Deferred income annuities (DIAs) are financial products designed to provide a guaranteed income stream starting at a future date, which can be particularly appealing for individuals planning for retirement. As people live longer and face uncertainties regarding Social Security and pension plans, DIAs offer a way to secure a steady income that can last throughout retirement. However, like any financial product, they come with both advantages and disadvantages that potential investors should carefully consider.
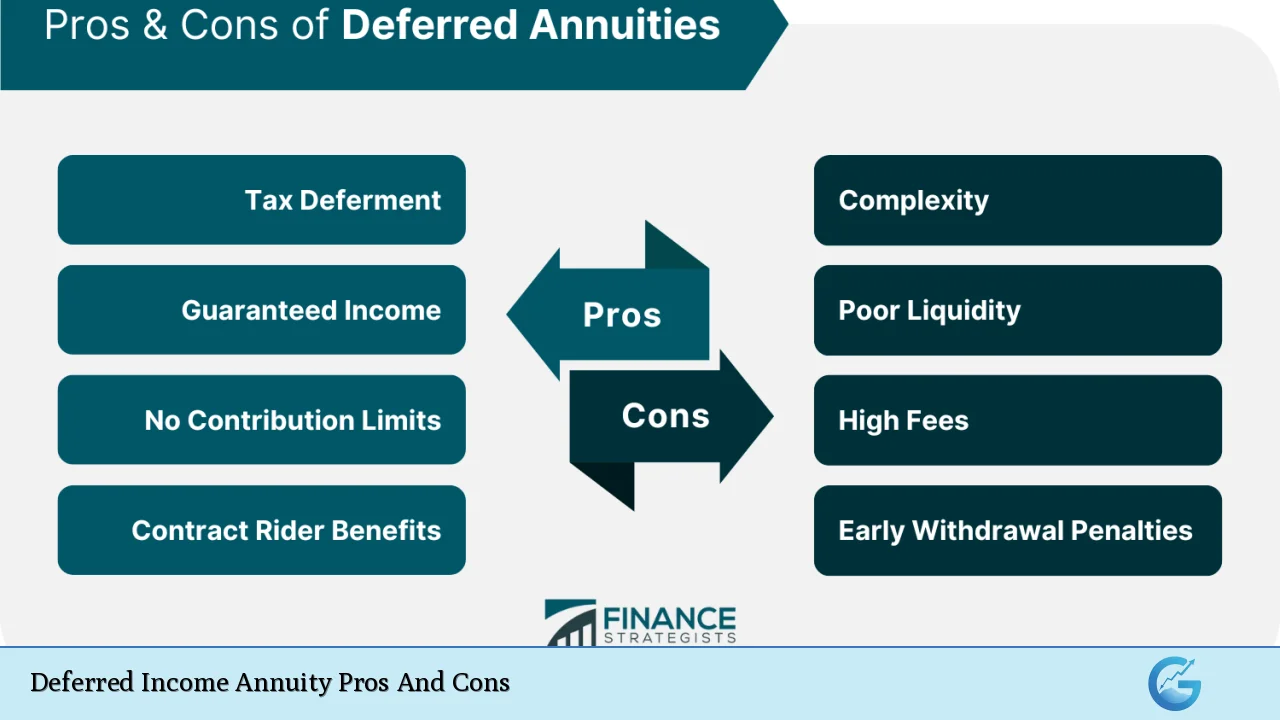
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Guaranteed income for life | Limited liquidity |
| Tax-deferred growth | Potentially lower returns compared to market investments |
| Flexibility in deferral period | Complexity of contracts |
| Protection against longevity risk | No inflation protection unless specified |
| Death benefits available in some contracts | High fees and surrender charges |
| Potential tax advantages as a QLAC | Restrictions on withdrawals before retirement age |
| Structured payments can help with budgeting | Risk of insurer default if not properly vetted |
Guaranteed Income for Life
One of the most significant advantages of a deferred income annuity is the promise of guaranteed income for life. This feature allows retirees to have peace of mind knowing that they will receive regular payments regardless of how long they live.
- Predictable payments: DIAs provide a predictable stream of income, which can help in budgeting retirement expenses.
- Joint options available: Many DIAs offer joint life options, ensuring that both partners receive income for their lifetimes.
Limited Liquidity
While DIAs provide guaranteed income, they are not very liquid. Once you invest in a DIA, your funds are generally locked in until the payout phase begins.
- Withdrawal restrictions: Most contracts do not allow for early withdrawals without incurring penalties.
- Surrender charges: If you need to access your funds before the specified period, surrender charges can significantly reduce your investment.
Tax-Deferred Growth
Another advantage is that the money invested in a deferred income annuity grows tax-deferred until it is withdrawn. This feature allows for potentially greater accumulation of wealth over time.
- Compounding interest: Since you do not pay taxes on the earnings until withdrawal, your investment can grow more significantly due to compounding.
- Tax management: This can be particularly beneficial for retirees who may find themselves in a lower tax bracket during retirement.
Potentially Lower Returns Compared to Market Investments
Despite the tax advantages, one of the drawbacks of DIAs is that they often provide lower returns compared to other investment options such as stocks or mutual funds.
