The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017, signed into law by President Donald Trump, represents the most significant overhaul of the U.S. tax code in over three decades. This legislation aimed to stimulate economic growth through substantial tax cuts for individuals and corporations, as well as various reforms intended to simplify the tax system. While proponents argue that the TCJA has fostered economic growth and job creation, critics contend that it disproportionately benefits high-income earners and exacerbates income inequality. This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of the TCJA in detail, providing insights for those interested in finance, investment, and economic policy.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower corporate tax rate boosts business investment. | Increased federal deficit due to significant revenue loss. |
| Higher standard deduction simplifies tax filing for individuals. | Temporary nature of many individual tax cuts creates uncertainty. |
| Encourages repatriation of overseas profits. | Disproportionate benefits to high-income earners increase inequality. |
| Immediate expensing of capital investments promotes growth. | Potential long-term negative impacts on federal funding for social programs. |
| Increased child tax credit supports families. | Complexity introduced in certain areas, such as pass-through income deductions. |
Lower Corporate Tax Rate Boosts Business Investment
One of the most significant features of the TCJA was the reduction of the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%. This change aimed to make American businesses more competitive globally and encourage domestic investment.
- Increased capital investments: Lower taxes on corporations can lead to higher levels of investment in infrastructure, technology, and workforce development.
- Job creation: With increased investments, companies are better positioned to expand operations and hire more employees.
- Global competitiveness: By lowering the corporate tax rate, U.S. companies may be less inclined to relocate operations overseas for tax advantages.
Increased Federal Deficit Due to Significant Revenue Loss
While the TCJA aimed to stimulate economic growth, it also resulted in a substantial increase in the federal deficit.
- Revenue loss: The Congressional Budget Office estimated a revenue loss of approximately $1.47 trillion over ten years due to the tax cuts.
- Long-term fiscal concerns: Increased deficits could lead to higher national debt levels, impacting future government spending on essential services.
- Potential for future tax increases: To address deficits, policymakers may need to consider raising taxes or cutting social programs in the future.
Higher Standard Deduction Simplifies Tax Filing for Individuals
The TCJA nearly doubled the standard deduction, making it easier for many taxpayers to file their returns without itemizing deductions.
- Simplified filing process: A higher standard deduction means fewer taxpayers need to navigate complex itemization rules.
- Increased take-home pay: Many families saw an immediate increase in their disposable income due to lower taxable income.
- Encouragement for low-to-middle-income families: The simplification can particularly benefit families who previously found itemizing cumbersome or unbeneficial.
Temporary Nature of Many Individual Tax Cuts Creates Uncertainty
Many provisions affecting individual taxpayers are set to expire after 2025, leading to uncertainty about future tax liabilities.
- Potential tax increases: As individual tax cuts expire, many households may face higher taxes unless new legislation is passed.
- Investment hesitancy: Uncertainty regarding future taxes can hinder long-term financial planning and investment decisions by individuals and businesses alike.
- Political risks: Changes in administration or congressional composition could lead to further alterations in tax policy, impacting taxpayer behavior.
Encourages Repatriation of Overseas Profits
The TCJA introduced provisions that incentivize U.S. companies to bring back profits held overseas at a lower tax rate.
- Boosting domestic investment: Repatriated funds can be reinvested into U.S. operations, leading to potential job growth and economic expansion.
- Strengthening U.S. economy: By encouraging companies to invest domestically rather than abroad, the TCJA aims to bolster overall economic activity within the country.
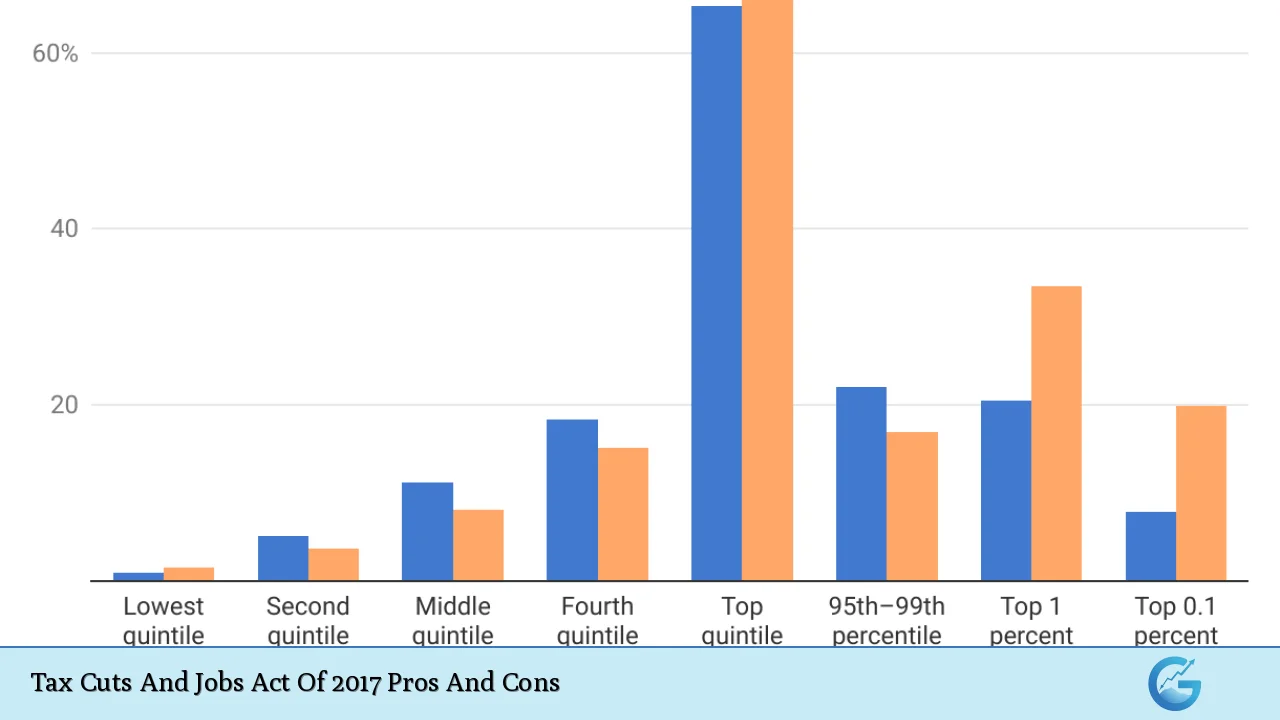
Disproportionate Benefits to High-Income Earners Increase Inequality
