offshoring of jobs, and negative impacts on economic growth. Policymakers must consider these factors when debating changes to corporate tax rates, ensuring that any adjustments support long-term economic stability while addressing pressing social needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Raising Corporate Taxes Pros And Cons
- What are the main benefits of raising corporate taxes?
Raising corporate taxes can increase government revenue for public services, promote equity in the tax system, encourage domestic investment, and help reduce federal deficits. - How do higher corporate taxes affect wages?
Higher corporate taxes often lead to reduced wages as businesses look to maintain profit margins by cutting labor costs. - Can raising corporate taxes hurt small businesses?
Yes, small businesses may suffer from increased operational costs if larger firms pass on their higher tax burdens through price increases. - What are the risks associated with raising corporate taxes?
The risks include potential job losses due to offshoring, reduced economic growth due to decreased investment incentives, and increased consumer prices. - How might higher corporate taxes impact foreign direct investment?
Higher corporate taxes could deter foreign direct investment by making a country less attractive compared to those with lower tax rates. - Are there any long-term benefits of raising corporate taxes?
If managed properly, increased revenue from corporate taxes can fund infrastructure improvements and social programs that yield long-term economic benefits. - What is the relationship between corporate taxes and innovation?
Higher corporate taxes may stifle innovation by reducing available capital for research and development investments. - How do proponents justify raising corporate taxes?
Proponents argue it ensures large corporations pay their fair share while providing necessary funding for public goods that benefit society.