- Fixed returns: Many DIAs offer fixed returns which may not keep pace with inflation or market growth.
- Opportunity cost: By locking funds into a DIA, investors may miss out on higher returns available through other investments.
Flexibility in Deferral Period
DIAs offer flexibility in choosing when to start receiving payments. This allows individuals to tailor their annuity according to their retirement plans.
- Customizable payout start dates: Investors can choose to begin receiving payments anywhere from 13 months to several decades after purchasing the annuity.
- Adjustable plans: Some contracts allow for one-time adjustments to the payout start date if personal circumstances change.
Complexity of Contracts
Deferred income annuities can be complex financial instruments that may be difficult for some investors to understand fully.
- Variety of options: The different types of DIAs (fixed, indexed, variable) and their associated features can be overwhelming.
- Need for professional advice: Many individuals may require assistance from financial advisors to navigate these complexities effectively.
Protection Against Longevity Risk
DIAs are particularly effective at addressing longevity risk—the risk of outliving one’s savings.
- Lifetime payments: By providing guaranteed payments for life, DIAs ensure that retirees do not run out of money regardless of how long they live.
- Financial security: This feature is especially appealing in an era where many people are living into their 90s or beyond.
No Inflation Protection Unless Specified
A significant drawback is that most DIAs do not automatically adjust for inflation unless specifically structured to do so.
- Fixed payment amounts: Without inflation protection, the purchasing power of fixed payments may erode over time as living costs rise.
- Consideration needed: Investors should carefully consider whether they need an inflation rider or other mechanisms to ensure their payments retain value over time.
Death Benefits Available in Some Contracts
Some deferred income annuities come with death benefit options that provide financial security for beneficiaries if the annuitant passes away before receiving total payouts equal to their premium.
- Beneficiary protection: If structured correctly, beneficiaries may receive remaining premiums or periodic payouts even after the annuitant’s death.
- Peace of mind: This feature can help investors feel more secure about their investment choices knowing their loved ones could benefit if they pass away prematurely.
High Fees and Surrender Charges
Deferred income annuities often come with high fees and potential surrender charges that can diminish overall returns.
- Management fees: These fees can eat into investment growth, making it essential for investors to understand all associated costs before purchasing an annuity.
- Surrender penalties: Early withdrawal penalties can be steep, discouraging access to funds when needed most.
Potential Tax Advantages as a QLAC
For those looking at long-term retirement planning, purchasing a deferred income annuity as a Qualified Longevity Annuity Contract (QLAC) offers unique tax benefits.
- RMD deferral: QLACs allow individuals to defer required minimum distributions (RMDs) until age 85, potentially lowering taxable income during retirement years.
- Tax-efficient strategy: This strategy can be beneficial for those who want to manage their tax liabilities effectively while ensuring a steady income stream later in life.
Restrictions on Withdrawals Before Retirement Age
Most deferred income annuities impose strict rules regarding early withdrawals.
- Penalties apply: Withdrawals made before age 59½ typically incur significant penalties along with ordinary income taxes on any gains withdrawn early.
- Long-term commitment required: Investors must be prepared for this commitment and should only invest funds they will not need access to until retirement begins.
Risk of Insurer Default If Not Properly Vetted
Investing in any insurance product carries the risk of insurer default.
- Due diligence necessary: It is crucial for investors to research and select reputable insurance companies with strong credit ratings before purchasing DIAs.
- State guarantees vary: While many states have insurance guarantees protecting policyholders up to certain limits, these protections vary by state and should be understood by potential buyers.
In conclusion, deferred income annuities present both compelling advantages and notable disadvantages. They offer guaranteed lifetime income and tax-deferred growth but come with liquidity issues and potential complexity. Individuals considering this investment should weigh these factors carefully against their personal financial goals and circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions About Deferred Income Annuity Pros And Cons
- What is a deferred income annuity?
A deferred income annuity is a type of insurance contract that provides guaranteed payments starting at a future date based on an initial lump-sum investment. - How does a deferred income annuity work?
You pay premiums upfront, which accumulate over time and convert into regular payments once you reach your chosen payout date. - What are the main benefits of deferred income annuities?
The primary benefits include guaranteed lifetime income, tax-deferred growth on investments, and protection against outliving your savings. - Are there any risks associated with deferred income annuities?
Yes, risks include limited liquidity, potential lower returns compared to other investments, high fees, and the risk of insurer default. - Can I access my money early from a deferred income annuity?
No; accessing funds early typically incurs penalties and taxes unless specific provisions are included in the contract. - Do deferred income annuities provide inflation protection?
Most standard DIAs do not automatically adjust for inflation unless specifically structured with an inflation rider. - What happens if I die before receiving my full investment back?
Some contracts offer death benefits that allow beneficiaries to receive remaining premiums or periodic payouts if you pass away before full payouts equal your initial premium. - How do I choose the right deferred income annuity?
Selecting the right DIA involves evaluating your financial goals, understanding contract terms, comparing providers’ reputations, and possibly consulting with a financial advisor.