Critics argue that while the TCJA provides some benefits across various income levels, it disproportionately favors wealthier individuals and corporations.
- Regressive nature of tax cuts: Studies have shown that high-income households received a larger share of tax cuts compared to lower-income households.
- Long-term implications for equity: The widening gap between high-income earners and middle/lower-income households could exacerbate existing social inequalities over time.
Immediate Expensing of Capital Investments Promotes Growth
The TCJA allows businesses to immediately deduct the cost of certain capital investments rather than depreciating them over time.
- Stimulating business spending: Immediate expensing encourages companies to invest in new equipment and technology sooner rather than later.
- Enhancing productivity: By investing in modern equipment, businesses can improve efficiency and productivity levels across various sectors.
Potential Long-Term Negative Impacts on Federal Funding for Social Programs
The significant revenue losses associated with the TCJA raise concerns about future funding for essential social programs.
- Impact on social safety nets: Reduced federal revenues could lead to cuts in programs like Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid if not addressed through other means.
- Challenges for state budgets: States that rely on federal funding may face budgetary pressures as federal resources dwindle over time.
Increased Child Tax Credit Supports Families
The TCJA expanded the child tax credit significantly, providing additional support for families with children.
- Financial relief for families: The increased credit helps alleviate some financial burdens faced by working families.
- Encouragement for family growth: By providing more resources per child, families may feel more secure in expanding their households or investing in education and childcare.
Complexity Introduced in Certain Areas, Such as Pass-Through Income Deductions
While some aspects of the TCJA simplified taxes, others introduced new complexities that can confuse taxpayers and accountants alike.
- Pass-through entity challenges: The new rules governing pass-through entities (like LLCs and S-corporations) can be intricate and difficult for business owners to navigate effectively.
- Compliance costs: Increased complexity may lead to higher costs associated with accounting services as taxpayers seek guidance on compliance with new regulations.
Closing Paragraph
In conclusion, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 presents a mixed bag of advantages and disadvantages. While it has succeeded in lowering corporate taxes and simplifying certain aspects of individual taxation, it has also raised concerns about increasing income inequality and long-term fiscal sustainability. As investors and finance professionals analyze its impact on markets and economic growth, understanding both its strengths and weaknesses is crucial for making informed decisions moving forward. The ongoing debates surrounding this legislation will likely shape future tax policy discussions as lawmakers consider how best to balance economic growth with equitable resource distribution across society.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tax Cuts And Jobs Act Of 2017
- What was the main goal of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act?
The primary aim was to stimulate economic growth by reducing taxes on individuals and corporations while simplifying certain aspects of the tax code. - How did the TCJA affect corporate taxes?
The act reduced the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, encouraging businesses to invest domestically. - Are individual tax cuts permanent?
No, many individual tax cuts are set to expire after 2025 unless Congress takes action to extend them. - Who benefits most from the TCJA?
The legislation primarily benefits high-income earners and corporations more than low-to-middle-income households. - What impact did TCJA have on federal revenue?
The act is projected to decrease federal revenues significantly over ten years, raising concerns about future deficits. - Did TCJA simplify or complicate taxes?
While it simplified some aspects like increasing the standard deduction, it also introduced complexities around pass-through income deductions. - What changes were made regarding capital investments?
The act allows businesses immediate expensing of certain capital investments instead of requiring depreciation over time. - How does TCJA affect family support?
The expanded child tax credit provides additional financial support for families with children under this legislation.