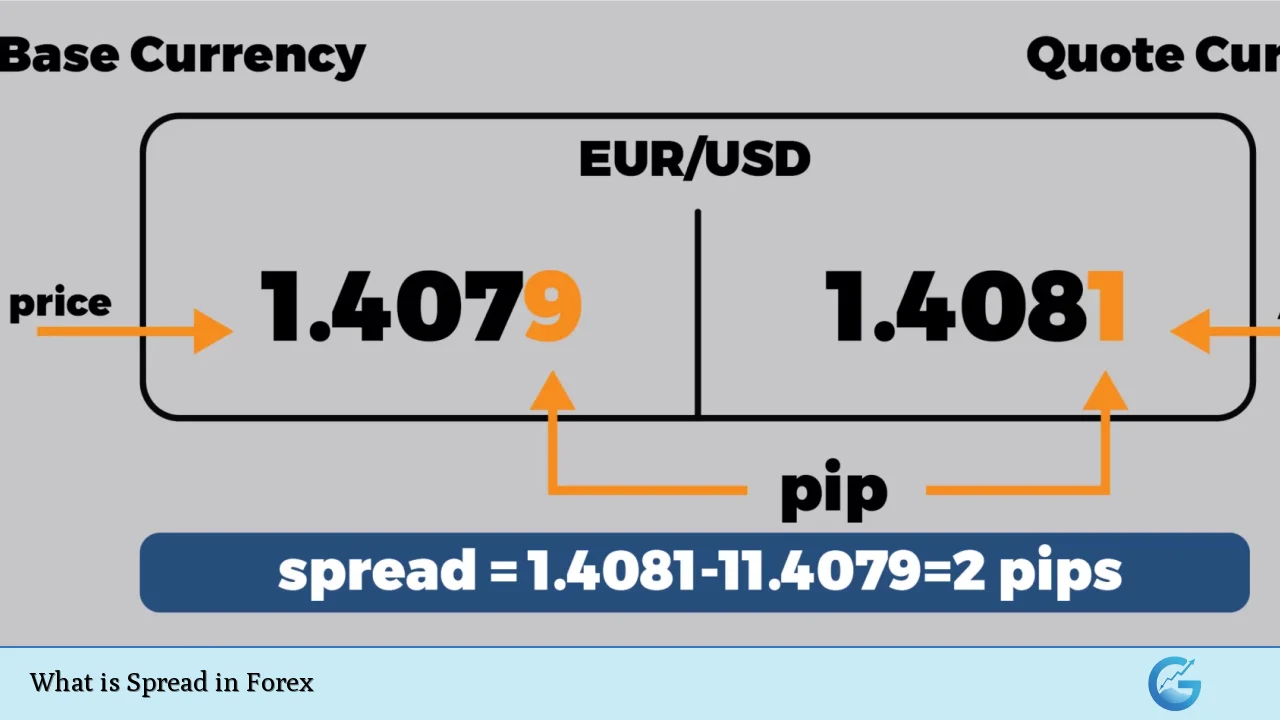
The spread in forex trading is a fundamental concept that every trader must understand. It refers to the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. The bid price is the amount a trader is willing to pay for the base currency, while the ask price is the amount a trader is willing to sell it for. This difference, measured in pips, represents the cost of executing a trade and is a primary way brokers earn their income.
In forex markets, spreads can vary significantly based on market conditions. For instance, during periods of high liquidity when many traders are active, spreads tend to be tighter (smaller). Conversely, during times of low liquidity or high volatility, spreads can widen considerably. Understanding how spreads work is crucial for traders as it directly affects their trading costs and potential profits.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Bid Price | The price at which you can sell a currency pair. |
| Ask Price | The price at which you can buy a currency pair. |
Types of Spreads
There are primarily two types of spreads in forex trading: fixed spreads and variable spreads.
Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. This means that even during volatile periods, the spread will not change. This can provide traders with predictability in their trading costs, making it easier to plan their trades.
Variable spreads, on the other hand, fluctuate based on market demand and liquidity. During times of high trading activity, such as when major financial centers are open, variable spreads tend to be narrower. However, during low activity or significant news events, these spreads can widen significantly.
