Home equity loans have become an increasingly popular financial tool for homeowners seeking to leverage the value of their property. These loans allow individuals to borrow against the equity they’ve built in their homes, providing access to substantial funds for various purposes. As with any financial product, home equity loans come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that borrowers must carefully consider before making a decision.
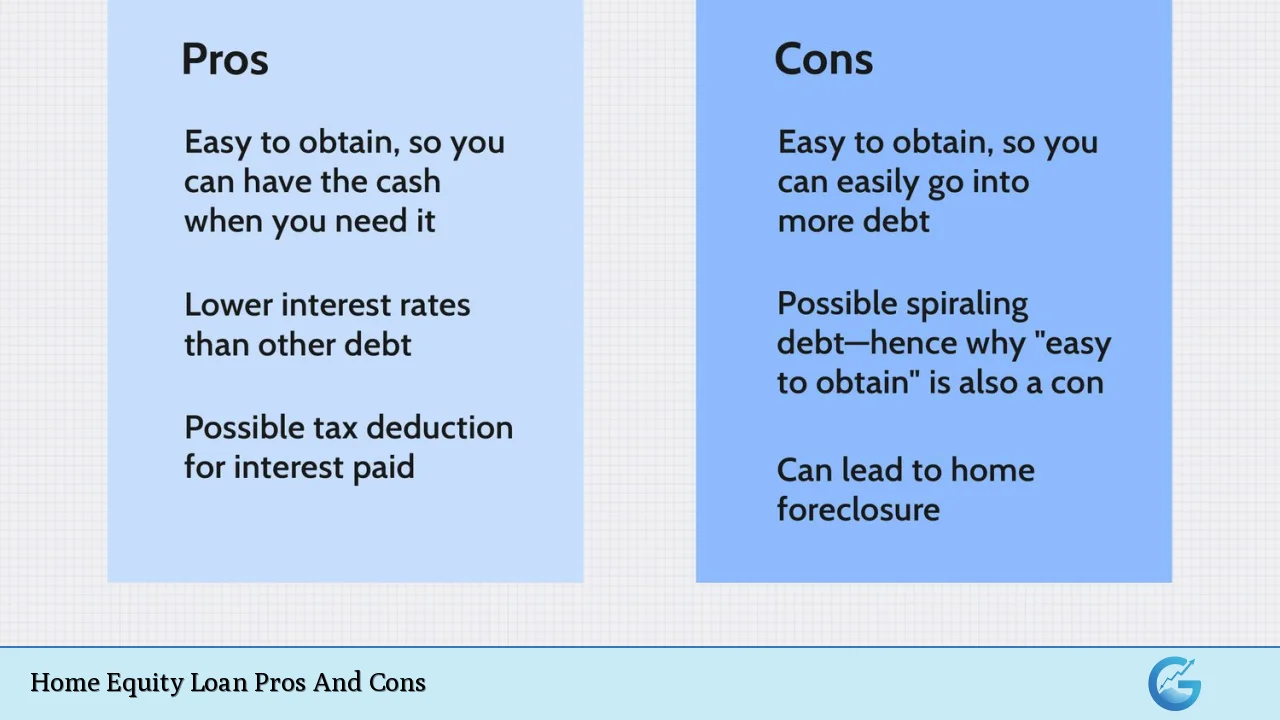
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans | Risk of foreclosure if payments are not met |
| Fixed interest rates and predictable payments | Reduces home equity and increases overall debt |
| Potential tax deductions on interest | Closing costs and fees associated with loan origination |
| Access to large sums of money | Temptation to overspend or misuse funds |
| Flexibility in use of funds | Long-term financial commitment |
| Opportunity for debt consolidation | Potential for negative equity if home values decline |
Advantages of Home Equity Loans
Lower Interest Rates
Home equity loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans, credit cards, or personal loans.
This is because the loan is secured by your home, which reduces the risk for lenders. The lower interest rates can translate to significant savings over the life of the loan, especially for large borrowing amounts.
- Interest rates are often several percentage points lower than credit card rates
- Can result in substantial savings on interest payments over time
- Makes borrowing larger sums more affordable for homeowners
Fixed Interest Rates and Predictable Payments
Unlike home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) which often have variable rates, home equity loans usually come with fixed interest rates. This feature provides borrowers with:
- Consistent monthly payments throughout the loan term
- Protection against interest rate fluctuations in the market
- Easier budgeting and financial planning
The stability of fixed rates can be particularly advantageous in a rising interest rate environment, offering peace of mind to borrowers concerned about potential payment increases.
Potential Tax Deductions
While tax laws have changed in recent years, there may still be opportunities for tax benefits associated with home equity loans. Under certain circumstances:
- Interest paid on home equity loans used for home improvements may be tax-deductible
- Consult with a tax professional to understand current IRS guidelines and eligibility
- Potential tax savings can further reduce the effective cost of borrowing
It’s important to note that tax laws can change, and deductions may be subject to limitations or phase-outs based on income levels and other factors.
Access to Large Sums of Money
Home equity loans allow homeowners to borrow substantial amounts based on the equity they’ve built in their property. This can be particularly useful for:
- Financing major home renovations or improvements
- Covering significant expenses such as college tuition or medical bills
- Investing in business opportunities or other large purchases
The ability to access large sums of money at relatively low interest rates makes home equity loans an attractive option for homeowners facing substantial expenses or investment opportunities.
