Index annuities, also known as equity-indexed annuities or fixed index annuities, have gained popularity among investors seeking a balance between market-linked growth potential and downside protection. These financial products offer a unique blend of features from both fixed and variable annuities, making them an intriguing option for those planning for retirement. However, like any investment vehicle, index annuities come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that warrant careful consideration.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Potential for higher returns than traditional fixed annuities | Complex product structure and terms |
| Downside protection against market losses | Limited upside potential due to caps and participation rates |
| Tax-deferred growth | Illiquidity and surrender charges |
| Guaranteed minimum interest rate | Fees can be higher than other investment options |
| Potential hedge against inflation | Exclusion of dividends in index calculations |
| No direct market risk exposure | Complexity in understanding crediting methods |
| Optional income riders for lifetime payments | Potential for lower returns compared to direct market investments |
| Death benefit for beneficiaries | Lack of FDIC insurance coverage |
Advantages of Index Annuities
Potential for Higher Returns
One of the most attractive features of index annuities is their potential to offer higher returns compared to traditional fixed annuities. By linking the annuity’s performance to a market index, typically the S&P 500, investors can benefit from market gains without directly investing in stocks. This feature appeals to those who want to participate in market upswings while maintaining a level of security.
- Opportunity to earn more than conservative fixed-rate products
- Participation in market growth without direct stock ownership
- Potential to outpace inflation over the long term
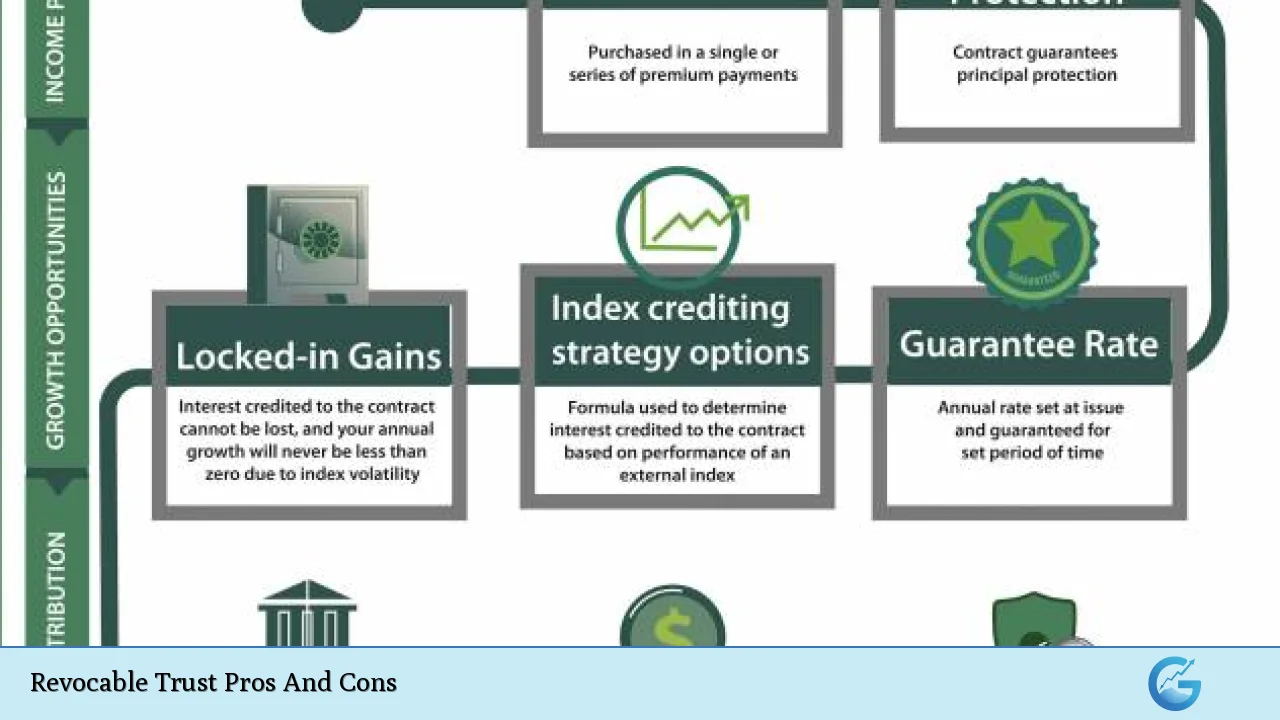
Downside Protection
Index annuities provide a safety net against market downturns, which is a significant advantage for risk-averse investors.
