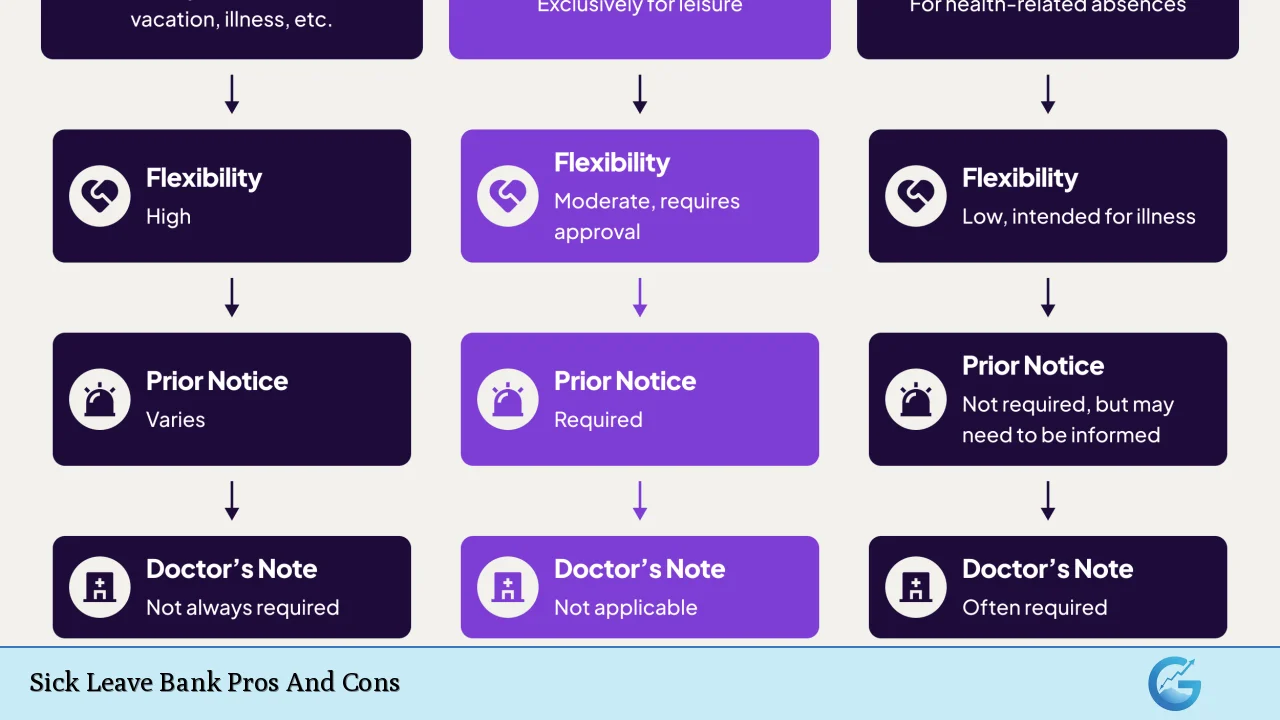
Sick leave banks are programs that allow employees to pool their unused sick leave days and make them available to colleagues who exhaust their own leave due to serious illness or injury. This system is often implemented in workplaces, especially in educational institutions and public sectors, to provide a safety net for employees facing catastrophic health issues. While sick leave banks can foster a supportive work environment, they also come with various advantages and disadvantages that need careful consideration.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides financial security for employees facing long-term illnesses | Can lead to potential abuse of the system |
| Encourages a culture of support among employees | Administrative complexity and potential for disputes |
| Reduces the financial burden on employers for extended sick leave | May create inequities among employees based on participation |
| Allows for flexibility in leave usage during critical health situations | Requires careful management and oversight to prevent misuse |
| Promotes employee retention and morale | Employees may feel pressured to donate days they might need themselves |
Provides Financial Security for Employees Facing Long-Term Illnesses
One of the most significant advantages of a sick leave bank is that it offers financial protection for employees who encounter severe health issues requiring extended time off work. Employees who might otherwise face financial hardship due to the exhaustion of their sick leave can access additional days from the bank, ensuring they receive pay during their recovery.
- Financial stability: Employees can maintain their income during prolonged illnesses.
- Peace of mind: Knowing there is a support system in place can alleviate stress for employees facing health challenges.
Encourages a Culture of Support Among Employees
Sick leave banks foster a sense of community and solidarity within the workplace. When employees contribute their unused sick days to help colleagues in need, it cultivates an environment of mutual support.
- Strengthened relationships: Employees may develop stronger bonds as they help each other.
- Positive workplace culture: A supportive atmosphere can enhance overall employee satisfaction.