Flexibility in Use of Funds
Unlike some other types of loans that are restricted to specific purposes, home equity loans offer considerable flexibility in how the funds can be used. Borrowers can utilize the money for:
- Home improvements and renovations
- Debt consolidation
- Education expenses
- Starting a business
- Emergency funds or unexpected costs
This versatility allows homeowners to address various financial needs or goals with a single loan product.
Opportunity for Debt Consolidation
Many homeowners use home equity loans to consolidate high-interest debts, such as credit card balances or personal loans. This strategy can offer several benefits:
- Potentially lower overall interest rates on existing debts
- Simplification of multiple payments into a single monthly payment
- Improved credit utilization ratio, which may positively impact credit scores
By consolidating debts with a home equity loan, borrowers may be able to save money on interest and streamline their financial obligations.
Disadvantages of Home Equity Loans
Risk of Foreclosure
The most significant risk associated with home equity loans is the potential for foreclosure if the borrower fails to make payments.
Since the loan is secured by the home:
- Defaulting on payments can result in the loss of your home
- The stakes are higher compared to unsecured loans
- Borrowers must be confident in their ability to repay the loan
This risk underscores the importance of careful financial planning and consideration before taking on a home equity loan.
Reduces Home Equity and Increases Overall Debt
Taking out a home equity loan effectively reduces the equity you’ve built in your home and increases your overall debt burden. This can have several implications:
- Decreased financial flexibility in the future
- Potential challenges if you need to sell or refinance your home
- Increased debt-to-income ratio, which may affect future borrowing capacity
Borrowers should carefully consider whether the benefits of accessing their home equity outweigh the long-term impact on their financial position.
Closing Costs and Fees
Like many financial products, home equity loans come with associated costs and fees:
- Appraisal fees to determine the current value of your home
- Application and origination fees
- Title search and insurance fees
- Potential points paid to lower the interest rate
These costs can add up to a significant amount, typically ranging from 2% to 5% of the loan amount.
It’s crucial to factor in these expenses when considering the overall cost of borrowing through a home equity loan.
Temptation to Overspend or Misuse Funds
The accessibility of a large sum of money can lead to potential financial pitfalls:
- Temptation to use funds for non-essential purchases
- Risk of overextending finances if not disciplined
- Potential for using home equity for short-term expenses, compromising long-term financial health
Borrowers should have a clear plan for the use of funds and avoid the temptation to spend on unnecessary items or expenses.
Long-term Financial Commitment
Home equity loans typically have terms ranging from 5 to 30 years, representing a significant long-term financial obligation:
- Extended repayment periods can result in substantial interest payments over time
- Reduces financial flexibility for future opportunities or changes in circumstances
- May impact retirement planning or other long-term financial goals
Borrowers should carefully consider whether they are comfortable with the long-term nature of this financial commitment before proceeding.
Potential for Negative Equity
If property values decline, borrowers may find themselves in a situation where they owe more on their combined mortgages than their home is worth, known as negative equity or being “underwater”:
- Limits options for selling or refinancing the home
- Can create financial stress if relocation becomes necessary
- May result in a short sale or foreclosure if financial difficulties arise
This risk is particularly relevant in volatile real estate markets or economic downturns.
In conclusion, home equity loans can be a powerful financial tool when used responsibly and for the right purposes. They offer homeowners access to substantial funds at competitive rates, which can be invaluable for major expenses, investments, or debt consolidation. However, the risks associated with using one’s home as collateral, coupled with the potential for overextension and long-term financial implications, necessitate careful consideration and planning.
Before deciding to take out a home equity loan, homeowners should thoroughly assess their financial situation, future goals, and ability to manage the additional debt.
Consulting with financial advisors, tax professionals, and comparing offers from multiple lenders can help ensure that a home equity loan aligns with your overall financial strategy and objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Home Equity Loan Pros And Cons
- How much can I borrow with a home equity loan?
Typically, you can borrow up to 80-85% of your home’s value minus your outstanding mortgage balance. The exact amount depends on factors like your credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio. - Are home equity loan interest rates always fixed?
While most home equity loans offer fixed rates, some lenders may provide variable rate options. It’s important to clarify the rate structure with your lender before committing to a loan. - Can I still deduct home equity loan interest on my taxes?
Interest may be tax-deductible if the loan is used to buy, build, or substantially improve the home that secures the loan. Consult a tax professional for advice on your specific situation. - How does a home equity loan differ from a HELOC?
A home equity loan provides a lump sum with fixed payments, while a HELOC offers a revolving credit line with variable rates. Home equity loans are better for one-time expenses, while HELOCs suit ongoing or variable costs. - What happens to my home equity loan if I sell my house?
When you sell your house, you’ll need to pay off the home equity loan along with your primary mortgage from the sale proceeds. This may reduce the amount you receive from the sale. - Can I get a home equity loan with bad credit?
While it’s possible, bad credit will likely result in higher interest rates or potential rejection. Lenders typically prefer credit scores of 620 or higher for home equity loans. - Is there a prepayment penalty for home equity loans?
Some lenders may charge prepayment penalties, while others don’t. It’s crucial to review the loan terms carefully and ask about any potential penalties before agreeing to the loan. - How long does it take to get approved for a home equity loan?
The approval process typically takes 2-4 weeks, including the application, home appraisal, and underwriting. Some lenders may offer expedited processes, potentially reducing this timeframe.