Home equity loans (HEIs) have emerged as a popular financial tool for homeowners looking to leverage the equity in their properties. These loans allow individuals to borrow against the value of their homes, providing funds that can be used for various purposes such as home improvements, debt consolidation, or major purchases. While HEIs can offer significant benefits, they also come with inherent risks and disadvantages. This article explores the pros and cons of home equity loans in detail, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in finance, cryptocurrency, forex, and money markets.
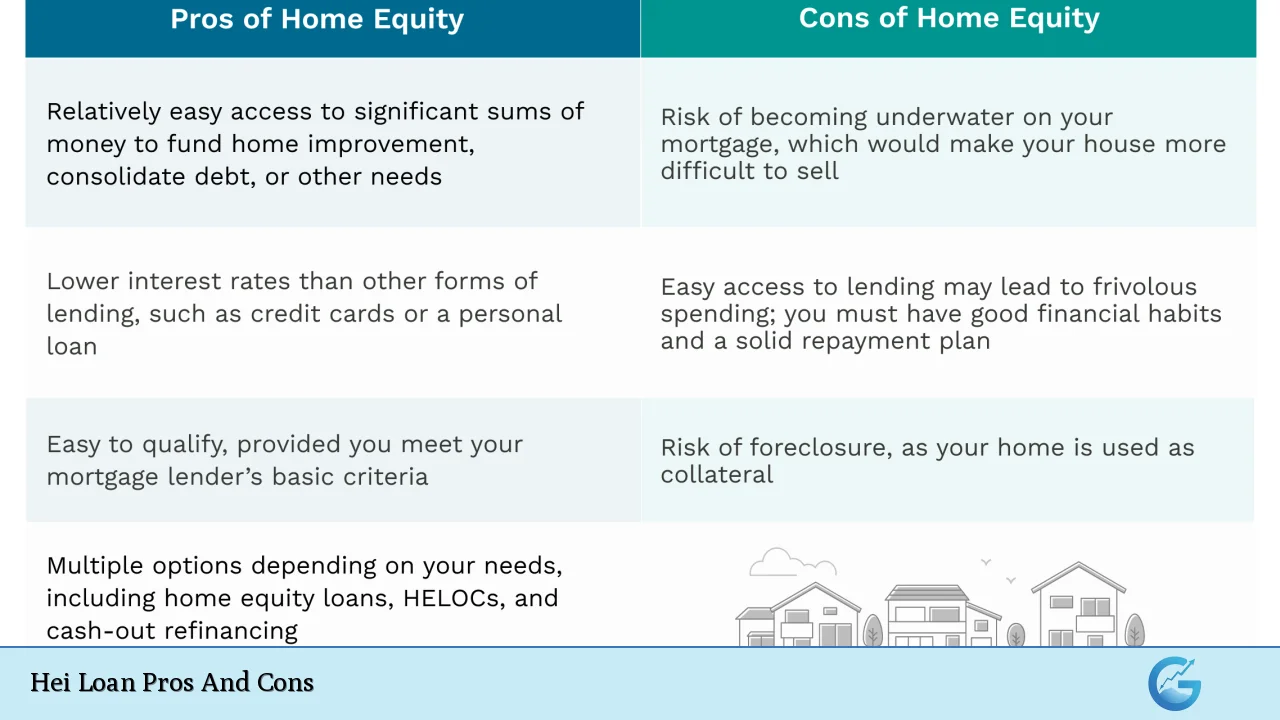
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fixed interest rates provide predictable payments. | Your home is used as collateral, increasing the risk of foreclosure. |
| Access to large sums of cash based on equity. | Potential for negative equity if property values decline. |
| Flexible use of funds for various purposes. | Longer application and funding processes compared to personal loans. |
| Tax-deductible interest in some cases. | Fees and closing costs can add up significantly. |
| Extended repayment periods can lower monthly payments. | Strict qualification criteria may exclude some borrowers. |
Fixed Interest Rates Provide Predictable Payments
One of the primary advantages of home equity loans is that they typically come with fixed interest rates. This means that borrowers will have consistent monthly payments throughout the life of the loan, making it easier to budget and plan for future expenses.
- Predictability: Fixed payments help homeowners avoid surprises in their financial planning.
- Stability: In a fluctuating interest rate environment, fixed rates can shield borrowers from potential increases.
Your Home Is Used As Collateral, Increasing The Risk Of Foreclosure
While home equity loans offer significant benefits, they also carry substantial risks. The most notable risk is that these loans are secured by the borrower’s home. If repayments are not made, lenders have the right to foreclose on the property.