Reduces the Financial Burden on Employers for Extended Sick Leave
From an employer’s perspective, sick leave banks can mitigate the costs associated with extended sick leaves. By pooling sick days, companies may find it easier to manage staffing needs without incurring additional costs for temporary replacements.
- Cost-effective: Employers may save money by reducing the need for substitutes.
- Better resource allocation: Funds can be directed toward other employee benefits or operational needs.
Allows for Flexibility in Leave Usage During Critical Health Situations
Sick leave banks provide flexibility regarding how employees can use their leave. This adaptability is crucial during emergencies or serious health crises when traditional sick leave policies may not suffice.
- Tailored support: Employees can draw from the bank as needed, depending on individual circumstances.
- Emergency preparedness: The system allows organizations to respond more effectively to unexpected health issues among staff.
Promotes Employee Retention and Morale
Having a sick leave bank can enhance employee morale and retention rates. When employees feel cared for and supported by their employer, they are more likely to remain loyal to the organization.
- Increased loyalty: Employees are more likely to stay with an employer that supports them in times of need.
- Higher job satisfaction: A caring workplace contributes positively to employee happiness.
Can Lead to Potential Abuse of the System
Despite its benefits, one significant disadvantage of a sick leave bank is the potential for abuse. Some employees may take advantage of the system by feigning illness or overusing banked days.
- Misuse risk: Employees might exploit the system if not properly monitored.
- Impact on trust: Abuse can erode trust among colleagues and between employees and management.
Administrative Complexity and Potential for Disputes
Managing a sick leave bank involves administrative challenges. Setting up eligibility criteria, managing contributions, and overseeing withdrawals require significant effort and can lead to disputes if not handled transparently.
- Resource-intensive: Administrators must dedicate time and effort to manage the program effectively.
- Conflict potential: Disagreements over eligibility or contributions can create tension among staff.
May Create Inequities Among Employees Based on Participation
Participation in a sick leave bank is often voluntary, which can lead to disparities among employees regarding access to benefits. Those who do not participate may find themselves at a disadvantage when needing additional sick leave.
- Inequality issues: Non-participating employees may feel excluded or disadvantaged.
- Pressure to conform: Employees might feel compelled to join even if they are uncomfortable doing so.
Requires Careful Management and Oversight to Prevent Misuse
To ensure that a sick leave bank functions effectively, careful oversight is necessary. This includes monitoring contributions, withdrawals, and ensuring compliance with established policies.
- Need for governance: Clear policies must be established and enforced.
- Ongoing evaluation: Regular assessments of the program are essential to maintain its integrity.
Employees May Feel Pressured to Donate Days They Might Need Themselves
Another downside is that employees might feel obligated to donate their unused sick days, potentially leaving them vulnerable should they face health issues later on. This pressure can create resentment among staff members.
- Emotional burden: The expectation to donate can weigh heavily on some employees.
- Fear of future needs: Employees may worry about their own needs if they contribute too many days.
In conclusion, while sick leave banks offer numerous advantages such as financial security, community support, cost savings for employers, flexibility in usage, and improved morale, they also pose challenges including potential abuse, administrative complexities, inequities among participants, management requirements, and emotional pressures on employees. Organizations considering implementing a sick leave bank should weigh these pros and cons carefully to ensure it aligns with their goals and values while fostering a supportive workplace environment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sick Leave Bank Pros And Cons
- What is a sick leave bank?
A sick leave bank is a program where employees contribute unused sick days into a pool that other employees can draw from when they exhaust their own sick leave due to serious health issues. - How does participation in a sick leave bank work?
Employees typically must donate a certain number of their unused sick days to join the bank and may withdraw days only after exhausting their personal paid leave. - What are the main benefits of having a sick leave bank?
The main benefits include financial protection during long-term illnesses, fostering community support among coworkers, reducing costs associated with temporary replacements, and enhancing employee morale. - What are some risks associated with sick leave banks?
Risks include potential abuse of the system by some employees, administrative complexities in managing contributions and withdrawals, and possible inequities between participating and non-participating employees. - Can employers control how many days are withdrawn from the bank?
Yes, employers typically set limits on how many days an employee can withdraw based on established policies. - What happens if an employee donates days but later needs them?
Once donated, those days cannot be reclaimed; this creates potential concerns for employees about future needs. - Are there eligibility criteria for accessing funds from a sick leave bank?
Yes, most programs require that an employee exhaust all personal paid leave before accessing funds from the bank. - How do organizations ensure fair use of the sick leave bank?
Organizations must establish clear policies regarding contributions and withdrawals along with oversight mechanisms to monitor usage effectively.