Interest-bearing loans are financial instruments that allow borrowers to access funds while agreeing to pay back the principal amount along with interest over a specified period. These loans can serve various purposes, from financing personal needs to supporting business operations. Understanding the pros and cons of interest-bearing loans is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, especially in the context of finance, cryptocurrency, forex, and money markets. This article delves into the advantages and disadvantages of interest-bearing loans, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in investing and financial management.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Access to immediate funds | Cost of borrowing due to interest payments |
| Builds credit history | Risk of debt accumulation |
| Potential for lower interest rates compared to credit cards | Fixed repayment obligations can strain finances |
| Flexibility in loan amounts and terms | Fees and penalties may apply |
| Opportunity to leverage investments | Market fluctuations can affect repayment ability |
| Variety of loan types available (personal, business, etc.) | Potential for high-interest rates on unsecured loans |
| Can be used for debt consolidation | May require collateral for secured loans |
| Tax-deductible interest in some cases (e.g., mortgages) | Long-term financial commitment required |
Access to Immediate Funds
One of the most significant advantages of interest-bearing loans is the immediate access to funds they provide. This can be particularly beneficial in emergencies or when unexpected expenses arise.
- Quick funding: Many lenders offer fast approval processes, allowing borrowers to receive funds within days.
- Versatility: Borrowers can use these funds for various purposes, including home repairs, medical expenses, or business investments.
Builds Credit History
Taking out an interest-bearing loan can help individuals build their credit history and improve their credit score.
- Positive credit impact: Regular, on-time payments demonstrate responsible borrowing behavior, which can enhance a borrower’s credit profile.
- Access to better rates: A good credit score can lead to lower interest rates on future loans.
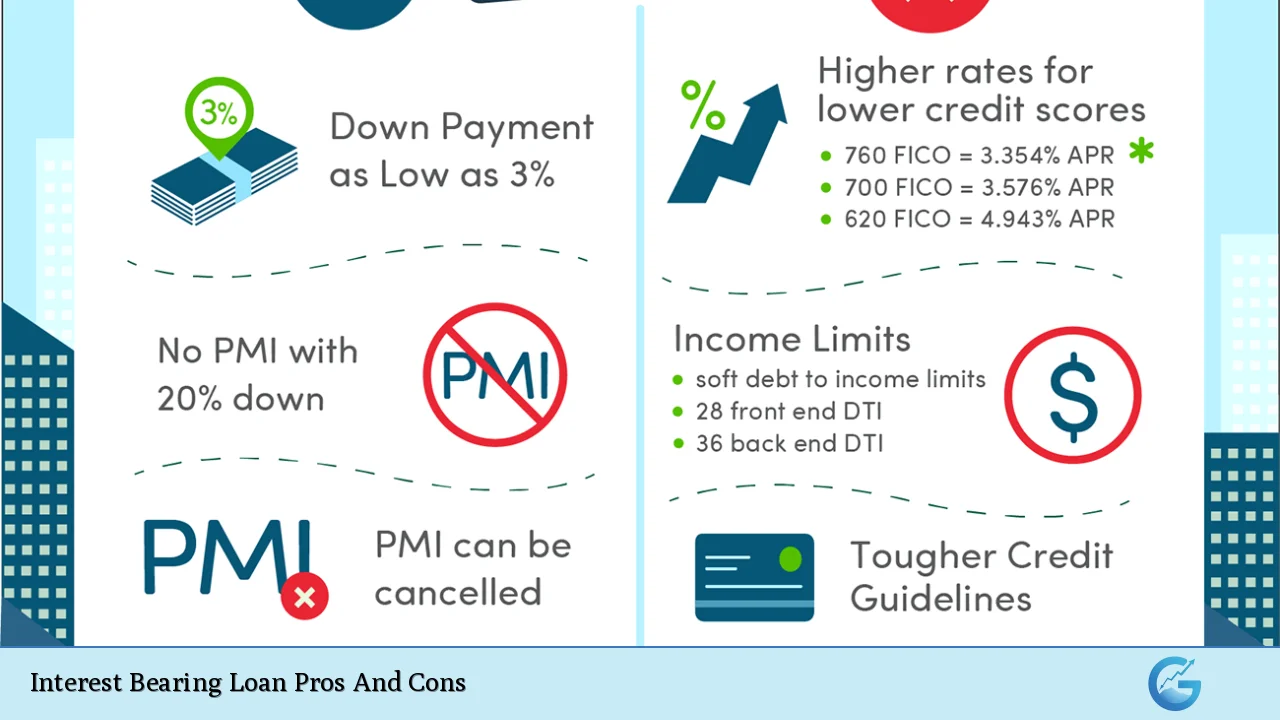
Potential for Lower Interest Rates Compared to Credit Cards
Interest-bearing loans often have lower interest rates than credit cards, making them a more cost-effective option for borrowing.
- Lower APRs: Personal loans typically offer annual percentage rates (APRs) that are significantly lower than those found on credit cards.
- Fixed payments: Many interest-bearing loans have fixed repayment terms, providing predictability in monthly budgeting.
Flexibility in Loan Amounts and Terms
Interest-bearing loans come with various options regarding amounts and repayment terms.