When the linked index experiences negative performance, the annuity’s value typically does not decrease. This principal protection feature ensures that investors don’t lose their initial investment due to market volatility.
- Preservation of capital during market declines
- Peace of mind for conservative investors
- Stability in retirement planning
Tax-Deferred Growth
Like other annuity products, index annuities offer tax-deferred growth. This means that any earnings within the annuity are not taxed until withdrawal, potentially allowing for more substantial compound growth over time. For investors in higher tax brackets, this feature can be particularly beneficial.
- Earnings grow tax-free until distribution
- Potential for higher overall returns due to compounding
- Flexibility in managing taxable income during retirement
Guaranteed Minimum Interest Rate
Many index annuities come with a guaranteed minimum interest rate, providing a floor for returns even in years when the linked index performs poorly. This feature ensures that the annuity will grow by at least a small percentage, regardless of market conditions.
- Assurance of some growth even in down markets
- Additional layer of security for principal
- Predictable minimum return for financial planning
Potential Hedge Against Inflation
In an environment of rising prices, index annuities can serve as a potential hedge against inflation. By offering returns linked to market performance, these products may provide better growth prospects than fixed-rate alternatives, helping to maintain purchasing power over time.
- Opportunity for returns that may outpace inflation
- Protection of real value of savings
- Adaptive performance based on economic conditions
No Direct Market Risk Exposure
Investors in index annuities do not directly own the underlying securities of the linked index. This structure eliminates direct market risk exposure, providing a buffer against the volatility associated with stock ownership.
- Insulation from day-to-day market fluctuations
- Reduced emotional stress during market turbulence
- Simplified investment experience without stock selection
Optional Income Riders
Many index annuities offer optional income riders that can provide guaranteed lifetime income. These riders can be valuable for retirees seeking a stable income stream that they cannot outlive, regardless of market performance or annuity value.
- Guaranteed income for life
- Customizable payout options
- Additional security for retirement planning
Death Benefit for Beneficiaries
Index annuities typically include a death benefit, ensuring that the contract value or a guaranteed minimum is passed on to beneficiaries. This feature can be an important consideration for estate planning and providing for loved ones.
- Financial protection for heirs
- Potential to avoid probate process
- Flexibility in legacy planning
Disadvantages of Index Annuities
Complex Product Structure and Terms
The complexity of index annuities is often cited as their primary drawback.
These products can be challenging to understand, with various crediting methods, participation rates, and caps that determine how returns are calculated. This complexity can make it difficult for investors to accurately assess the potential performance of their annuity.
- Difficulty in comparing different annuity offerings
- Risk of misunderstanding contract terms
- Potential for unsuitable product selection
Limited Upside Potential
While index annuities offer participation in market gains, they typically cap the upside potential. This means that even if the linked index experiences significant growth, the annuity’s returns will be limited to a predetermined maximum. Participation rates may also reduce the percentage of index gains credited to the annuity.
- Capped returns during strong market performance
- Participation rates may limit credited gains
- Potential opportunity cost compared to direct market investments
Illiquidity and Surrender Charges
Index annuities are designed as long-term investments, often with substantial penalties for early withdrawals. Surrender charges can be significant, especially in the early years of the contract, limiting an investor’s access to their funds without incurring costs.
- Limited access to funds during surrender period
- Potential for high fees on early withdrawals
- Reduced flexibility in responding to financial needs
Higher Fees Compared to Other Options
The fees associated with index annuities can be higher than those of other investment options, such as mutual funds or ETFs. These fees can include mortality and expense charges, administrative fees, and costs for optional riders, which can erode returns over time.
