The classification of workers as either W-2 employees or 1099 independent contractors is a critical decision for both employers and employees. Each classification comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact financial outcomes, tax obligations, and overall job satisfaction. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals navigating the finance, crypto, forex, and money markets, as well as for businesses looking to optimize their workforce.
This article will delve into the pros and cons of W-2 and 1099 classifications, providing a comprehensive overview that will help readers make informed decisions regarding employment status.
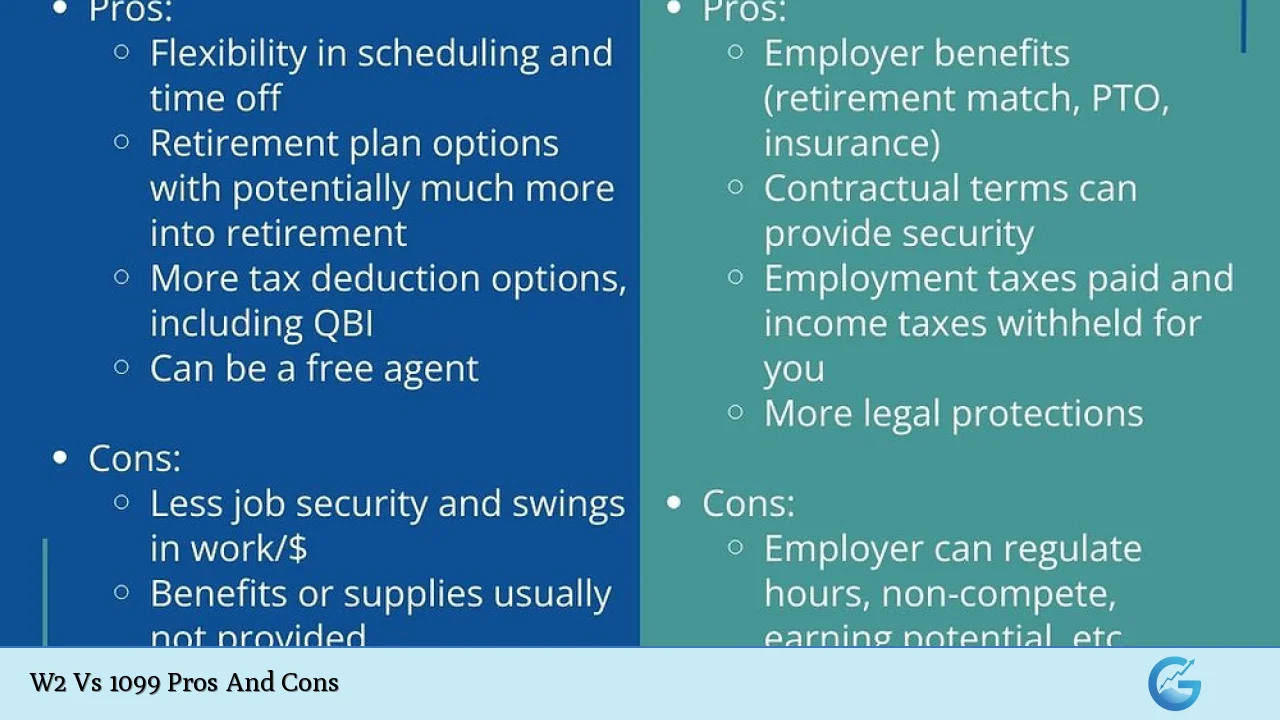
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| W-2 employees receive benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. | Higher costs for employers due to taxes and benefits. |
| Greater job stability and security for W-2 employees. | Less flexibility in work arrangements for W-2 employees. |
| W-2 employees are protected by labor laws. | More regulatory burdens for employers with W-2 employees. |
| 1099 contractors can deduct business expenses from taxes. | 1099 workers must manage their own taxes and insurance. |
| Flexibility in work hours and projects for 1099 contractors. | No guaranteed income or benefits for 1099 workers. |
| Lower administrative burden for employers hiring 1099 contractors. | Potential instability in workforce due to high turnover among 1099 contractors. |
Advantages of W-2 Employees
1. Access to Benefits
W-2 employees typically enjoy a range of benefits that are not available to independent contractors. These benefits often include:
- Health Insurance: Employers usually provide health insurance plans, which can significantly reduce out-of-pocket medical costs.
