Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period, known as the “term.” If the insured person passes away during this term, the policy pays a death benefit to the beneficiaries. This form of insurance is often chosen for its affordability and simplicity, making it an attractive option for individuals looking to ensure financial security for their loved ones. However, like any financial product, term insurance comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential buyers should carefully consider.
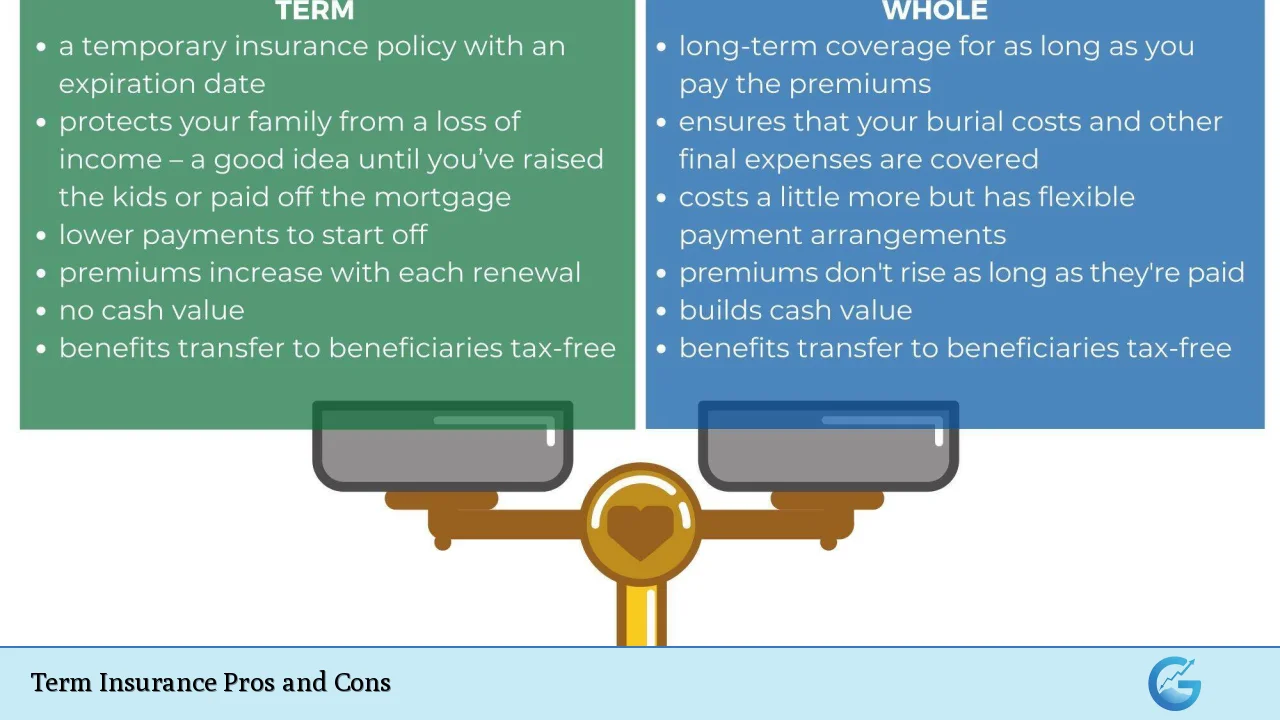
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Affordability with lower premiums than permanent life insurance. | Coverage is temporary and ends when the term expires. |
| High death benefit relative to the premium paid. | No cash value accumulation; no investment component. |
| Simplicity and ease of understanding. | Premiums typically increase upon renewal as the insured ages. |
| Flexible terms available (10, 20, 30 years). | Potential for inadequate coverage if long-term needs arise. |
| Renewal or conversion options may be available. | Health-based eligibility can limit options for older applicants. |
Affordability
One of the most significant advantages of term insurance is its affordability.
- Lower Premiums: Compared to permanent life insurance policies, term life insurance generally offers lower premiums. This allows individuals to secure substantial coverage without straining their finances.
- Cost-Effective Coverage: This affordability makes it accessible to a broader audience, enabling families to protect their financial future without excessive costs.
High Death Benefit
Term insurance policies often provide a high death benefit relative to the premiums paid.
- Financial Security: In case of the insured’s untimely death, beneficiaries receive a lump sum that can cover living expenses, debts, or educational costs.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that loved ones will be financially secure can alleviate stress and provide peace of mind during challenging times.
Simplicity
The straightforward nature of term insurance is another appealing aspect.
