Renting a home is a significant decision that can impact your financial situation and lifestyle. As individuals navigate the complexities of housing, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of renting is essential, particularly for those interested in finance, crypto, forex, and money markets. This article will explore the pros and cons of renting, providing a comprehensive overview to help potential renters make informed decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
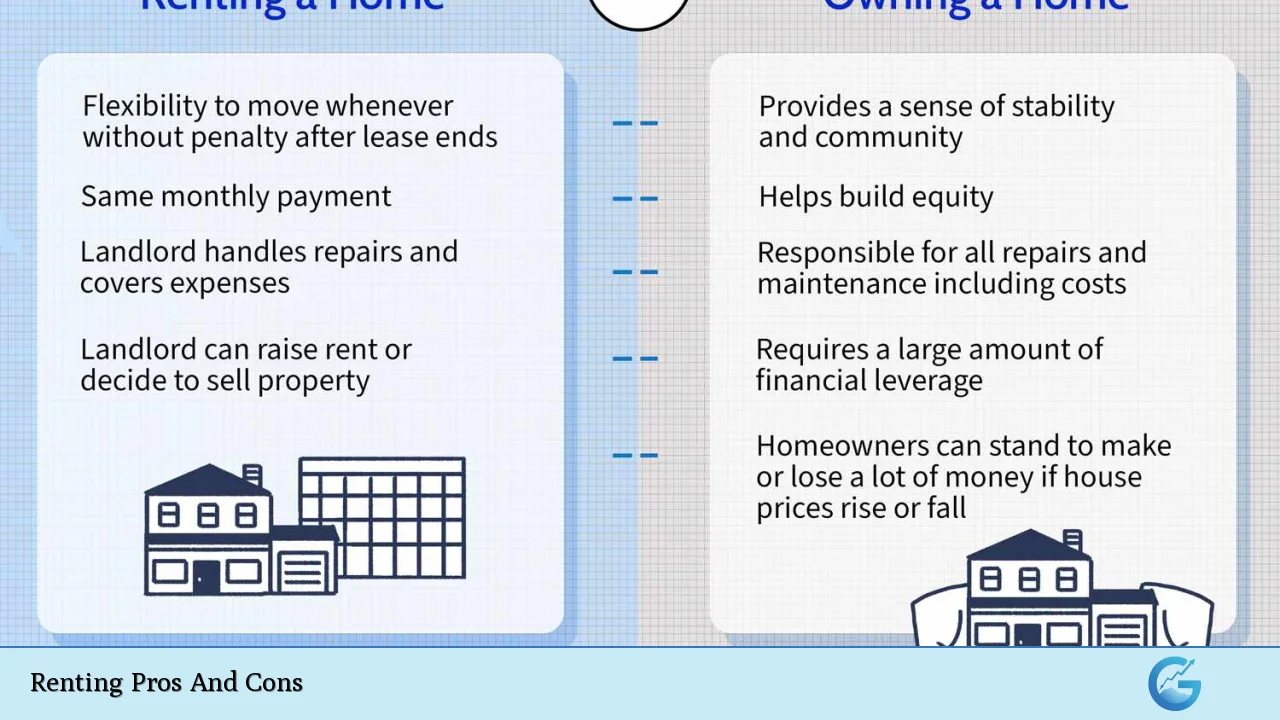
| Flexibility in relocation | No equity building |
| Lower upfront costs | Potential for rent increases |
| No maintenance responsibilities | Limited control over property modifications |
| No property taxes | Restrictions on pets and guests |
| Predictable monthly expenses | Insecurity of tenancy |
| Access to amenities without long-term commitment | Less stability compared to homeownership |
| Opportunity to test different neighborhoods | Potential for eviction or lease termination |
| Financial predictability in budgeting | No tax benefits available to renters |
Flexibility in Relocation
One of the primary advantages of renting is the flexibility it provides. Renters can often sign short-term leases or month-to-month agreements, allowing them to relocate easily for job opportunities or personal reasons. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for young professionals or those who travel frequently.
- Quick relocation: Renters can move without the lengthy process of selling a home.
- Trial living in different areas: Renting allows individuals to explore various neighborhoods before committing to a purchase.
Lower Upfront Costs
Renting typically requires significantly lower upfront costs compared to buying a home.
- Minimal initial investment: Most rentals require only a security deposit and first month’s rent, making it easier for individuals to manage their finances.
- No large down payment: Unlike purchasing a home, which often requires a substantial down payment, renting allows for immediate occupancy with less financial strain.
No Maintenance Responsibilities
Another significant benefit of renting is that tenants are generally not responsible for property maintenance and repairs.
- Landlord responsibilities: Renters can report issues to their landlord without worrying about repair costs or time spent managing maintenance tasks.
- Financial relief from unexpected repairs: Major repairs, such as roof replacements or plumbing issues, are typically handled by landlords, alleviating financial burdens on renters.
No Property Taxes
Renters do not pay property taxes, which can represent a significant annual expense for homeowners.