- Retirement Plans: Many companies offer retirement savings plans, such as 401(k)s, with employer matching contributions.
- Paid Time Off: W-2 employees often receive paid vacation days, sick leave, and holidays.
2. Job Stability
W-2 employment generally offers greater job security compared to 1099 contracting. Employees are more likely to have a consistent paycheck, which can be crucial for financial planning and stability.
3. Legal Protections
W-2 employees are covered by various labor laws that protect their rights in the workplace. This includes protections against discrimination, harassment, and wrongful termination. They also have access to unemployment benefits if they lose their job.
Disadvantages of W-2 Employees
1. Higher Costs for Employers
Employers face higher costs when hiring W-2 employees due to:
- Payroll Taxes: Employers must pay Social Security, Medicare taxes, and unemployment taxes on behalf of their employees.
- Benefits Costs: Providing health insurance and retirement benefits can be expensive.
2. Less Flexibility
W-2 employees often have less flexibility in terms of work hours and locations. They may be required to adhere to a specific schedule and work onsite, which can be limiting compared to the freedom enjoyed by independent contractors.
3. Regulatory Burdens
Employing W-2 workers comes with increased regulatory responsibilities. Employers must comply with various labor laws, which can require significant administrative effort.
Advantages of 1099 Contractors
1. Tax Deductions
One of the primary advantages of being classified as a 1099 contractor is the ability to deduct business expenses from taxable income. This can include:
- Home office expenses
- Travel costs related to work
- Equipment purchases
2. Flexibility in Work Arrangements
1099 contractors often enjoy greater flexibility in choosing when and where they work. This independence allows them to balance multiple projects or clients simultaneously.
3. Lower Administrative Burden for Employers
Hiring 1099 contractors reduces the administrative responsibilities for employers since they do not need to withhold taxes or provide benefits. This can lead to lower overhead costs.
Disadvantages of 1099 Contractors
1. No Employee Benefits
Unlike W-2 employees, 1099 contractors do not receive benefits such as health insurance or retirement plans from their clients. This means they must secure their own coverage, which can be costly.
2. Tax Responsibilities
Independent contractors are responsible for managing their own taxes, including self-employment taxes that cover Social Security and Medicare contributions. This requires diligent financial planning and may involve quarterly estimated tax payments.
3. Income Instability
Contractors often face income instability due to the project-based nature of their work. They may experience gaps between contracts or fluctuations in demand that can impact their earnings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between W-2 employment and 1099 contracting involves weighing various pros and cons that affect both workers and employers. While W-2 employees benefit from stability, legal protections, and access to benefits, they also face higher costs and less flexibility. Conversely, 1099 contractors enjoy independence and tax deductions but must navigate income instability and lack employee benefits.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for individuals involved in finance, crypto, forex, and money markets as they strategize their career paths or make hiring decisions within their organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions About W2 Vs 1099 Pros And Cons
- What is the main difference between W-2 and 1099?
The primary difference lies in employment status; W-2 workers are employees with taxes withheld by employers, while 1099 workers are independent contractors responsible for their own taxes. - Are W-2 employees entitled to benefits?
Yes, W-2 employees typically receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. - Can 1099 contractors deduct expenses?
Yes, independent contractors can deduct various business-related expenses from their taxable income. - Which option is better for employers?
This depends on the business needs; hiring 1099 contractors can reduce costs but may lead to less control over the workforce. - Do W-2 employees have job security?
Generally, yes; W-2 employees tend to have more job stability compared to independent contractors. - What are the tax implications of being a 1099 contractor?
Contractors must pay self-employment taxes and manage their own tax filings without employer withholding. - Can I choose between being a W-2 employee or a 1099 contractor?
This choice depends on the nature of your work arrangement; it is determined by how much control an employer has over your work. - What are the risks associated with misclassification?
Misclassifying workers can lead to significant penalties for employers regarding unpaid taxes and employee rights violations.
This comprehensive analysis provides insights into the advantages and disadvantages of W-2 vs. 1099 classifications, equipping readers with the knowledge necessary to navigate this important aspect of employment in today’s economy.