Understanding these types allows traders to choose their brokers and trading strategies more effectively based on their risk tolerance and trading style.
How Spreads are Calculated
Calculating the spread in forex involves a straightforward process. It is determined by subtracting the bid price from the ask price. For example, if the GBP/USD currency pair has an ask price of 1.3091 and a bid price of 1.3089, the spread would be calculated as follows:
$$
\text{Spread} = \text{Ask Price} – \text{Bid Price} = 1.3091 – 1.3089 = 0.0002 \text{ or } 2 \text{ pips}
$$
This calculation is essential for traders as it helps them understand how much they will pay to enter or exit a trade.
Factors Influencing Spread Size
Several factors can influence the size of the spread in forex trading:
- Market Liquidity: High liquidity typically results in tighter spreads because there are more buyers and sellers in the market, making it easier to match trades.
- Market Volatility: During volatile market conditions—such as significant economic announcements—the spread may widen due to increased uncertainty and risk.
- Currency Pair: Major currency pairs like EUR/USD usually have tighter spreads compared to exotic pairs like USD/THB due to differences in trading volume and liquidity.
- Time of Day: Spreads can vary throughout the day depending on market hours. For instance, during overlapping trading sessions (like London and New York), liquidity increases, leading to tighter spreads.
Traders should be aware of these factors as they can significantly impact trading costs and strategies.
Importance of Spread in Trading Strategy
The spread plays a crucial role in determining overall trading costs and profitability. A tighter spread means lower costs for entering and exiting trades, which is particularly beneficial for strategies that rely on small price movements, such as scalping.
Conversely, wider spreads increase transaction costs and can erode potential profits. Therefore, traders need to consider the spread when developing their trading strategies:
- Scalping: Traders who engage in scalping need to focus on currency pairs with tight spreads since they aim to profit from small price changes over numerous trades.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders may tolerate wider spreads since they hold positions longer and focus on larger price movements.
Understanding how spreads affect different trading strategies allows traders to optimize their approaches for better profitability.
How to Reduce Spread Costs
Reducing spread costs is essential for maximizing profits in forex trading. Here are some strategies that traders can employ:
- Choose the Right Broker: Different brokers offer varying spreads; therefore, comparing brokers before opening an account is crucial.
- Trade During Peak Hours: Engaging in trades during times of high liquidity (when major markets overlap) often results in tighter spreads.
- Focus on Major Currency Pairs: Major pairs typically have lower spreads due to higher trading volumes compared to exotic pairs.
- Use Limit Orders: Limit orders allow traders to enter at specific prices rather than market prices, helping avoid wider spreads during volatile periods.
By implementing these strategies, traders can effectively manage their costs associated with spread.
Risks Associated with Spread Changes
Traders must be aware that spreads can change rapidly due to various factors such as economic news releases or unexpected market events. This variability poses risks:
- Increased Costs: If a trader places an order during high volatility without considering potential spread widening, they may incur higher costs than anticipated.
- Margin Calls: In extreme cases where spreads widen significantly after a position has been opened, traders may face margin calls if their account balance falls below required levels due to increased costs.
To mitigate these risks, traders should always monitor economic calendars for upcoming events that could impact market conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of spread in forex is vital for any trader looking to succeed in this dynamic market. The spread not only represents a cost but also reflects market conditions such as liquidity and volatility. By grasping how spreads work and implementing strategies to manage them effectively, traders can enhance their overall performance and profitability in forex trading.
FAQS About Spread in Forex
- What is a forex spread? – A forex spread is the difference between the bid price and ask price of a currency pair.
- How do I calculate the spread? – The spread is calculated by subtracting the bid price from the ask price.
- Why do spreads change? – Spreads change due to factors like market liquidity, volatility, time of day, and economic news releases.
- What are fixed and variable spreads? – Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions while variable spreads fluctuate based on supply and demand.
- How can I reduce my spread costs? – You can reduce your spread costs by choosing the right broker, trading during peak hours, focusing on major currency pairs, and using limit orders.