- Cost savings: This aspect can contribute to overall lower living costs for renters compared to homeowners who must budget for property taxes.
Predictable Monthly Expenses
Renting offers predictable monthly expenses that can simplify budgeting.
- Fixed rent payments: Renters usually have a clear understanding of their monthly costs, which helps in financial planning.
- No surprise costs: Unlike homeowners who may face unexpected repair bills, renters know their expenses are limited to rent and utilities.
Access to Amenities Without Long-Term Commitment
Many rental properties come with amenities such as pools, gyms, and community spaces without the long-term commitment associated with homeownership.
- Convenience: Renters can enjoy these facilities while avoiding the responsibilities of maintenance and upkeep.
Opportunity to Test Different Neighborhoods
Renting allows individuals to experience different neighborhoods before making a long-term commitment.
- Exploration: This opportunity enables renters to find the area that best suits their lifestyle and preferences without the pressure of purchasing a home immediately.
No Equity Building
A significant disadvantage of renting is that tenants do not build equity in the property they occupy.
- Wealth accumulation: Rent payments contribute to the landlord’s wealth rather than building an asset for the renter.
- Long-term investment loss: Over time, homeowners build equity as they pay down their mortgage and benefit from property appreciation—renters miss out on this potential financial growth.
Potential for Rent Increases
Renters face the risk of rent increases at the end of their lease term or during renewal periods.
- Budgeting challenges: Unexpected increases can strain finances and require adjustments in spending or living arrangements.
- Market fluctuations: In competitive rental markets, landlords may raise rents significantly based on demand, impacting affordability.
Limited Control Over Property Modifications
Renters often have limited control over how they can modify their living space.
- Restrictions on personalization: Many landlords impose rules regarding decorating or making changes to the property, which can hinder renters’ ability to create a personalized living environment.
- Approval required for alterations: Tenants must seek permission from landlords before making any significant changes, which can be frustrating for those who wish to customize their homes.
Restrictions on Pets and Guests
Many rental agreements come with strict policies regarding pets and guests.
- Pet limitations: Finding pet-friendly rentals can be challenging, and some properties may charge additional fees or deposits for pet owners.
- Guest restrictions: Landlords may limit overnight guests or impose rules about who can stay at the property, affecting renters’ lifestyles.
Insecurity of Tenancy
Renters may experience insecurity regarding their housing situation due to factors beyond their control.
- Eviction risks: Landlords have the authority to terminate leases or evict tenants under certain conditions, creating uncertainty for renters.
- Dependence on landlord decisions: Tenants rely heavily on their landlord’s decisions regarding lease renewals and property management practices, which can lead to instability.
Less Stability Compared to Homeownership
While renting offers flexibility, it also comes with less stability than owning a home.
- Frequent relocations may be necessary: Changes in rental agreements or personal circumstances may force tenants to move more often than homeowners would need to sell their properties.
- Market volatility impact: Economic downturns can affect rental markets just as they do housing markets, leading to increased competition and potential displacement for tenants.
Conclusion
Deciding whether to rent or buy involves weighing various factors related to personal circumstances and financial goals. Renting offers numerous advantages such as flexibility, lower upfront costs, no maintenance responsibilities, and predictable expenses. However, it also presents drawbacks like lack of equity building, potential rent increases, limited control over modifications, restrictions on pets and guests, insecurity of tenancy, and less stability compared to homeownership.
Ultimately, individuals must assess their priorities—whether they value flexibility over investment potential—before making this crucial decision. Understanding these pros and cons will empower prospective renters to navigate their housing choices more effectively while considering their broader financial strategies in areas like finance, crypto investments, forex trading, and money markets.
Frequently Asked Questions About Renting Pros And Cons
- What are the main benefits of renting?
The main benefits include flexibility in relocation, lower upfront costs compared to buying a home, no maintenance responsibilities, predictable monthly expenses, and access to amenities without long-term commitments. - What are the disadvantages of renting?
The disadvantages include no equity building with rent payments going towards someone else’s mortgage, potential rent increases upon lease renewal, limited control over property modifications, restrictions on pets or guests, insecurity regarding tenancy status due to landlord decisions. - Is renting cheaper than buying?
In many cases, renting is cheaper upfront due to lower initial costs; however, over time buying may become more financially advantageous as homeowners build equity. - Can I personalize my rented space?
This largely depends on your lease agreement; most landlords require tenants to seek approval before making significant changes. - What happens if my landlord raises my rent?
You will need to decide whether you can afford the new rate; if not, you may need to consider moving when your lease expires. - Aren’t there tax benefits associated with owning?
Yes; homeowners often receive tax deductions on mortgage interest and property taxes that renters do not benefit from. - How does renting affect my credit score?
While paying rent does not directly build credit like mortgage payments do, timely rent payments can positively influence your credit history if reported by landlords. - What should I look for when renting?
You should consider factors such as location convenience, rental price relative to your budget, lease terms including duration and conditions regarding pets or modifications.