- Customizable options: Borrowers can select loan amounts that fit their financial needs and choose repayment periods that align with their budgets.
- Diverse offerings: Options include personal loans, auto loans, mortgages, and business loans, catering to different financial situations.
Opportunity to Leverage Investments
Borrowers can use interest-bearing loans strategically to invest in opportunities that may yield higher returns than the cost of borrowing.
- Investment potential: For example, real estate investors often use borrowed funds to purchase properties that generate rental income.
- Business growth: Entrepreneurs can leverage loans to expand operations or invest in new projects that drive revenue growth.
Variety of Loan Types Available
Interest-bearing loans encompass a wide range of products tailored to different needs.
- Personal vs. business loans: Individuals can choose personal loans for personal expenses or business loans for operational needs.
- Secured vs. unsecured options: Borrowers can select between secured loans (backed by collateral) or unsecured loans (not requiring collateral), depending on their risk tolerance and financial situation.
Can Be Used for Debt Consolidation
Interest-bearing loans can serve as effective tools for consolidating high-interest debts into a single payment.
- Simplified payments: Consolidating multiple debts into one loan reduces the number of monthly payments and simplifies financial management.
- Lower overall costs: If the consolidation loan has a lower interest rate than existing debts, borrowers may save money over time.
Cost of Borrowing Due to Interest Payments
The primary disadvantage of interest-bearing loans is the cost associated with borrowing money through interest payments.
- Total repayment amount: Borrowers must repay more than they borrowed due to accumulated interest over time.
- Interest accrual: Depending on the loan structure (fixed vs. variable rates), borrowers may face increasing costs if market rates rise.
Risk of Debt Accumulation
Borrowers may find themselves accumulating debt if they do not manage their finances carefully after taking out an interest-bearing loan.
- Over-reliance on credit: Individuals may be tempted to take out multiple loans or max out credit lines without addressing underlying spending habits.
- Debt cycle risk: This can lead to a cycle of borrowing where individuals continually rely on new loans to pay off old debts.
Fixed Repayment Obligations Can Strain Finances
The obligation to make fixed monthly payments can create financial strain for borrowers, especially during economic downturns or personal financial crises.
- Budget constraints: Fixed payments reduce flexibility in budgeting and may limit the ability to save or invest elsewhere.
- Financial distress: If income decreases unexpectedly (due to job loss or medical emergencies), meeting these obligations can become challenging.
Fees and Penalties May Apply
Many lenders impose fees that can add to the overall cost of borrowing through interest-bearing loans.
- Origination fees: Some lenders charge fees upfront when processing a loan application, which increases the total cost of borrowing.
- Late payment penalties: Missing a payment deadline often results in additional charges that exacerbate financial difficulties.
Potential for High Interest Rates on Unsecured Loans
Unsecured personal loans generally carry higher interest rates compared to secured options due to the increased risk for lenders.
- Higher costs for borrowers: Those with poor credit scores may face significantly higher APRs, making these loans more expensive over time.
- Risk assessment: Lenders assess borrower risk based on credit history; those deemed higher risk will pay more in interest charges.
May Require Collateral for Secured Loans
While secured loans often come with lower interest rates, they require collateral which poses risks if repayments are not met.
- Asset risk: Borrowers must be cautious as failing to repay could result in losing valuable assets (e.g., homes or vehicles).
- Limited access: Individuals without sufficient collateral may only qualify for unsecured options with higher costs attached.
Long-Term Financial Commitment Required
Interest-bearing loans typically involve long-term commitments that require careful consideration before borrowing.
- Extended repayment periods: Borrowers must plan their finances over months or years based on agreed repayment schedules.
- Impact on future borrowing capacity: Existing loan obligations affect debt-to-income ratios, potentially limiting future borrowing opportunities.
In conclusion, while interest-bearing loans offer several advantages such as immediate access to funds and opportunities for building credit history, they also come with significant risks including high costs associated with borrowing and potential debt accumulation. It is essential for individuals considering these financial products to weigh both the benefits and drawbacks carefully.
Frequently Asked Questions About Interest Bearing Loans
- What is an interest-bearing loan?
An interest-bearing loan is a type of loan where the borrower pays back the principal amount plus an additional amount as interest over time. - What are common uses for interest-bearing loans?
They are commonly used for personal expenses like home renovations, medical bills, education costs, or business financing. - How do I choose between secured and unsecured loans?
Your choice should depend on your creditworthiness; secured loans typically have lower rates but require collateral. - Can I consolidate my debts using an interest-bearing loan?
Yes, many people use these loans to consolidate high-interest debts into one manageable payment. - What happens if I miss a payment?
Missing a payment may result in late fees and could negatively impact your credit score. - Are there tax benefits associated with these loans?
In some cases, like mortgage interests, you may be able to deduct the paid interest from your taxable income. - How do I improve my chances of getting approved?
A strong credit score and stable income significantly improve your chances of approval. - What should I consider before taking out an interest-bearing loan?
You should evaluate your ability to repay it without straining your finances while considering all associated costs.
Understanding both sides of the coin when it comes to interest-bearing loans will empower you as an investor or consumer in finance-related markets. Make informed decisions by analyzing your financial situation thoroughly before engaging in any borrowing activities.