- Risk of Losing Your Home: Defaulting on a loan could lead to severe financial consequences, including losing your residence.
- Emotional Stress: The prospect of foreclosure can cause significant anxiety for homeowners.
Access To Large Sums Of Cash Based On Equity
Home equity loans allow homeowners to access substantial amounts of cash based on the equity they have built up in their properties. This can be particularly beneficial for those needing funds for major expenses.
- Large Loan Amounts: Borrowers can often access tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Immediate Cash Availability: This lump sum can be used immediately for urgent needs such as medical bills or educational expenses.
Potential For Negative Equity If Property Values Decline
A significant disadvantage of home equity loans is the risk of negative equity. If property values decline significantly after taking out a loan, homeowners may owe more than their homes are worth.
- Underwater Mortgages: This situation can make it difficult to sell the property or refinance the loan.
- Financial Strain: Homeowners may face challenges if they need to relocate or sell due to job changes or other life events.
Flexible Use Of Funds For Various Purposes
Another advantage of home equity loans is their flexibility regarding how borrowed funds can be used. Unlike some loan types that restrict usage, HEIs offer borrowers considerable freedom.
- Diverse Applications: Funds can be used for home renovations, debt consolidation, education expenses, or even investments.
- Personalized Financial Solutions: Borrowers can tailor their use of funds to meet specific financial goals.
Longer Application And Funding Processes Compared To Personal Loans
Despite their advantages, obtaining a home equity loan typically involves a longer application and funding process compared to unsecured personal loans.
- Time-Consuming: The application process may take weeks due to necessary appraisals and documentation.
- Urgency Issues: For individuals needing quick access to cash, this delay can be problematic.
Tax-Deductible Interest In Some Cases
In certain situations, the interest paid on home equity loans may be tax-deductible. This potential tax benefit can make these loans more attractive from a financial perspective.
- Tax Benefits: Homeowners may be able to deduct interest payments from their taxable income if the funds are used for qualifying expenses.
- Increased Affordability: This deduction can effectively lower the cost of borrowing.
Fees And Closing Costs Can Add Up Significantly
Home equity loans often come with various fees and closing costs that can significantly increase the overall expense of borrowing.
- Hidden Costs: Borrowers should be aware of origination fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs that may not be immediately evident.
- Budgeting Challenges: These additional costs can strain budgets and reduce the net amount available for use.
Extended Repayment Periods Can Lower Monthly Payments
Home equity loans typically offer extended repayment periods, which can result in lower monthly payments compared to other forms of borrowing.
- Affordability: Longer terms allow borrowers to spread payments over many years, making them more manageable.
- Financial Flexibility: Lower monthly obligations free up cash flow for other expenses or savings.
Strict Qualification Criteria May Exclude Some Borrowers
Despite their benefits, home equity loans have stringent qualification criteria that may prevent some potential borrowers from accessing these funds.
- Credit Score Requirements: Many lenders require good credit scores and stable income levels.
- Debt-to-Income Ratios: High existing debt levels may disqualify applicants from receiving a loan.
In conclusion, while home equity loans present several advantages such as predictable payments and access to significant cash sums, they also carry notable risks including potential foreclosure and negative equity. Understanding both sides is crucial for homeowners considering this financial option. By weighing these pros and cons carefully against personal financial circumstances and goals, individuals can make informed decisions about whether a home equity loan aligns with their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hei Loans
- What is a home equity loan?
A home equity loan allows homeowners to borrow against the value of their property by using it as collateral. - How do I qualify for a home equity loan?
Qualification typically requires good credit scores, sufficient income levels, and a low debt-to-income ratio. - What are common uses for home equity loans?
Funds from HEIs can be used for various purposes including home renovations, debt consolidation, education costs, or major purchases. - Are interest payments on home equity loans tax-deductible?
Yes, in some cases interest payments may be tax-deductible if used for qualifying expenses. - What happens if I default on my home equity loan?
If you default on your HEI payment obligations, you risk foreclosure on your property since it serves as collateral. - How long does it take to get a home equity loan?
The process can take several weeks due to necessary appraisals and documentation requirements. - Can I use my home equity loan funds for anything?
Yes, there are generally no restrictions on how you use the funds from a home equity loan. - What are the risks associated with taking out a home equity loan?
The main risks include losing your home due to foreclosure and potentially owing more than your home’s value if market conditions change negatively.