- Easy to Understand: The structure of term life insurance is simple: pay premiums for a specified term, and if you pass away during that time, your beneficiaries receive the death benefit.
- Less Confusion: This simplicity helps individuals make informed decisions without getting bogged down by complex investment components found in other types of life insurance.
Flexible Terms
Term life insurance offers flexible policy options tailored to individual needs.
- Variety of Terms: Policies are available in various lengths, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. This flexibility allows individuals to choose coverage that aligns with their financial responsibilities, such as mortgage payments or children’s education.
- Customization: Some policies allow for customization based on changing financial needs over time.
Renewal and Conversion Options
Many term policies include options for renewal or conversion.
- Renewal Options: At the end of the term, policyholders may have the option to renew their coverage without undergoing a medical exam. This can be beneficial if health conditions change over time.
- Conversion to Permanent Insurance: Some policies allow conversion to permanent life insurance, providing continued coverage even after the initial term ends.
Temporary Coverage
Despite its advantages, one major drawback of term insurance is its temporary nature.
- Coverage Ends: Once the policy term expires, coverage ceases. If you outlive your policy and still need life insurance, you may face higher premiums or be unable to secure new coverage due to age or health changes.
- No Death Benefit After Term: If you survive beyond the policy’s duration, your beneficiaries will not receive any payout, which can be seen as a disadvantage compared to permanent policies that offer lifelong protection.
No Cash Value Accumulation
Term life insurance does not build cash value like permanent policies do.
- No Investment Component: Unlike whole life insurance, which accumulates cash value over time, term life focuses solely on providing a death benefit. This means that there are no savings or investment returns associated with term policies.
- Limited Financial Utility: Policyholders cannot borrow against their policy or withdraw funds during their lifetime, limiting its utility beyond providing a death benefit.
Increasing Premiums Upon Renewal
Another disadvantage is that premiums typically increase upon renewal at the end of the term.
- Higher Costs with Age: As you age, renewing your policy can lead to significantly higher premiums. This can make it cost-prohibitive for some individuals who wish to maintain coverage later in life.
- Budgeting Challenges: The unpredictability of premium increases can complicate financial planning and budgeting for long-term coverage needs.
Potential for Inadequate Coverage
Term insurance may not adequately address long-term financial needs.
- Specific Coverage Duration: Since it is designed for temporary needs (like raising children or paying off debt), it may not provide sufficient protection if your financial situation changes or if you develop long-term obligations later in life.
- Need for Additional Policies: Individuals might find themselves needing additional coverage as they age or as their responsibilities grow, which could lead to higher overall costs if multiple policies are necessary.
Health-Based Eligibility
The availability and cost of term insurance are heavily influenced by health factors at application time.
- Higher Premiums for Health Issues: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher premiums or difficulty obtaining coverage altogether.
- Age Limitations: As people age, they may find it increasingly challenging to secure affordable term life insurance due to escalating health risks associated with aging.
Closing Thoughts
In summary, term insurance presents both compelling advantages and notable disadvantages. Its affordability and high death benefits make it an attractive option for many individuals seeking financial protection for their loved ones. However, potential buyers must also consider its temporary nature and lack of cash value accumulation.
Ultimately, choosing whether term insurance aligns with your financial goals requires careful consideration of your current situation and future needs. By understanding both the pros and cons, you can make an informed decision that best protects your family’s financial future in case of unforeseen circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions About Term Insurance
- What is term insurance?
Term insurance provides coverage for a specified period; if the insured passes away during this time, beneficiaries receive a death benefit. - How does term insurance differ from permanent life insurance?
Term insurance covers a specific duration without accumulating cash value, while permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage and builds cash value over time. - Can I convert my term policy into a permanent one?
Many term policies offer conversion options that allow you to switch to permanent coverage without undergoing additional medical exams. - What happens if I outlive my term policy?
If you outlive your policy’s duration, you will not receive any benefits; however, some policies may allow renewal at higher premiums. - Is term insurance suitable for everyone?
While it offers many benefits, individuals should assess their long-term financial needs before purchasing term insurance as it may not cover all eventualities. - Are premiums fixed throughout the policy’s duration?
No; while some policies offer fixed premiums initially, they often increase upon renewal based on age and health status. - Can I get a refund on my premiums if I don’t claim?
No standard term policies do not return premiums if no claims are made; however, some variations like Return of Premium (ROP) plans do exist. - How much coverage should I buy?
A general guideline suggests purchasing coverage equal to 8–10 times your annual income; however, individual circumstances vary widely.