- Impact of fees on overall performance
- Complexity in understanding total cost structure
- Potential for lower net returns due to expenses
Exclusion of Dividends in Index Calculations
Most index annuities do not include dividends when calculating returns based on the linked index. Given that dividends have historically contributed significantly to total market returns, this exclusion can result in lower overall performance compared to directly investing in the index.
- Loss of dividend income component
- Potential for underperformance relative to total market return
- Reduced benefit from dividend-paying stocks’ growth
Complexity in Understanding Crediting Methods
The methods used to calculate and credit interest to index annuities can be intricate and vary widely between products. This complexity can make it challenging for investors to predict or understand their actual returns, leading to potential disappointment or confusion.
- Various crediting methods (point-to-point, averaging, etc.)
- Difficulty in forecasting future performance
- Risk of misaligned expectations
Potential for Lower Returns Compared to Direct Investments
While index annuities offer downside protection, this safety comes at the cost of potentially lower returns compared to direct investments in the market. Over long periods, this trade-off can result in significantly lower overall growth of assets.
- Opportunity cost during bull markets
- Reduced potential for wealth accumulation
- Impact on long-term financial goals
Lack of FDIC Insurance Coverage
Unlike bank products, index annuities are not covered by FDIC insurance. While they are backed by the financial strength of the issuing insurance company, there is a theoretical risk of loss if the insurer were to become insolvent.
- Reliance on insurance company’s financial stability
- Importance of carrier ratings and financial health
- Potential for loss in case of insurer failure
Index annuities represent a unique financial product that blends elements of security with growth potential. They can serve as a valuable component of a diversified retirement strategy, particularly for investors seeking a balance between risk and reward. However, the complexity and limitations of these products necessitate careful consideration and thorough understanding before investment.
Prospective investors should weigh the potential benefits against the drawbacks, considering their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
Consulting with a qualified financial advisor can provide valuable insights into whether an index annuity aligns with one’s overall financial plan. As with any significant financial decision, due diligence and a clear understanding of the product’s features, costs, and potential outcomes are essential for making an informed choice in the context of one’s broader investment portfolio and retirement planning objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Index Annuity Pros And Cons
- How do index annuities differ from variable annuities?
Index annuities offer limited market participation with downside protection, while variable annuities provide direct market exposure with higher risk and potential return. Index annuities typically have lower fees but more complex terms than variable annuities. - Can I lose money in an index annuity?
Generally, you cannot lose your principal in an index annuity due to market performance. However, you may incur losses if you withdraw funds early and face surrender charges or if the insurance company becomes insolvent. - Are index annuities a good investment for retirees?
Index annuities can be suitable for retirees seeking growth potential with downside protection. They offer a balance between security and market participation, but individual circumstances and goals should be considered before investing. - How are returns calculated in an index annuity?
Returns are typically based on the performance of a linked market index, subject to caps, participation rates, and spreads. The specific crediting method varies by product and can include annual point-to-point, monthly sum, or other calculations. - What happens to my index annuity if the market crashes?
In a market crash, your index annuity’s principal is protected from loss. You may receive no interest credit for that period, but your account value will not decrease due to negative market performance. - Can I withdraw money from my index annuity without penalties?
Most index annuities allow for limited free withdrawals, typically 10% of the contract value annually. Withdrawals beyond this amount or during the surrender period may incur charges. Some contracts offer penalty-free withdrawals for specific circumstances. - How do taxes work with index annuities?
Earnings in an index annuity grow tax-deferred. Upon withdrawal, gains are taxed as ordinary income. If the annuity is held in a qualified retirement account, the entire withdrawal may be taxable. - Are index annuities FDIC insured?
No, index annuities are not FDIC insured. They are backed by the financial strength of the issuing insurance company and may be protected by state guaranty associations, subject to limits and conditions.